ANSWERSPracticeTestWeeks1and2
advertisement

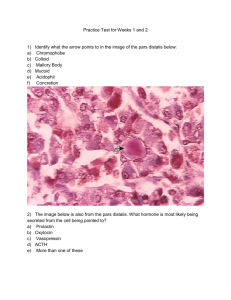
ANSWERS Practice Test for Weeks 1 and 2 1) a) b) c) d) e) f) Identify what the arrow points to in the image of the pars distalis below: Chromophobe Colloid Mallory Body Mucoid Acidophil Concretion 2) The image below is also from the pars distalis. What hormone is most likely being secreted from the cell being pointed to? a) Prolactin b) Oxytocin c) Vasopressin d) ACTH e) More than one of these 3) a) b) c) d) e) What is the specific structure where MSH is produced and stored? Pars intermedia Pars distalis Pars tuberalis Pars nervosa Par 3 4) a) b) c) d) e) f) Developmentally, what eventually forms the adenohypophysis? Floor of Telencephalon Floor of Diencephalon Neural ectoderm Neural endoderm Oral Ectoderm Oral Mesoderm 5) a) b) c) What statement is true about how TSH affects thyroid cells? More vacuoles are seen as more colloid is resorbed Lipid droplet removal out of the cell is upregulated Mitochondria begin being broken down by lysosomes d) Cisternae of ER and Golgi begin to condense in preparation for material resorption 6) a) b) c) d) What type of tissue is this slide from? Thyroid Gland Pineal Gland Pars nervosa Pars intermedia 7) a) b) c) d) e) Embryological origin of parathyroid glands? Pharyngeal pouches 1 and 2 Pharyngeal pouches 2 and 3 Pharyngeal pouches 3 and 4 Pharyngeal pouch 5 Rathke’s Pouch 8) a) b) c) d) e) f) Cell type being pointed to in this image below: Oxyphil cells Fat cells Basophilic cells Colloid Myxoid cells Chief cells 9) The type of cells that the arrow points to below, would cause what changes in your blood when activated? a) Increase blood calcium b) Decrease blood calcium c) Increase melatonin d) Decrease melatonin e) Increase cortisol levels f) Decrease cortisol levels g) Release a hormone that will induce labor in high enough concentrations The arrow points to a parafollicular cell or “C Cell” in between the thyroid follicles. These cells secrete Calcitonin when activated. Calcitonin stimulates Ca uptake and deposition into bone, thus lowering serum Ca. 10) Why are hypothalamic and pituitary hormone secreted in pulses? a) In order to avoid over-use of cholesterol in the serum b) Due to the mechanism of release it is not possible for them to be excreted continuously c) Prevents desensitization of downstream targets d) Continuous administration would cause an upregulation of hormone receptors causing an excess of hormone signaling 11) Which statement is MOST correct? a) Hypothalamic hormones and tertiary endocrine hormones are only proteins b) Hypothalamic hormones and tertiary endocrine hormones are only amino acids c) Hypothalamic hormones are steroids whereas tertiary endocrine hormones are proteins or amino acids d) Hypothalamic hormones are proteins, steroids or amino acids whereas tertiary endocrine are steroids. e) Hypothalamic hormones are only proteins whereas tertiary endocrine hormones are proteins, steroids, or amino acids 12) Which statement is most correct? a) Response rate to protein hormone binding take minutes and to steroid hormones is hours b) Response rate to steroid hormone binding takes hours and to protein hormones takes minutes c) Reponses to both steroid and protein hormone binding takes minutes d) Reponses to both steroid and protein hormone binding takes hours 13) Name the hormone that MOST inhibits Growth Hormone Release: a) Prolactin b) JAK c) Somatostatin d) IGF-1 e) Glucocorticoid Remember Dopamine will also inhibit GH release Good way to remember this is SOMA(body) and STASIS(stop) 14) Which hormone is most important for stimulating chondrogenesis at the epiphyseal growth plate? a) IGF-1 b) Somatostatin c) GH d) Prolactin e) PTH More important than GH in this regard 15) A patient of yours comes in because he is peeing a ton lately, feeling very thirsty and hungry and overall just unwell. He says this is bad because he is a body-builder and says he needs to “get swole” right now. He is evasive when you ask if he is using any performance enhancers. What could be going on? a) He is so ripped that it’s literally making him sick b) Anabolic steroids can cause polyphagia and polydipsia c) He is taking GH hormone, which can be diabetogenic d) He likely has Hyperkalemia caused by excessive laxative abuse e) He has polyphagia because he thinks that Marijuana is a performance enhancer Remember both GH and cortisol can cause hyperglycemia. 