Interest Rate and Foreign Exchange Rate Derivative
advertisement
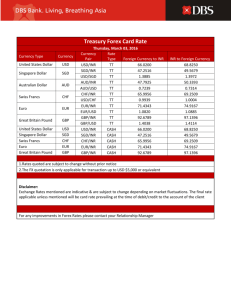
Derivatives Markets In Interest Rate & Foreign Exchange Rate Utility For Importer & Exporter NEHA ABHISHEK, BANGALORE Batch: 22, (5th July to 30th August, 2014) Agenda • Derivatives • List of Derivatives under various categories • Concept of Hedging • Exposure of Importer and Exporter • Derivatives on Foreign Exchange • Forwards Contracts • Future • Option Contract • Interest Rate Derivatives • Forwards Rate Agreement (FRA) • SWAP • Interest Rate Option Derivatives As per Clause (a) of Section 45U of RBI Act 1934 "derivative" means an instrument, to be settled at a future date, whose value is derived from change in interest rate, foreign exchange rate, credit rating or credit index, price of securities (also called "underlying"), or a combination of more than one of them and includes • • • • • • • interest rate swaps, forward rate agreements, foreign currency swaps, foreign currency-rupee swaps, foreign currency options, foreign currency-rupee options or such other instruments as may be specified by the Bank from time to time; List of Derivatives under various categories Derivatives Location Basic Variable Real Assets Commodities Metals Real Estates Plant & Equipment Financial Assets Bonds Shares Loan Currencies Price Risk Forwards Futures Options Others Weather Power Insurance Interest Rate Risk Swaps Futures Options OTC Forwards Options Swaps ETC Futures Options Nature Forwards Future Options Swap Concept of Hedging Exporter Gain Foreign Currency Local Currency Importer Gain Foreign Currency Local Currency Exposure of Importer and Exporter Month USD/INR April 14 60.22 August 14 August 14 March 15 March 15 59.27 59.27 62.85 62.85 Importers Hedged (Y) Happy (H) Unhedged (N) Unhappy (U) Exporters Hedged (Y) Happy (H) Unhedged (N) Unhappy (U) Remarks Reference Rate N Y N Y (H) (U) (U) (H) N Y N Y (U) (H) (H) (U) Forward Contract • • • • • • A foreign exchange forward is an OTC contract Purchaser agrees to buy from the seller, and Seller agrees to sell to the buyer, A specified amount of a specified currency On a specified date in future. In India there are two types of Forward Contract • Fixed Forward Contract: Delivery of foreign exchange should take place on specified future date. • Option Forward Contract: The customer can sell or buy from the bank foreign exchange at any given period of time at a predetermined rate of exchange. The Option Period of delivery should not exceed one month. Future An agreement entered into with the specified future exchange to buy or sell standard amount of foreign currency at a specified price for delivery on specified future date. Maximum Limit in currency future is USD 5 million or 6% of the open interest, whichever is higher. The Features of Currency Future in India Currency Size Quotation The contract is available on US Dollar/ Indian Rupee. The Size of one Future is USD 1,000. The future is quoted in rupee terms with a minimum price charge of 0.25 paise. However the outstanding position is reckoned in dollar terms. Maturities Due Date The contract is available with maturity ranging from 1 to 12 months. The contract expire on last working day of the month, excluding Saturday. Outstanding contract are settled on this day. Two days before the expiry date. The Settlement price is fixed on last trading day at the Reserve’s Bank reference rate. The contract is settled by payment in Indian Rupee. The difference between the strike price and settlement price is exchanged between the buyer and seller. No delivery of Dollar take place. Trading can be done between 9a.m. to 5p.m. Last Trading Day Settlement Price Settlement Trading Hours Option Option Call Buy Importer Right to Buy Sell Exporter Obligation to Sell Put Buy Exporter Right to Sell Sell Importer Obligation to Buy Concept of In the Money (ITM), At the Money (ATM) and Out of the Money (OTM) Nature of Option Based on Strike In the Money (ITM) At the Money (ATM) Out of the Money (OTM) Exporter Importer Illustration Strike Price of Buy Put > Strike price of Buy Call < FRR = 45 Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Buy USD Put @ 46 Buy USD Call @ 44 Strike Price of Buy Put = Strike price of Buy Call = FRR = 45 Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Buy USD Put @ 45 Buy USD Call @ 45 Strike Price of Buy Put < Strike price of Buy Call > FRR = 45 Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Forward Reference Rate (FRR) Buy USD Put @ 44 Buy USD Call @ 46 Option - Exporter Assume that FRR for maturity on 31st December 2011 is INR 45 for USD/ INR currency pair. Buy USD Put at INR 45 (ATM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 1. Buy USD Put at INR 46 (ITM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 