Media – platforms or vehicles that industries have developed for the
advertisement

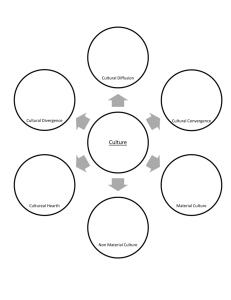
Understanding Mass Media, Convergence, and the Importance of Media Literacy Week One MEDIA CONVERGENCE Media – platforms or vehicles that industries have developed for the purposes of creating and sending messages - telephones - movies - television Convergence – takes place when products are typically linked to one medium show up on many media - music that you can share across multiple devices - tweeting about the game during the Super Bowl MASS COMMUNICATION Related to a technology and the size of its audience AUDIENCE FRAGMENTATION– the process of dividing audience members into segments based on background and lifestyle in order to send them messages targeted to their specific characteristics FIGURE 1.1 Audience Fragmentation 3 MASS COMMUNICATION ELEMENTS OF PRODUCTION • Thinking about the way communications content is created • MASS PRODUCTION PROCESS Creates the potential for reaching a large number of diverse, anonymous people at around the same time • INDUSTRIAL NATURE Considering the various companies that work together to create content MASS COMMUNICATION ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION • COMMUNICATION • MESSAGES • INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION • MEDIATED INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION • MEDIUM INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION SOURCE - ENCODES the MESSAGE RECEIVER – DECODES the MESSAGE The MESSAGE travels through a CHANNEL from the SOURCE to the RECIEVER. - ex. Voice/sounds waves FIGURE 1.2 Interpersonal Communication 6 COMPARING ELEMENTS TABLE 1.1 Comparing Elements Across Different Forms of Communication 7 ELEMENTS OF MASS COMMUNICATION ON AN INDUSTRIAL SCALE FIGURE 1.3 Mass Communication 8 MASS MEDIA AND CONVERGENCE THE THREE C’S OF MASS MEDIA CONVERGENCE • CONTENT – messages • CORPORATIONS – The companies that interact to create and distribute the content • COMPUTERS – The tool corporations use to disseminate content MASS MEDIA AND CONVERGENCE ANALOG – electronic transmission accomplished by adding signals of varying frequency of amplitude to carrier waves of a given frequency of alternating electromagnetic current. DIGITAL – electronic technology that generates, stores, processes and transmits data in the form of strings of 0s and 1s; each of these digits is referred to as a bit - Allows for convergence HOW DO WE USE THE MASS MEDIA IN OUR DAILY LIVES? • Enjoyment • Social currency • Companionship • Parasocial interaction • Surveillance • Interpretation HOW DO THE MASS MEDIA INFLUENCE CULTURE? CULTURE – ways of life that are passed on to members of a society through time and that keep the society together SUBCULTURES SOCIETY – large numbers of individuals, groups, and organizations that live in the same general area and consider themselves connected to one another through the sharing of a culture The Mass media present ideas of the culture… HOW DO THE MASS MEDIA INFLUENCE CULTURE? Identifying and discussing codes of acceptable behavior Learning what and who counts in our world – and why Determining what others think of us – and what people “like us” think of others CRITICISMS OF MASS MEDIA’S INFLUENCE ON CULTURE STEREOTYPES – predictable depictions that reflect (and sometimes create) cultural prejudices POLITICAL IDEOLOGIES – beliefs about who should hold the greatest power within a culture MEDIA LITERACY A MEDIA-LITERATE PERSON IS • Knowledgeable about the influences that guide media organizations • Up-to-date on political issues relating to the media • Sensitive to ways of seeing media content as a means of learning about culture • Sensitive to the ethical dimensions of media activities • Knowledgeable about scholarship regarding media effects • Able to enjoy media materials in a sophisticated manner How to become a more Media Literate individual MEDIA LITERACY TOOLS AND PRINCIPLES FIGURE 1.4 Principles of Media Literacy 16