Task 1 - Shawlands Academy
advertisement

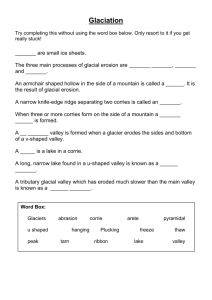
LITHOSPHERE In this unit we will look at… • • • Glaciated Landscapes Limestone Landscapes Coastal Landscapes You will… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Learn about the landforms associated with each landscape Have to be able to describe and explain the formation of the landforms Have to be able to draw sketches of some landforms Have to know the processes that shaped these landscapes Learn how to identify landscape features on an O.S map Glaciated Landscapes Throughout the lithosphere unit you will use O.S maps to identify features, using 4 and 6 figure grid references. Task 1; Look at the O.S map of the Cairngorms on the next slide and describe the evidence which shows that this area was once affected by glaciation. Find features of glaciation on the map extract, and use 4 and 6 figure grid references to show where the features are on the map. Corrie Remember! Contour lines are very close together showing very steep land. Arete The contour lines are curved showing a bowlshape Sometimes a tarn is evident U-Shaped Valley Where two corries form back to back. Contour lines are very close together showing very steep land. There is a long strip of white in the middle showing flat land. The arete (ridge) is shown as a black rugged line D C B 08 E 07 07 A 06 06 05 05 04 03 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 D U-Shaped Valley and Mis fit stream C B Tarn 08 E corries 07 07 A 06 06 corries 05 05 Tarn 04 fiord 03 91 92 Arete 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 3 Corries 3 Corries 2 Corries U – Shaped Valley Misfit Stream Fiord U-shaped valleys and corries are features of glacial erosion. But what processes have shaped these landforms, and other landforms of glacial erosion? Plucking; • When rocks have become weakened by freeze-thaw, the moving glacier freezes onto the valley sides and floor • As the glacier moves downslope by gravity, the rocks that the glacier has frozen onto are torn away from the valley sides and floor • This produces rough, jagged rock surfaces • By tearing away huge rocks, the valley sides are left very steep and the base very flat. Abrasion; • The jagged rocks and stones embedded at the base of the glacier or ice sheet, scrapes along the valley sides and base. • This is like a sandpapering effect, where the valleys sides and base become smooth • Where the rocks embedded in the glacier scratch along the surface, striations may be left on the rock surface. Striations are scratch marks on the rock surface. Freeze-Thaw (Frost Action) •Occurs when temperature rise and fall •When it rains, snows etc, water enters the cracks in the rocks •When temperatures fall below zero, possibly at night, the water freezes and expands; frozen water can expand by 9%. This exerts huge pressure on the rock. •When temperatures rise again, during the day, the ice melts, releasing the pressure on the rocks. •This continuous freezing and thawing causes the rocks to become very weak, cracks widen and pieces of rock break off. •Rocks that have broken off, fall to the foot of the slope, shatter and become scree or talus. Before Glaciation During Glaciation After Glaciation Homework For tomorrow… Answer the 1998 past paper question on Glaciation (3b) 3b) is worth 4 marks so you are looking for 8 points to make Task 1: Using the information that you have just heard and your notes, answer the following question; Select one feature of glacial erosion and explain the processes involved in the formation of this feature. Annotated diagrams may be used. 3 marks