16) An adult patient is obese, has reduced muscle mass, a lack of energy, and reduced cardiac output. They are also very short with some features of dwarfism. What test is BEST to know if their condition is caused by hyposecretion of GH? a) Insulin tolerance test b) Glucagon Test c) Random Serum GH d) Random Serum GHRH e) Urine Somatostatin 17) What is the etiology for Laron-type dwarfism? a) Loss of single X chromosome in Turner syndrome b) Overproduction of somatostatin hormone c) Autoantibodies target GH d) GH receptor variant has weak binding to GH 18) Mecasermin is a recombinant IGF-1 therapy. Which of these statements is FALSE about the drug? a) Fewer side effects than GH therapy b) Should not be given to kids with cancer c) Will only be effective in patients with closed epiphyses d) Hypoglycemia is part of the side effect profile Will only be effective in kids that have OPEN epiphyseal growth plates. Not effective for adults either because of this. 19) BEST treatment for GH secreting pituitary tumors, matched up with its CORRECT mechanism of action: a) Pegvisomant: GH receptor antagonist b) Bromocriptine: Somatostatin analog c) Octreotide: Dopamine Agonist d) Omnitrope: Oversensitize receptors to decrease GH effect Correct Treatment Possibilities: Pegvisomant = GH receptors antagonist which reduces IGF Bromocriptine = Dopamine Agonist Octreotide = long-acting somatostatin analog 20) BEST treatment for prolactin-secreting tumor AND its correct mechanism: a) Oxytocin: Binds to prolactin hormones b) Cabergoline: Dopamine agonist c) Bromocriptine: Dopamine antagonist d) Pegvisomant: Reduce IGF release Correct Treatment Possibilities: Cabergoline and Bromocriptine = dopamine agonists D2 receptors are often present on prolactin-secreting tumors, which makes dopamine agonists a good choice 21) Which statement is false a) T3 is more active than T4 b) Most T3 is converted to T4 c) T3 has a shorter half life than T4 d) Both T3 and T4 bind thyroid hormone receptors 23) Which deiodinases are important for activation and deactivation of thyroid hormones? a) Activation: 1&2 Deactivation: 4 only b) Activation: 1&2 Deactivation: 1&3 c) Activation: 1&3 Deactivation: 1&2 d) Activation: 1&2 Deactivation: 3 only 24) Is it hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism that causes infertility? What is the mechanism? a) Hyperthyroidism – impairs GnRH and regulation of ovulation b) Hypothyroidism – Can cause anovulation and amenorrhea c) Both of these are correct Other points to remember: Hyperthyroidism can cause precocious puberty as well as gynecomastia in men. 25) Which test is best for confirming a case of Grave’s disease instead of any other hyperthyroid condition? a) TSH b) Free T3 and T4 c) TSI Test d) Hgb A1C 26) What part of a Grave’s Disease patient’s past medical history would make them a poor candidate for use of PTU thioamide therapy? a) Extensive alcoholism b) Morbid obesity c) COPD d) Arrythmia Remember: In the 1st trimester of pregnancy PTU is probably a better choice than methimazole for Grave’s disease. Apart from that, Methimazole is preferred. PTU has risk of serious liver damage, so I assume you would want to avoid giving it to someone with an already-damaged liver. This might not be 100% accurate though. 27) Which antibody test is MOST specific for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis in a female patient with myxedema and a big painless thyroid? a) Anti-peroxidase antibody b) Antithyroglobulin antibody c) Anti-TSH receptor antibody d) Anti-FUN antibody Remember that A, B, and C can all be present 28) A patient’s big, sore thyroid displays the pathology below. He shows signs of hypothyroidism. He has also had a recent URI. What is the diagnosis? a) Grave’s disease b) DeQuervain Thyroiditis c) Reidel Thyroiditis d) Silent Thyroiditis e) Hashimoto Thyroiditis 29) You are following up with a female patient 5 months post-partum with her first child. She has a history of SLE. She says for the first 4 months or so she had a lot of anxiety, irritability, and trouble sleeping. She didn’t come in because she has been told post-partum depression is normal. She has come in today because things have rapidly changed to the opposite