Costs 3 - ME EN 282 Manufacturing Processes
advertisement

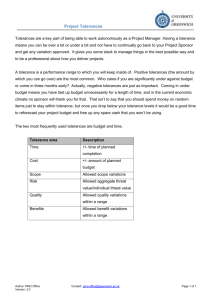
Manufacturing Costs Breakdown BREAKDOWN Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Importance Your company wants to make money! Profit and price (and ultimately your salary) depend on how you manage manufacturing costs. You will have to address costs and economics in presentations about your work Manufacturing Cost Analysis 3 Overview Non-Manufacturing Costs Manufacturing Costs Manufacturing Cost Analysis 3 Direct Materials Definition: Any material that is a part of the finished product that significantly adds to the weight or volume of the item Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Materials Definition: Any material that is a part of the finished product that significantly adds to the weight or volume of the item Examples: ◦ Wood used to make furniture Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Materials Definition: Any material that is a part of the finished product that significantly adds to the weight or volume of the item Examples: ◦ Wood used to make furniture ◦ Plastic used to make a Frisbee Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Materials Definition: Any material that is a part of the finished product that significantly adds to the weight or volume of the item Examples: ◦ Wood used to make furniture ◦ Plastic used to make a Frisbee ◦ Material used to make the soles of shoes Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Examples: ◦ Glue Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Examples: ◦ Glue ◦ Screws Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Examples: ◦ Glue ◦ Screws ◦ Cleaning materials Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Examples: ◦ Glue ◦ Screws ◦ Cleaning materials ◦ Lubricants Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Materials Definition: Material that does not significantly add weight or volume to the product, or that is used for something indirectly related to the product. Examples: ◦ Glue ◦ Screws ◦ Cleaning materials ◦ Lubricants ◦ Shelves used to store paint, tools, or other items Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Labor Definition: Any labor done directly on the product that affects the physical properties of the item Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Labor Definition: Any labor done directly on the product that affects the physical properties of the item Examples: ◦ Putting together furniture Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Labor Definition: Any labor done directly on the product that affects the physical properties of the item Examples: ◦ Putting together furniture ◦ Cutting chocolate bars into special shapes Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Labor Definition: Any labor done directly on the product that affects the physical properties of the item Examples: ◦ Putting together furniture ◦ Cutting chocolate bars into special shapes ◦ Painting bicycle frames Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Direct Labor Definition: Any labor done directly on the product that affects the physical properties of the item Examples: ◦ Putting together furniture ◦ Cutting chocolate bars into special shapes ◦ Painting bicycle frames ◦ Injection molding plastic smartphone cases Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Examples: ◦ Materials purchasing Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Examples: ◦ Materials purchasing ◦ Quality control Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Examples: ◦ Materials purchasing ◦ Quality control ◦ Janitorial labor Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Examples: ◦ Materials purchasing ◦ Quality control ◦ Janitorial labor ◦ Production management Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Indirect Labor Definition: Labor important to production that is not performed directly on the item being produced. Examples: ◦ Materials purchasing ◦ Quality control ◦ Janitorial labor ◦ Production management ◦ Tech support Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Manufacturing Overhead Definition: Total of all indirect costs that are required in order to manufacture a product. Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Manufacturing Overhead Definition: Total of all indirect costs that are required in order to manufacture a product. Examples of included costs: ◦ Indirect Materials Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Manufacturing Overhead Definition: Total of all indirect costs that are required in order to manufacture a product. Examples of included costs: ◦ Indirect Materials ◦ Indirect Labor Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Manufacturing Overhead Definition: Total of all indirect costs that are required in order to manufacture a product. Examples of included costs: ◦ Indirect Materials ◦ Indirect Labor ◦ Depreciation of machinery and property values Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Manufacturing Overhead Definition: Total of all indirect costs that are required in order to manufacture a product. Examples of included costs: ◦ Indirect Materials ◦ Indirect Labor ◦ Depreciation of machinery and property values ◦ Manufacturing plant property taxes Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Review Manufacturing Cost Analysis 3 Homework Problem (MC 3) Give a definition for each cost classification below. Also give 2 examples for each. ◦ A) Direct Labor ◦ B) Direct Materials ◦ C) Indirect Labor ◦ D) Indirect Materials ◦ E) Manufacturing Overhead Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3 Sources: Direct / Indirect Materials ◦ http://www.microbuspub.com/pdfs/chapter4.pdf ◦ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Direct_materials_cost ◦ http://www.accountingtools.com/questions-and-answers/what-are-indirect-materials.html Direct / Indirect Labor ◦ http://www.microbuspub.com/pdfs/chapter4.pdf ◦ http://www.accountingtools.com/definition-direct-labor ◦ http://www.accountingtools.com/definition-indirect-labor Manufacturing Overhead ◦ http://www.microbuspub.com/pdfs/chapter4.pdf ◦ http://www.accountingcoach.com/manufacturing-overhead/explanation ◦ http://www.accountingtools.com/questions-and-answers/what-is-manufacturing-overhead.html Images ◦ http://www.freeimages.com Manufacturing Cost Analysis Dimensioning & Tolerances 2 3