Covalent_Bonding
advertisement

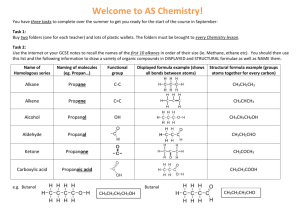
Bonding: Part Two • Ionic bonding is one way that atoms attain a stable electron condition – that is satisfy the octet rule. • In this section we will look at metallic bonding, covalent bonding, and the formation of acids and polymers • All forms of bonding involve valence electrons, and the tendency to satisfy the “octet rule” Metallic Bonding The nuclei of metal atoms are held together by their attraction to free-floating valence electrons that are found between adjacent nuclei Web Elements Covalent Bonding: when atoms share electrons Atoms still obey the octet rule Nitrogen: another diatomic • You try it !!!! Electrons are shared in a triple bond There are 7 diatomic atoms • Hydrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, iodine, bromine, and nitrogen. • Some satisfy the octet rule with a single covalent bond, others use a double or a triple bond. Why not try them all Geometric shapes of Molecules • The Shape of the molecule depends on how many bonds and how many unshared pairs of electrons are present • Work out the Lewis structures for the following molecules: • H2O BF3 NH3 CH4 CO2 How about water? Bent linear BF3: Trigonal planar Pyramidal and Tetrahedral NH3 CH4 Build a molecule tutorial Electrons try to be as far apart as they can be: Carbon dioxide is a linear molecule Prefixes are used in the names of molecular compounds • mono- one • di-two • tri-three • tetra-four • penta-five • hexa-six • hepta-seven • octa-eight • nona-nine • deca-ten N2O5 : dinitrogen pentoxide Naming compounds 1. The more metallic element is named first. The full name of the element is used 2. The second element is named as if it were an anion. 3. The number of atoms of each element is shown by a prefix, but the prefix mono- is never used for the first element. 4. If the second element is oxygen and a prefix ends with either an o or an a, these letters are dropped from Lets try some!!!! CO2 P2O5 NO SiO2 Al2O3 SO2 SO3 NO2 CO2 Carbon dioxide P2O5 Diphosphorous pentoxide NO Nitrogen monoxide SiO2 Silicone dioxide Al2O3 Aluminum oxide SO2 Sulfur dioxide SO3 Sulfur trioxide NO2 Nitrogen dioxide Boron trifluoride Silver fluoride Copper (II) fluoride Magnesium chloride Manganese (I) chloride Nitrogen dichloride Ammonium carbonate Dinitrogen heptoxide Gold (II) oxide Try it !!! Boron trifluoride Silver fluoride Copper (II) fluoride Magnesium chloride Manganese (I) chloride Nitrogen dichloride Ammonium carbonate Dinitrogen heptoxide Gold (II) oxide Heptoxide monofloride BF3 AgF CuF2 MgCl2 MnCl NCl2 (NH4)2CO3 N2O7 AuO O7F Acids – special molecular compounds 1. When hydrogen is the first element, the compound has special characteristics, and is named as an acid 2. Acids are electrolytes (like ionic compounds) 3. Acids are reactive, and dissasociate to form ions when placed in water 4. HCl H+ + Cl- Acids get their own names Identify and name the anion Use the following rules ones you know the name of the anion: 1. ide hydro ________ ic acid (HCl) 2. ite ____________ous acid (HClO2) 3. ate _____________ic acid (HClO3) (hydrochloric acid, chlorous acid, chloric H 3N Try Naming some acids !!! HNO2 HNO3 H 2S H2SO4 H2SO3 H2CO3 H3PO4 H 3N Try Naming some acids !!! Hydronitric acid HNO2 Nitrous acid HNO3 Nitric acid H 2S Hydrosulfuric acid H2SO4 Sulfuric acid H2SO3 Sulfurous acid H2CO3 Carbonic acid H3PO4 Phosphoric acid Write some formulas Hydrobromic acid Hypochlorous acid Perchloric acid Permanganic acid Chromatic acid Hydrosulfuric acid Hydrohydroxic acid Acetic acid Oxylic acid Nitrous acid Write some formulas Hydrobromic acid HBr Hypochlorous acid HClO Perchloric acid HClO4 Permanganic acid Chromatic acid HMnO4 Hydrosulfuric acid H2CrO4 H2SO4 Hydrohydroxic acid HOH Acetic acid HC2H3O2 Oxylic acid H2C2O4 Nitrous acid HNO2 Organic molecules • These have there own rules, and their own prefixes that indicate how many carbons: • The alkanes have the formula CnH2n+2 • Methane (one carbon) • Ethane (two carbons) • Propane (three carbons) • Butane (four carbons) • Pentane (five carbons) • Hexane (six carbons) • Heptane (seven carbons) • Octane (eight carbons) Each carbon develops 4 bonds methane Ethane : C2H6 Propane: C3H8 Link to bondit Benzene