effects. She feels tired all the time, very depressed, cannot tolerate exercise, and is gaining back the weight she lost in the months after her delivery. What could be going on? a) SLE exacerbation causing all symptoms b) She was taking cocaine, now she’s on Benzos c) Silent Thyroiditis d) Reidel Thyroiditis e) Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis 30) You are trying to palpate a thyroid for the 100th time and finally feel something different. It is rock-hard! Patient says their breathing has been a little troubled lately. What do you think it could be? a) Grave’s disease b) DeQuervain Thyroiditis c) Reidel Thyroiditis d) Silent Thyroiditis e) Hashimoto Thyroiditis 31) Which statement is false? Thyroid nodules more likely to be malignant if: a) Patient is female b) Nodule is solitary c) Nodule is cold d) There is a history of radiation 32) After biopsying a suspicious nodule you begin having a hay-day with all of the interesting pathology shown in the images below. What is the diagnosis? a) Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma b) Benign hyperplastic goiter c) Hashimoto Thyroiditis d) Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma e) Papillary Carcinoma Hint: 1) pseudoinclusion 2) Psammoma Body 3) Orphan Annie Nuclei 33) Which thyroid cancer is an endocrine tumor? (A malignancy of C cells) a) Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma b) Papillary Carcinoma c) Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma d) Anaplastic thyroid Carcinoma e) All of these Big in MEN 2! 34) Which of these is NOT an action of PTH? a) Increase bone reabsorption b) Increase renal reabsorption of Ca c) Increase renal reabsorption of Phosphate d) Increase renal conversion of Vit D to its active form e) Increase gut absorption of Ca 35) Which is NOT ac action of Vitamin D? a) Stimulate gut to absorb Ca and phosphorus b) Help PTH remove Ca from bone c) Stimulate kidney to reabsorb Ca d) All are effects of Vit D 36) Primary lab findings of hyperparathyroidism: a) Increase Serum PTH / Decrease Serum Ca / Increase Serum Phosphate b) Increase Serum PTH / Increase Serum Ca / Decrease Serum Phosphate c) Increase Serum PTH / Increase Serum Ca / Increase Serum Phosphate d) Decrease Serum PTH / Decrease Serum Ca / Increase Serum Phosphate 37) Which of the following is correct and necessary for osteoclast activation of osteoclast precursors? a) Phosphate binds and stimulates receptors on the osteoclast precursor membrane b) Ca binds and stimulates receptors on the osteoclast precursor membrane c) The RANKL ligand of the precursor osteoclast binds to the RANK receptor of the osteoblast d) The M-CSF ligand of the osteoblast binds to the M-CSFr receptor of the precursor osteoclast 38) Commonest cause of PRIMARY hyperparathyroidism? a) Grave’s Disease b) Parathyroid Adenoma c) Vit D overdose d) Diet poor in Ca e) Parathyroid hyperplasia 39) You are examining a patient of yours who has DiGeorge syndrome. He presents with perioral numbness and teeth pictured in the image below. Physical exam findings show a positive Chvostek’s sign (stroke cheek and face twitching occurs) and a positive Trousseau’s sign (blood pressure cuff on arm causes hand-cramping). What is your first thought? a) Abuse b) Hyperparathyroidism c) Hypoparathyroidism d) Renal Failure e) Diet poor in calcium 40) Which statement is false about cortisol’s actions? a) Maintain BP b) Break down bone c) Suppress inflammation d) Suppress immune system e) Suppress Gluconeogenesis Cortisol STIMULATES gluconeogenesis! 41) A woman presents in your clinic with hirsutism, truncal obesity, moon facies, and a foot fracture. What is your first thought? a) Cushing Syndrome b) Grave’s Disease c) Addison’s Disease d) Hyperaldosteronism e) Lack of diet and exercise 42) Which of these could NOT be a cause of this woman’s symptoms: a) Pitutiary adenoma b) Current steroid use c) Paraneoplastic syndrome from cancer d) Adrenal hyperplasia e) All are possible 43) Which association is INCORRECT? a) Zona glomerulosa secretes mineralcoticoids b) Zona fasciculata secretes aldosterone c) Zona reticularis secretes androgens d) Medulla secretes Epinephrine and Noreprinephrine e) All are correct Fasciculata secretes glucocorticoids! 