Molecular Models Activity
advertisement
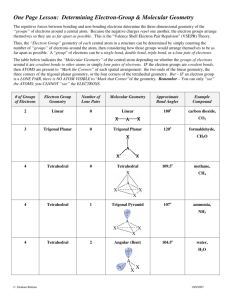
Molecular Models Activity carbon tetrachloride ammonia methane hydrogen monochloride water trichloromethane ethane urea ethyne propane dihydrogen monosulfide butane carbon dioxide nitrogen triiodide (video) supplies Bonding and Shape of Molecules Number of Bonds Number of Unshared Pairs 0 3 0 4 0 3 1 2 2 Shape Examples -Be- Linear BeCl2 Trigonal planar BF3 Tetrahedral CH4, SiCl4 Pyramidal NH3, PCl3 Bent H2O, H2S, SCl2 B C : 2 Covalent Structure : N O: Lewis Structures 1) Count up total number of valence electrons 2) Connect all atoms with single bonds - “multiple” atoms usually on outside - “single” atoms usually in center; C always in center, H always on outside. 3) Complete octets on exterior atoms (not H, though) - no unpaired electrons (free radicals) 4) Check - valence electrons match with Step 1 - all atoms (except H) have an octet; if not, try multiple bonds - any extra electrons? Put on central atom Carbon tetrachloride Cl Cl C Cl Cl CCl4 Cl C Cl 109.5o Cl Cl Tetrahedral geometry Carbon tetrachloride – “carbon tet” had been used as dry cleaning solvent because of its extreme non-polarity. Methane H HCH H H C H 109.5o H H Tetrahedral geometry Methane –The first member of the paraffin (alkane) hydrocarbons series. a.k.a. (marsh gas, CH4). Water d(-) SO2 Bent geometry O H H d(+) Polar molecule Ethane C = 1s22s22p2 H H HC CH H H Lewis dot notation ball-and-stick C2H4 molecular formula space-filling molecule Ethane H H HC CH H H Lewis dot notation ball-and-stick C2H6 molecular formula space-filling molecule Ethyne No octet each C “feels” 6 electrons HC CH C2H2 HC CH each C “feels” 7 carbons Ethyne – a.k.a. “acetylene” 6 electrons = triple bond HC CH Stable octet Dihydrogen monosulfide SO2 S H H Bent Carbon dioxide O C O CO2 O C Linear geometry O O C O Ammonia .. .. NH3 N HH H N H H H Trigonal Pyramidal geometry N H 107o H H Amino Acids – Functional Groups Amine Base Pair Carboxylic Acid R- COOH NH21lose H+ NH21- H+ NH3 NH41+ 1+ : 1- : : H N N N H H amine H H H ammonia H H H ammonium ion Hydrogen monochloride H Cl HCl d(+) d(-) HCl(g) + H2O(l) HCl(aq) hydrogen chloride Polar molecule water hydrochloric acid Trichloromethane d(+) H Cl C Cl Cl CHCl3 H C Cl 109.5o Cl Cl Tetrahedral geometry H Cl C Cl Cl d(-) Polar molecule Urea NOT “di-urea” H H N O C N H H H H N O C N H H CO(NH2)2 Urea – The first organic compound to be synthesized (Wohler, 1828). Propane H H H HC C CH H H H C 3H 8 H H C H H C H C H H H Butane H H H H HC C C CH H H H H H H H H-C-C-C-C-H H H H H C4H10 H H C H H H C H H C H H C H H Nitrogen triiodide .. N I I I NI3 N I 107o I I Trigonal Pyramidal geometry Video clip: (slow motion) detonation of NI3 Supplies 15 black 8 green 1 yellow 4 blue 4 red 42 hydrogen 67 bonds (carbon) (chlorine and iodine) (sulfur) (oxygen) (nitrogen) (hydrogen) (bonds) C Cl S I Cl Cl C Cl Cl H HCH H CCl4 CH4 HCl CHCl3 H O C O H Cl C Cl Cl H Cl HC CH C2H2 O N CO2 S H H SH2 H H H H HC C C CH H H H H N H HH H H H HC C CH H H H N I I I Decomposition of Nitrogen Triiodide Decomposition of Nitrogen Triiodide N2 NI3 2 NI3(s) I2 N2(g) + 3 I2(g) H H .. .. C N O 109.5o H H H CH4, methane lone pair electrons 107o H H 104.5o H NH3, ammonia H2O, water .. O O O O O3, ozone H O O The VSEPR Model The Shapes of Some Simple ABn Molecules SO2 .. O N S O C O O Linear O Bent F S O F F O Trigonal planar Trigonal pyramidal AB6 F F F Cl F F T-shaped F F F Square planar Brown, LeMay, Bursten, Chemistry The Central Science, 2000, page 305 F F P Xe F F F S F F F F F Trigonal bipyramidal Octahedral