Circulation
advertisement
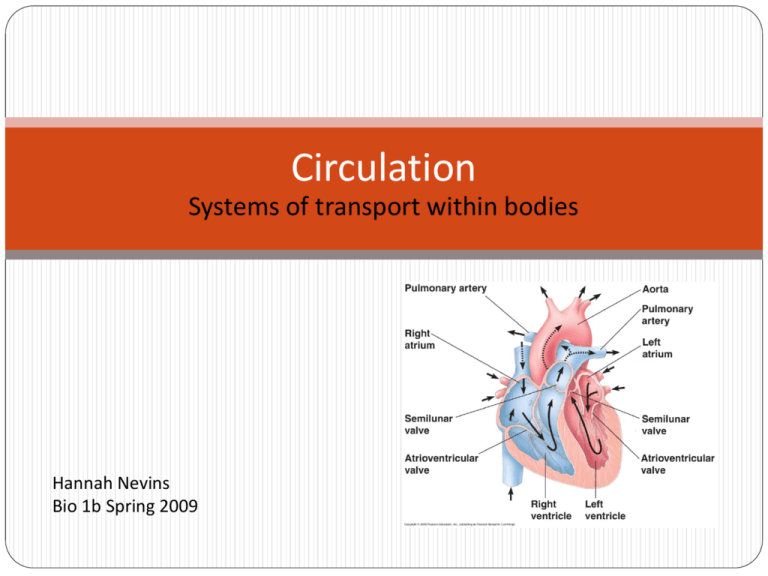
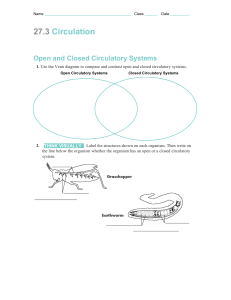
Circulation Systems of transport within bodies Hannah Nevins Bio 1b Spring 2009 Transportation to and from cells Nutrients – e.g. fatty acids, glucose Metabolites – wastes Hormones – signaling cells, organs Gases – O2, CO2 How are gases carried? Circulatory System Components: Circulatory fluid – carry solutes, gases, immune cells, RBCs Vessels – “roads” for transport Pump – to move fluid Valves – to keep flow unidirectional (why?) Cell Types: Red & White Components of (vertebrate) blood Simple Circulation: Ciliated Systems Bodies <1 mm don’t need a complex system Why not? Gastrovascular system is used for circulation Cnidarians Platyhelminthes – Ciliated digestive cavity with branching extensions Open Circulatory System: E.g. Arthropods, Molluscs Hemolymph is fluid Fluid exits dorsal vessel – returns via ostia (veins) Drawbacks: Backwaters & eddies Not efficient Poor oxygenation Poor diffusion gradients How can it be improved? Open Circulatory System: Hemolymph is fluid Fluid exits dorsal vessel – returns via ostia (veins) Drawbacks: Backwaters & eddies Not efficient Poor oxygenation Poor diffusion gradients How could this system be improved? Open Closed Closed Circulatory System: More efficient circulation = higher activity levels Some invertebrates Annelids - have multiple hearts Cephalopods – 3 hearts: one to each gill and 1 for body Hemodynamics: Capillaries greatly increase area – Is this important? Why? Velocity changes with distance from heart High resistance in capillaries Pressure varies with cardiac output **watch movie Venous flow – helped by muscle action Fish Two-chambered heart Drawbacks: Systemic blood is not pressurized As heart works harder, it gets blood that has reduced O2 Amphibians & some Reptiles Two atria & 1 ventricle Blood mixed in ventricle Greater systemic pressure = > higher activity levels Heart gets fresher blood -Which of these has a greater density of skin capillaries? Why? Variations in the circulatory system: Four-chamber heart: Crocodiles, Birds and Mammals No mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood What is the advantage of this? Human Circulation: Capillaries are everywhere! 2000/ mm2, usually <2% open Surface area = 1000 sq. miles!! (SC Co = 446 sq. mi.) Capillary action One-celled thick -leaky Allows for diffusion of nutrients & gases Hydrostatic pressure forces blood out… Capillary action One-celled thick -leaky Allows for diffusion of nutrients & gases Hydrostatic pressure forces blood out Osmotic pressure recaptures it Lymph system captures the rest…