44) Cells in the adrenal cortex layer shown in the image below are most likely to secrete which substance? a) Aldosterone b) Cortisol c) Androgens d) Epinephrine e) TSH 45) Two hormones resulting from pituitary process of POMC? a) FSH and LH b) TSH and MSH c) ACTH and TSH d) MSH and ACTH e) LH and ACTH Remember that both ACTH and MSH can bind to skin MC1-R and stimulate melanocyte production of melanin. This is the process behind the hyperpigmentation co-incident with high levels of POMC in Addison’s disease. 46) Why is it that both aldosterone and cortisol can have equal affinity to a Mineralocoticoid receptor, and yet the cell only responds to aldosterone? a) The affinity is the same, but tissues like the kidney enzymatically inactivate cortisol b) The affinity is the same, but cortisol binds to a site on the MR that has no effect c) The affinity is the same, but it is not possible for cortisol to ever find its way to the MR d) The affinity is the same, but macrophages immediately engulf cells with bound cortisol 47) Which are true about the comparison in symptoms between a deficiency in 21hydroxylase or 11-beta-hydroxylase? Why? a) Both cause virilization because more of the pathway is shunted into making androgens b) 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency causes hypotension because there is a decrease in aldosterone synthesis c) 21-hydroxylase deficiency causes hypotension because of a decrease in aldosterone synthesis d) 11-beta-hydroxylase causes hypertension due to mineralocorticoid activity of deoxycortisone and 11-deoxycortisol e) B and C f) A, B, and C g) A, C, and D Remember that deoxycortisone and 11-deoxycortisol have weak mineralcorticoid activity. I thought this chart was MUCH more helpful than the one in class… 21 hydroxylase is the MOST COMMON genetic defect Remember that with both of these deficiencies there will be adrenal hyperplasia and adrenal insufficiency. 48) One of your patient’s has Cushing syndrome and you are trying to discover the cost. You use a dexamethasone challenge test and find that the cortisol secretion has been suppressed. What is the cause of the Cushing syndrome? a) Iatrogenic b) Pituitary problem c) Adrenal Problem d) Paraneoplasic problem e) None of these You know this is a Pituitary cause because it is the only type of Cushing Syndrome that will respond well to a Dexamethasone challenge. Check out our handy chart if you have questions: 49) 45 year old woman presents to your family practice clinic with chronic HTN and hypokalemia. HTN began in her 20’s and became severe in her 40’s. The HTN has been resistant to all attempted drug regimens. At first you were worried about compliance to medication, but her daughter is with her today and says she has seen her taking the meds faithfully. Labs today show slightly low potassium, elevated aldosterone, and VERY low renin. What’s the cause of her problems? a) Lack of compliance –admit for IV meds b) Primary hyperaldosteronism c) Secondary hyperaldosteronism due to congestive heart failure d) Sesondary hyperaldosteronism due to a renin-producing tumor Remember: The dynamic between renin and aldosterone is going to tell you a lot. High aldosterone and low renin means that aldosterone is being produced despite lack of stimulus from renin. A high renin level is going to tell you that the effect is secondary and driving the disease process. You know hyperaldosteronism part of the process for both primary and secondary because the potassium is low and the aldosterone is at least slightly elevated usually. 50) What adrenal syndrome is caused by bilateral massive adrenal hemorrhage and linked to bacterial infection? a) Pheochromocytoma b) Waterhouse-Friedrichsen Syndrome c) Addison Disease d) Wilson Syndrome 51) Pheochromocytoma symptoms are caused by increased serum catecholamines (episodic HTN, headaches, palpitations, tachycardia, and sweating) How do you diagnose this tumor? a) Serum renin and angiotensin b) Serum Dopamine c) Urine metanephrines/VMA d) Urine epinephrine Serum metanephrines also work 52) The pathological image below is Neuroblastoma, derived from neural crest cells. What are the circular formations seen in this image? a) Signet Rings b) Flexner-WinterSteiner Rosettes c) Perivascular Pseudorosettes d) Homer-Wright Rosettes 53) Cortisol (hydrocortisone) has a 1:1 ratio of effect on glucocorticoid vs mineralocorticoid receptors, whereas