Economic Decision Makers

Economic Decision Makers
ECO 2013
Chapter 3
Households
Play a starring role in a market economy
Determines what gets produced
Supplies labor, capital, natural resources and entrepreneurial ability
Maximize utility
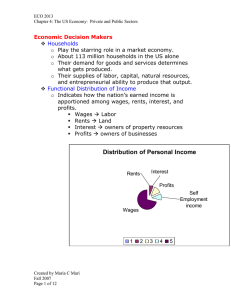
Functional Distribution of Income
Indicates how the nation’s earned income is apportioned among
Wages labor
Rents land
Interest owners of property resources
Profit owners of businesses
Functional Distribution of Income
Distribution of Personal Income
Rents
Interest
Profits
Self
Employment income
Wages
1 2 3 4 5
Personal Distribution of Income
How the nation’s money income is divided among individual households.
Top 20% earn over 50% of the income
Households
Income spent
Personal taxes – 12%
Personal savings – 0%
Personal consumption – 88%
Households
Three categories of spending:
Durable goods
Goods expected to last three or more years
Households
Nondurable goods
Goods such as food and gasoline
Household
Services
Businesses
Constitute the second major part of the private sector
Is a business organization that owns and operates plants.
Types of Firms
Sole proprietorships
A firm with a single owner who has the right to all profits and who bears unlimited liability for the firm’s debts.
Partnerships
A firm with multiple owners who share the firm’s profits and who bears unlimited liability for the firm’s debts.
Corporations
A legal entity owned by stockholders whose liability is limited to the value of their stock.
Distinct and separate from the individual stockholders who own it.
Government
Extensive role of the public sector
Levels of Government
Federal
State
Local
Role of Government
Providing legal structure
Promoting competition
Regulating monopolies
Redistributing income
Transfer payments
Market invention
Taxation
Reallocating resources
Market failure
Role of Government
Externalities
A cost or benefit that falls on a third party and is therefore ignored by the two parties to the market transaction
Externalities
An externality occurs when some of the costs or the benefits of a good are passed to or spill over to someone other than the immediate buyer or seller.
Negative externality
Production or consumption costs inflicted on a third party without compensation
Environmental pollution
Positive externalities
Benefits
education
Role of government
Public good
A good that once produced is available for all to consume regardless of who pays
National defense
Government structure
Federal
National security
Economic stability
Market competition
State
Public higher education
Prisons
Transportation
Local
Education
protection
Size of Government
Government spending has increased over the years
Government is the green in the chart
1930 – 10% of economy
2004 – 36% of economy
Government Purchase and Transfers
Government purchases
Exhaustive
Directly absorb resources and are part of the domestic output
Transfer payments
Non-exhaustive
Federal Expenditures
Pension and income security
35%
National defense
20%
Health
21%
Interest on debt
7%
Sources of Government Revenue
Taxes
Bulk of government revenues at all levels
Tax principles
Ability to pay principle
Benefits received tax principle
Tax incidence
Distribution of tax burden among taxpayers
Proportional tax
Progressive
Regressive
Marginal tax rate
Types of taxes
Personal income tax
Tax on earnings of individuals
Progressive tax
All but six states have it
Single taxpayer
But not over--
If taxable income is over--
$0
$7,150
$29,050
$70,350
$146,750
$319,100
$7,150
$29,050
$70,350
$146,750
$319,100 no limit
The tax is:
10% of the amount over $0
$715.00 plus 15% of the amount over 7,150
$4,000.00 plus 25% of the amount over 29,050
$14,325.00 plus 28% of the amount over 70,350
$35,717.00 plus 33% of the amount over 146,750
$92,592.50 plus 35% of the amount over 319,100
Types of Taxes
Corporate income tax
Tax on earnings of corporations
Progressive tax
Federal and state
If taxable income (line 30, Form 1120, or line 26, Form 1120-A) on page
1 is:
Over
—
$0
But not over
—
$50,000
Tax is:
15%
Of the amount over —
$0
50,000 75,000 $ 7,500 + 25% 50,000
75,000
100,000
335,000
10,000,000
15,000,000
18,333,333
100,000
335,000
10,000,000
15,000,000
18,333,333
- - - - -
13,750 + 34%
22,250 + 39%
113,900 + 34%
3,400,000 +
35%
5,150,000 +
38%
35%
75,000
100,000
335,000
10,000,000
15,000,000
0
Types of taxes
Sales tax
Tax on purchases of goods and services
Some services excluded
Some goods excluded
Flat rate
State and local government
Types of taxes
Property taxes
Tax on the value of real property
Tax on the value of tangible property
Flat rate
Local governments
Excise taxes
Tax on consumption of specific goods
Alcohol, tobacco, and gasoline
Sin taxes
All levels of government
Level of Government
Federal
Services Provided
National defense
Transfer payments
Transfers to states
Taxes Imposed
Personal income tax
Corporate income tax
Excise taxes
State Public transportation
Welfare
Higher education
Personal income tax
Corporate income tax
Excise taxes
Sales taxes
Local Police and fire protection
Primary and Secondary education
Excise taxes
Property taxes