PHASE CHANGES
advertisement

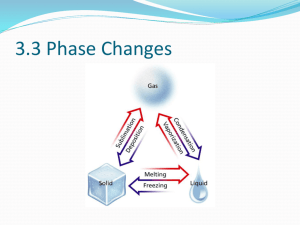
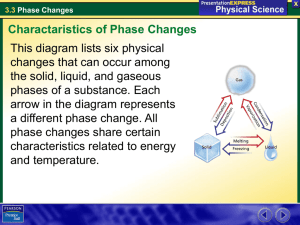
PHASE CHANGES SECTION 3.3 CHARACTERISTICS OF PHASE CHANGES A. A phase change is the reversible physical change that occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another B. Melting, freezing, vaporization, condensation, sublimation, and deposition are six common phase changes C. Temperature and Phase Changes 1. The temperature of a substance does not change during a phase change 2. When a solid changes to a liquid a. At first the temperature rises as a solid warms up b. At the melting point, the temperature stops rising c. and remains the same until the melting is complete The temperature will begin to rise again 3. When a liquid changes to a solid a. At first the temperature of the liquid will drop until it reaches the freezing point b. At the freezing point, the temperature will remain at that temperature until all of the liquid freezes c. After the freezing is complete, the temperature will begin to drop again 4. The temperature at which a substance freezes (its freezing point) is identical to the temperature at which it melts (its melting point) 5. When a liquid changes to a gas a. The temperature keeps rising until it reaches the boiling point b. The temperature then remains the same until the boiling is complete D. Energy and Phase Change 1. Energy is either absorbed or released during a phase change 2. During an endothermic change, the system absorbs energy from its surroundings a. Melting, vaporization, and sublimation are all b. examples of endothermic changes The heat of fusion is the amount of energy a substance must absorb in order to change from a solid to a liquid. Fusion is another term for melting 3. One gram of water releases 334 joules of energy to its surroundings as it freezes. a. This is the same amount of energy absorbed when one gram of ice melts b. Farmers use this release of energy to protect their crops 4. During an exothermic change, the system releases energy to its surroundings. Freezing, deposition, and condensation are examples of exothermic reactions MELTING AND FREEZING A. The arrangement of molecules in water becomes less orderly as water melts and more orderly as water freezes B. Melting 1. In ice, the attractions between water molecules keep the molecules in fixed positions 2. When ice is removed form the freezer, heat flows from the air to the ice 3. As the ice gains energy, the molecules vibrate more quickly. 4. At the melting point of water some molecules gain enough energy and move from their fixed position. 5. When all of the molecules gain energy melting is complete. C. Freezing 1. When liquid water is placed in a freezer, energy flows from the water to the air in the freezer 2. This process is the reverse of the melting process. VAPORIZATION & CONDENSATION A. Vaporization is the phase change in which a substance changes from a liquid into a gas. B. A substance must absorb energy in order to change from a liquid to a gas. C. The heat of vaporization for water is equal to 2261 joules of energy. D. There are two vaporization processes – boiling and evaporation. E. Evaporation takes place at the surface of a liquid. 1. Evaporation is the process that changes a substance form a liquid to a gas at temperatures below the boiling point. 2. A vapor is the gaseous phase of a substance 3. Vapor pressure is the pressure caused by the collisions of vapor and the walls of the container. F. Boiling 1. When vapor pressure becomes equal to atmospheric pressure, water boils. 2. The temperature at which this happens is the boiling point of water. 3. As temperature increases, water molecules move faster and faster. 4. When the temperature reaches 100°C, some molecules below the surface have enough kinetic energy to overcome the attraction of neighboring molecules. 5. Because water vapor is less dense than water, the bubbles rise to the surface. 6. The boiling point of a substance depends on the atmospheric pressure. a. At higher elevations the atmospheric pressure is lower b. This will cause the boiling point to occur at a lower temperature. c. Cooking will take longer at higher elevations G. Condensation is the phase change in which a substance changes from a gas or vapor to a liquid. This process is responsible for the dew on grass and the condensation on bathroom mirrors. SUBLIMATION & DEPOSITION A. Sublimation is the phase change in which a substance changes from a solid to a gas or vapor without changing to a liquid first. B. Example, at room temperature, dry ice can directly change from a solid to a colorless gas. C. As dry ice sublimes, the cold carbon dioxide vapor causes water vapor in the air to condense and form clouds. D. Deposition is the phase change that occurs when a gas or vapor changes directly into a solid without first changing to a liquid. E. Deposition causes frost to form on windows