Dexamethasone acts solely on Glucocorticoid receptors. Which compound acts overwhelmingly on Mineralcorticoid rather than glucocorticoid recptors? a) Predisone b) Methylprednisone c) Cortisol d) Fludrocortisone e) Dexamethasone Weirdly enough: Cortisol effects augmented by licorice – it slows doen conversion of cortisol to cortisone 54) First line therapy for treating Cushing’s Disease (NOT just Cushing’s syndrome) is a resection of the pituitary adenoma – problem resolves in about 70% of pts. If surgery doesn’t work there is also medical and radiation therapy available. What antifungal drug is sometimes used to block the production of cortisol when waiting for a definitve therapy? a) Terbinafine b) Ketoconazole c) Amphotericin B d) Caspofungin Enzyme Inhibitors of steroidogenesis: Ketoconazole, Metyrapone Dopamine Agonists: Cabergoline Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonist: Mifepristone Some info from UptoDate: Cabergoline, a drug used mostly to treat prolactin-secreting pituitary tumors, can normalize ACTH and cortisol production in about 30 percent of patients. Similarly, pasireotide can normalize ACTH and cortisol in 20 to 25 percent of patients with Cushing’s disease. This new drug has been approved in Europe and the United States. It is already available in Europe and is expected to available in the United States soon. Mifepristone is a medication that was approved in the United States to decrease the effects of excess cortisol on glucose, but its role on long-term therapy of Cushing’s disease is uncertain. Other drugs that block production of cortisol, such as ketoconazole, metyrapone or mitotane, can also be used to reduce high levels of cortisol while waiting for more definitive therapy. Radiation — Radiation can be a useful treatment when pituitary tumors cannot be completely removed by surgery. Radiation of pituitary tumors reduces cortisol levels in about half of adults and most children with Cushing's disease. Because this cortisol-lowering effect takes time (3 to 24 months), medications that lower adrenal cortisol production may be given while waiting for the effects of radiation. These medications include ketoconazole and metyrapone 55) Pick the most true statement about Insulin: a) Receptor is a tyrosine kinase AND Amylin is insulin’s co-conspirator b) Receptor is G-Protein coupled AND Amylin is insulin’s co-conspirator c) Receptor is a tyrosine kinase AND Ghrelin is insulin’s co-conspirator d) Receptor is G-Protein coupled AND Ghrelin is insulin’s co-conspirator Amylin is co-secreted with insulin from beta-cells in a 1:1 ration. It inhibits glucagon secretion AND induces satiety. 56) Which compound inhibits insulin, glucagon, and ghrelin AND is triggered by increased insulin. a) CCK b) Amylin c) GLP-1 d) Somatostatin 57) Ghrelin is secreted by epsilom cells during fasting. How does it affect glucagon levels? a) Increases b) Decreases c) Does not affect 58) What activates secretion of Insulin during the Gastrointestinal phase? a) Incretins b) Parasympathetic nerves c) Sympathetic nerves d) Amylin e) Glucagon Parasympathetics would also stimulate insulin release, but this would be during the oral phase. Keep in mind that this is why you get a greater insulin response with an oral dose rather than IV. Parasympathetics AND incretins would both be acting to increase secretion. Incretins = GLP-1 and GIP 59) Which GLUT transporter is insulin sensitive and which acts as a glucose level sensor in the pancreas? a) GLUT3 = glucose sensor in pancreas / GLUT5 = Insulin sensitive b) GLUT2 = glucose sensor in pancreas / GLUT4 = Insulin sensitive c) GLUT1 = glucose sensor in pancreas / GLUT2 = Insulin sensitive d) GLUT4 = glucose sensor in pancreas / GLUT2 = Insulin sensitive 60) You are studying a person with a rare genetic defect. You discover that their LKB1 is permanently blocked and cannot be activated. What drug would not work to control this patient’s diabetes? a) Metformin b) Januvia o Normally Metformin activates LKB1 to activate AMPK § AMPK stops CRTC2 (TORC2) from going into the nucleus for transcription · PGC1 is NEVER expressed o Gluconeogenesis is BLOCKED! 