Cell Junctions
advertisement
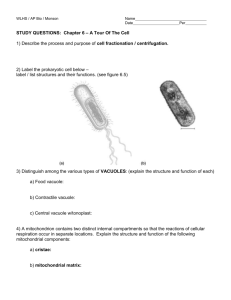
Cell Junctions and their Functions By Jennifer Romero and Endy Hernandez Cell Junctions -Intercellular bridges located between the cells of animals -2 major types Gap Junction -Made of 6 proteins called connexons -Connect the cytoplasm of adjacent animal cells -Permit free passage of molecules Plasmodesmata • Fine strands of cytoplasm • Connects cytoplasm of cell wall to that of its neighbors • Extension of plasma membrane • Proteins regulate permeability • Communication and transportation • Primary pit fields Tight Junctions -Belts of protein that close extracellular space -Prevent particles from going through the opening of 2 adjacent cells Gap and Tight Junctions Side to Side Desmosomes • Holds cells together • Attached to filaments of keratin in cytoplasm • Contains calcium molecules • Aid in electro-chemical communication between adjoining cells • Common in epithelia Summary Gap Junctions Plasmodesmata Tight Junctions Desmosomes Works Cited • kimball, J. "Junctions between cells." users.rcn.com. N.p., 17 feb 2011. Web. 16 Sep 2013. <http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/J/Junctions. html>. • Hannahs, Greg. "Plasmosdesmata." biology.kenyon.edu. N.p., n.d. Web. 16 Sep 2013. <http://biology.kenyon.edu/edwards/project/greg/pd.htm>. • Whitmer, Phil. "What Are Cell Junctions?." ehow. N.p.. Web. 16 Sep 2013. <http://www.ehow.com/info_8093238_cell-junctions.html>. • “Junctions Between Cells Simplified.” About Dbriers.com N.p. Web. 16 September 2013. http://www.dbriers.com/tutorials/2012/12/junctions-between-cellssimplified/