Slide 1 - WordPress.com
advertisement
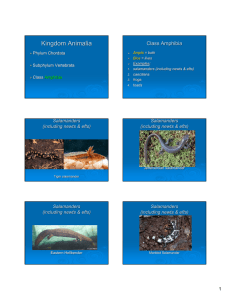
By Sarah Kahanic Grade: 6-8 Subject: Life Science Lay Eggs in Water Eggs don’t have shells Born with gills Cold-blooded Moist Skin Develop lungs and legs Live on land at maturity All amphibians start life as an egg in a ball of jelly. The eggs are laid in water. The egg hatches and the young amphibian breaks out of the jelly. We call the young of a frog or toad a tadpole. The young amphibian has gills to breathe underwater and a tail with a fin so it can swim. When it gets bigger it starts to grow legs. When it is full grown it changes quickly to its adult body shape. It loses its gills and grows lungs to breathe air. It loses its tail fin and its legs grow much larger. Then it leaves the water to live on land. It looks like an adult now, only much smaller.It takes a couple of years for an amphibian to grow to its adult size. In spring the adult will return to the pond, lake or stream where it was born to look for a mate. Then the females lay eggs to start the cycle over again. (Nature North) Frogs Toads Salamanders Newts Newts and Salamanders are both belong to the group “Urodela” which are amphibians with four legs and a tail at maturity. These amphibians resemble lizards Newts are a subset of the Salamander species All newts are salamanders, but not all salamanders are newts Newts Salamanders Poisonous Nocturnal Brightly Colored Spends most of life in or Active during the day More complex life cycle (spends days away from water) by water Please select the button and reread the section on Newts before continuing Both Frogs and Toads belong to the group “Anura” that lacks tails and have long hind legs well-adapted for jumping and swimming Frog two bulging eyes Toads stubby bodies with short strong, long, webbed hind feet that are adapted for leaping and swimming smooth or slimy skin (generally, frogs tend to like moister environments) Frogs tend to lay eggs in clusters. hind legs (for walking instead of hopping) warty and dry skin (usually preferring dryer climates) paratoid (or poison) glands behind the eyes The chest cartilage of toads is different also. Toads tend to lay eggs in long chains. Please select the button and reread the differences between toads and frogs before continuing Congratulations! You have finished this mini lesson. This mini lesson was created by Sarah Kahanic for EDU 103 For more information Email: srhkhnc@dordt.edu Life Science by Mc Dougal Littell (2006) http://www.scienceclarified.com/Al- As/Amphibians.html http://allaboutfrogs.org/weird/general/frogtoad.html http://www.flickr.com/groups/salamanders/discuss/7 2157594451142303/ http://www.naturenorth.com/1np/Species/amphibian /Lifcyc/Flfcyc.html