61) What is Dinitrophenol’s future mechanism of action for diabetes tx? a) Extremely rapid weight loss b) Activates LKBI to activate AMPK, which stops CRTC2 from transcribing PGC1 c) Insulin Analogue d) Mitochondrial Uncoupler e) Increases adiposity 62) What is the autosomal dominant genetic mutation in pancreatic beta cells behind MODY2? (Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young type 2) a) Mutation in Ca channels b) Mutation in Glucokinase c) Mutation in K channels d) Mutation in Akt Remember general order of events: · Glucose enters GLUT2 channel and is phosphorylated by glucokinase and oxidized to produce ATP · ATP stops K channels and causes cell depolarization · V-gated Ca channels open letting in Ca · Ca-dependent proteins cause insulin vesicles to fuse and release insulin 63) One model explaining the cause of Type1 diabetes explains that T cells carrying TCR’s for self-peptides were never weeded out during development. What protein’s allele variants has a high correlation with T1D? a) MHC 1 b) MHC 2 c) IgG d) IgM - Specific MHC II alleles are strongly associated with T1D. - Different MHC II alleles have different peptide binding capabilities and determine which proteins might be presented to TCR. - High risk MHC II alleles can’t bind pancreatic beta “self” cells strongly and T cells carrying the TCR for these petides are NOT weeded out. - Can eventually lead to autoimmune attack Not the whole story. Twin concordance only 40-60%. 64) How is TNF-alpha, secreted from macrophages, connected to Insulin resistance in adipose tissue? a) TNF activates JNK, which inactivates IRS1, which stops Glut4 placement into membrane b) TNF activates JNK, which inactivates IRS1, which stops Glut2 placement into membrane c) TNF inactivates IRS1, which activaes JNK, which stops Glut2 placement into membrane d) TNF activates IRS1, which activates JNK, which stops Glut4 placement into membrane Macrophages secrete TNF-alpha TNF leads to insulin resistance! TNF binds to receptor on adipocyte (1) Activates JNK (2) JNK phosphorylates and inactivates IRS1 (3) IRS1 makes insulin signaling ineffective EFFECT: insulin can bind but can’t translocate Glut4 to uptake glucose 65) TNF-alpha is not the only compound that can activate JNK and cause IRS1 to block Glut4 translocation. What is another compound that does this? a) Glucagon b) Insulin c) Excess glucose d) Excess free fatty acids Other pathways are also involved. FFA binds to TLR4 causing IRS phosphorylation FFAs metabolized to form DAG, which activates Protein kinase C to phosphorylate IRS FFA metabolized to ceramide, which inactivates Akt 66) One of the most damaging effect of diabetes are the vascular changes responsible for CV disease, end-stage kindey disease, adult-onset blindness, etc caused by Advanced Glycation End products. How does RAGE, the soluble form of this, cause damage? a) RAGE binds to macrophages and promotes ROS release b) RAGE is an ROS, which has direct oxidative effects c) RAGE directly stimulates fibrin formation d) RAGE stimulates clotting factors 67) Which diabetes drug is a GLP analogue? a) Lispro b) Metformin c) Exenatide d) Glimeperide e) Pramlintide 68) Mechanism of action of sitagliptan: a) Stop DDP-IV from degrading incretins b) Amylin Mimetic c) Increase synthesis and transport of GLUT d) Insulin secretagogue 69) Mechanism of action of Nateglinide: a) Stop DDP-IV from degrading incretins b) Amylin Mimetic c) Increase synthesis and transport of GLUT d) Insulin secretagogue 70) Which diabetes drug binds to amylin receptors for effect? a) Lispro b) Metformin c) Exenatide d) Glimeperide e) Pramlintide 71) Which of these insulin drugs is intermediate acting? a) Glargine b) Lispro c) NPH d) Regular e) Detemir 72) Which of these drugs is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor? a) Repaglinine b) NPH c) Pioglitazine d) Exenatide e) Miglitol 73) The most important drug-induced hyperglycemia? a) b) c) d) Oral contraceptives Statins Niacin Glucocorticoids 74) Hb A1C over 6.4% constitutes diabetes. What would be an exception to the rule of trying to keep diabetic patients under 7% with therapy? a) Elders b) Youth c) Extremely obese d) Those with depression I would say that extremely obese is maybe a possibility too? Main exception is age though, as we talked about in class. 75) What is the most common symptom that will bring a patient into the doctor’s office for metabolic syndrome? a) Polyuria b) Weight gain c) Weight loss d) Low BP e) No symptoms