Week 1
advertisement
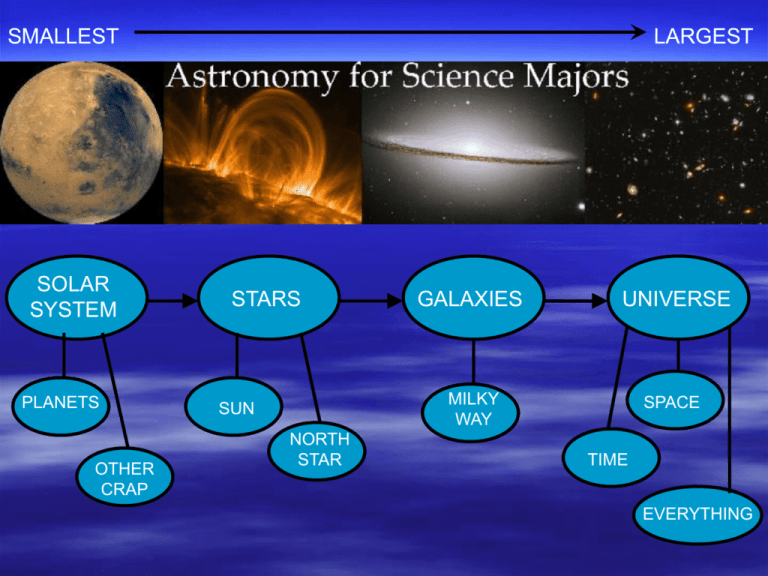
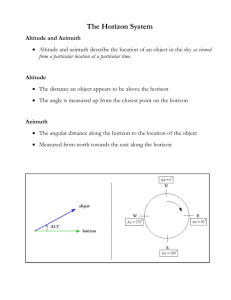
SMALLEST SOLAR SYSTEM PLANETS OTHER CRAP LARGEST STARS SUN NORTH STAR GALAXIES UNIVERSE MILKY WAY SPACE TIME EVERYTHING Thought Question: If you could see stars during the day, this is what the sky would look like at noon on a given day. The Sun is near the stars of the constellation Gemini. Near which constellation would you expect the Sun to be located at sunset? A. Leo B. Cancer C. Gemini D. Taurus E. Pisces Thought Question Which of the following describes when constellations are visible from San Diego (if it is dark enough and the clouds cooperate)? A. You could observe any constellation tonight at midnight. B. You could observe any constellation sometime during the night. C. You could observe any constellation on some night during the next year. D. Some constellations will never be visible from here. CONSTELLATIONS: for orienting ourselves in the sky: NORTH STAR Being a Good Astronomer ATMOSPHERE Complications in finding things: • Earth is a sphere (people in different places see different stars) • Earth rotates (stars continually move across sky) • Earth orbits the Sun (stars don’t appear in same place from month to month) • Some of our targets are moving too… Being a Good Astronomer LOW ALTITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE ATMOSPHERE High in the sky is best because… the more atmosphere you have to look through: • the more light is blocked • the more the colors are affected Where in the Sky? ZENITH NORTH STAR E N NORTH STAR To describe position in sky, need two coordinates: • Altitude (ALT): angle above horizon 0º: horizon S 90º: zenith W E N W • Direction (DIR): angle clockwise from N measured around horizon 0º: N 180º: S S 90º: E 270º: W Being a Good Astronomer ATMOSPHERE Best telescopes usually scheduled months in advance: • must be able to predict when an object will be up • light from Sun, Moon should not interfere Stars Move? Thought Question In the past, several TV shows (NBC Nightly News, The Daily Show) had opening graphics which showed the Earth spinning the wrong way. If you were watching Earth from a stationary position out in space (as shown below), what direction does it spin? A. Left to right B. Right to left Celestial Sphere Stars appear to move as if attached to a sphere rotating around Earth • Celestial poles: above Earth’s N and S poles • Celestial equator: directly above Earth’s equator Earth Surface Coordinates NORTH POLE 90º N EQUATOR 0º SOUTH POLE 90º S Celestial Coordinates NORTH CELESTIAL POLE RIGHT ASCENSION LINES NORTH CELESTIAL POLE CELESTIAL EQUATOR DECLINATION LINES SOUTH CELESTIAL POLE SOUTH CELESTIAL POLE Celestial Coordinates north celestial pole declination (DEC): like latitude on Earth north celestial pole: +90º celestial equator: 0º south celestial pole: -90º right ascension (RA): like longitude on Earth BUT… counted in hrs, increases toward east The Sky from San Diego circumpolar: stars that don’t rise or set for a person Most stars rise in east half of sky, and set in west half: LOOKING NORTH LOOKING SOUTH NORTH CELESTIAL POLE E S N W HORIZON Thought Question If you watched the star pictured below from San Diego over several hours, what would happen? A. Its altitude and direction wouldn’t change. B. Its altitude would change, but direction wouldn’t. C. Its direction would change, but altitude wouldn’t. D. Both its direction and altitude would change. E N S W HORIZON Using a Telescope A telescope pointing at one ALT and DIR doesn’t move BUT a star’s ALT and DIR both change during night • Is there a better way?