Ideal Gas Law
advertisement
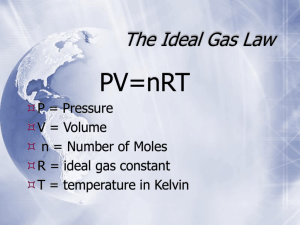
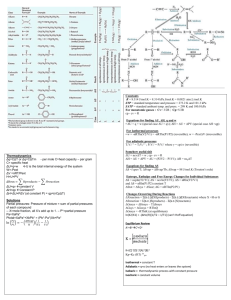
IDEAL GAS LAW IDEAL GAS • Follows all gas laws under all conditions of temperature and pressure • Follows all conditions of the Kinetic Molecular Theory (KMT) • An ideal gas does not exist in real life REAL GAS • Follows some gas laws under some conditions of temperature and pressure • Does not conform to the Kinetic Molecular Theory. Real gases have a volume and attractive and repulsive forces • A real gas differs from an ideal gas the most at low temperature and high pressure IDEAL GAS LAW EQUATION PV = nRT P= pressure (atm, torr, mmHg, kPa) V= volume (L, mL) n = # of moles (mol) R = Ideal Gas Constant T = temperature in Kelvin (K, ˚C +273) IDEAL GAS CONSTANT R = 0.0821L atm = 8.314 L kPa = 62.4 L mmHg = 62.4 L torr mol K mol K mol K mol K * Use the same unit as your given pressure EXAMPLE 1 Calculate the number of moles of gas contained in a 3.00L vessel at 298K with a pressure of 1.50 atm. V = 3.00L T = 298K P = 1.50atm n=? R = 0.0821 L atm mol K PV=nRT (1.50)(3.00) = n (0.0821) (298) n= 0.184 mol EXAMPLE 2 What will the pressure (in kPa) be when there are 0.400 mol of gas in a 5.00L container at 17.0˚C? V = 5.00L T = 17.0˚C = 290K P = ? kPa n = 0.400 mol R = 8.314 L atm mol K PV=nRT P(5.00) = (0.400)(8.314) (290) P= 193 kPa