chordates
advertisement

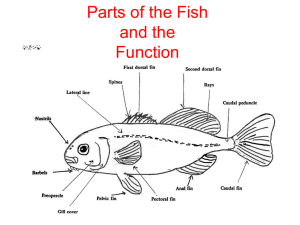
Biology 112 A chordate is an animal with the following four features: A hollow nerve cord that runs along the back of the body A notochord is a support rod that runs just below the nerve cord Pharyngeal pouches are paired structures in the throat A tail that extends beyond the anus Most chordates are vertebrates Most have a backbone made up of vertebrae The backbone replaces the notochord and supports and protects the spinal cord It also gives muscles a place to attach Tunicates Ocean-living filter feeders Have no notochord or tail As larva, they possess all the characteristics of chordates Lancelets Small, fish-like animals Adults possess all four characteristics Have a definite head region Aquatic vertebrates Most have paired fins, scales and gills Jaws and paired fins marked an evolutionary turning point for fish Jaws improved defense and expanded food choices Paired fins improved controlled movement In order to survive in water, special adaptations include: Various modes of feeding Specialized structures for gas exchange Paired fins for locomotion May be herbivores, carnivores, parasites, filter feeders, or detritus feeders One fish may feed in many different ways, depending on the food available Most fish breathe with gills Gills have many tiny blood vessels that provide a large surface area for gas exchange Fish pull water into their mouths Water moves over the gills and out of the body through openings in the sides of the pharnyx Fish have a closed circulation system It pumps blood in a loop from its heart to gills to the body and then back to the heart The heart consists of two chambers: an atrium and a ventricle Most fish get rid of wastes as ammonia Some diffuse wastes through the gills into the water Others remove wastes from the blood through the kidneys Kidneys help control the amount of water in their bodies Well developed with a brain housing several parts Cerebrum responsible for smell Cerebellum coordinates movement Medulla oblongata controls internal organs A lateral line system senses currents and vibrations in the water Most move by contracting muscles on either side of the backbone Fins pull the fish forward and help it steer Many have a gas-filled organ called a swim bladder that prevents its from sinking Eggs may be fertilized internally or externally Oviparous fish Lay eggs Eggs develop and hatch outside the mother’s body Ovoviviparous fish Develop eggs inside the mother Egg provides food to the young while inside mother Young are born alive Viviparous fish Mother provides food to the young while inside mother Young are born alive Jawless fish Lampreys and hagfish Bodies are supported by a notochord Do not have true teeth or jaws Parasites and scavengers Cartilaginous fish Sharks, rays and skates Have a skeleton made of cartilage Most have tooth-like scales covering their bodies Bony fish Skeletons made of bone Most are ray-finned fishes Fins have thin, bony spines that are joined by a thin layer of skin Vertebrates that live mostly in aquatic environments as a larva and on land as an adult As adults, breath with lungs, have moist skin that contains mucous glands and lack scales and claws In order for amphibians to adapt to living on land, from an evolutionary standpoint: Bones became stronger Lungs and breathing tubes developed The breastbone (sternum) developed a bony shield to support organs As larvae, they are filter feeders or herbivores; adults are carnivores Gas exchange occurs through skin and gills (larvae) and lungs (adults) Adults have three heart chambers; circulation is a double loop system Kidneys remove wastes from blood Eggs are laid in water and then the male fertilizes them Eggs hatch into larvae, called tadpoles They have good vision and can sense sound vibrations Salamanders Long bodies, four legs and long tails Frogs and Toads Do not have tails and can jump Frogs live close to water, toads live in moist wooded areas Caecilians Do not have legs Live in water or burrow in moist soil