2. Buy USD Put at INR 44 (OTM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 0.50. Table plot the exercisability and payoff matrix for maturity by taking some random market rates. Market Rate FRR = 45 BP = 45 P/L matrix BP = 46 P/L matrix BP = 44 P/L matrix compared with Prem. =1 compared Prem. = 2 compared Prem. = .5 FRR (ATM) with FRR (ITM) with FRR (OTM) 43 45 Y -1 Y -1 Y -1.5 44 45 Y -1 Y -1 Y -1.5 45 45 Y -1 Y -1 N -0.5 46 45 N 0 Y -1 N 0.5 Assume that FRR for maturity on 31st December 2011 is INR 45 for USD/ INR currency pair. Sell USD Call at INR 45 (ATM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 1. Sell USD Call at INR 46 (OTM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 0.50. Sell USD Call at INR 44 (ITM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 2. Table plot the exercisability and payoff matrix for maturity by taking some random market rates. Market Rate FRR = 45 BC = 45 P/L matrix BC = 44 P/L matrix BC = 46 P/L matrix compared Prem. =1 compared Prem. = 2 compared Prem. = 0.5 with FRR (ATM) with FRR (ITM) with FRR (OTM) 43 45 N 1 N 2 N 0.5 44 45 N 1 Y 2 N 0.5 45 45 Y 1 Y 1 N 0.5 46 45 Y 0 Y 0 Y 0.5 Option - Importer Assume that FRR for maturity on 31st December 2011 is INR 45 for USD/ INR currency pair. Buy USD Call at INR 45 (ATM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 1. Buy USD Call at INR 46 (OTM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 0.50. Buy USD Call at INR 44 (ITM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 2. Table plot the exercisability and payoff matrix for maturity by taking some random market rates. Market FRR = 45 BC = 45 P/L matrix BC = 44 P/L matrix BC = 46 Rate Prem. =1 compared Prem. = 2 compared Prem. = 0.5 (ATM) with FRR (ITM) with FRR (OTM) 43 45 N 1 N 0 N 44 45 N 0 Y -1 N 45 45 Y -1 Y -1 N 46 45 Y -1 Y -1 Y Assume that FRR for maturity on 31st December 2011 is INR 45 for USD/ INR currency pair. Sell USD Put at INR 45 (ATM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 1. Sell USD Put at INR 46 (ITM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 2. Sell USD Put at INR 44 (OTM Option) – premium paid upfront INR 0.50. Table plot the exercisability and payoff matrix for maturity by taking some random market rates. Market Rate FRR = 45 BP = 45 P/L matrix BP = 46 P/L matrix BP = 44 Prem. =1 compared Prem. = 2 compared Prem. = .5 (ATM) with FRR (ITM) with FRR (OTM) 43 45 Y -1 Y -1 Y 44 45 Y 0 Y 0 Y 45 45 Y 1 Y 1 N 46 45 N 1 Y 2 N P/L matrix compared with FRR 1.5 0.5 -0.5 -1.5 P/L matrix compared with FRR -0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Exchange Rate Derivatives - Importer Perspective On 12th Jan, an Indian Firm knows that it has $600000 payable, on 12 th March. The Spot Rate is 40.45/$, while 2month forward rate is Rs.40.62/$. 2month INR/USD Interest Rate is 10%/4% p.a. resp. $ future for maturity ending March is Rs.40.65/$. Call and Put option on $ at E = Rs.40.60/$ traded at premium of .40p & .50p respectively. On 12 th March Spot Rate Rs.40.7/$. Future traded at Rs.40.74/$. The outflow in the following situation will be as follows: Outflow on 12th March= Total $ Payable × Spot Rate on 12th March No Hedging $600,000×Rs.40.7/$ = Rs.24,420,000 Money Market The firm will invest in PV of $600000 i.e. $600,000 = $ 596,027 Cover 1 + .04 (Invest- Buy6 Therefore, Present Outflow = $596,027 × Rs.40.45/$ = Rs.24,109,292 Borrow) And, Total Outflow = Rs.24,109,292 ( 1 + 0.1 ) = Rs.24,511,114 6 th Outflow on 12 March = Total $ Payable × Forward Rate Forward Cover $600,000 × Rs.40.62/$ = 24,372,000 Profit on Squaring Future on 12th March = ( Rs.40.74/$ - Rs.40.65/$ ) × $600,000 Future Cover = Rs.54,000 th On 12 March $ Purchase at $600,000 × Rs.40.7/$ = Rs.24,420,000 Therefore, Total Outflow under Future = Rs.24,420,000 – Rs.54,000 = Rs.24,366,000 FV of Premium Outflow on C+ = ( $600,000 × 0.4p ) × ( 1 + 0.1 ) = Rs. 244,000 Option 6 Call exercised as Spot Price > E, therefore Buy $ at $600,000 × Rs.40.6/$ = Rs.24,360,000 Total Outflow on 12th March = Rs.24,360,000 + Rs.244,000 = Rs.24,604,000. Exchange Rate Derivatives - Exporter Perspective On 12th Dec, an Indian Firm knows that it has $600000 receivable, on 12th March. The Spot Rate is 60.45/$, while 2month forward rate is Rs.60.62/$. 2month INR/USD Interest Rate is 10%/4% p.a. resp. $ future for maturity ending March is Rs.60.65/$. Call and Put option on $ at E = Rs.60.60/$ traded at premium of .40p & .50p respectively. On 12th March Spot Rate Rs.60.7/$. Future traded at Rs.60.74/$. The Inflow in the following situation will be as follows: No Hedging Inflow on 12th March= Total $ Receivable × Spot Rate on 12th March $600,000×Rs.60.7/$ = Rs.36,420,000 Money Market The firm will Borrow in PV of $600000 i.e. $600,000 = $ 594,059 Cover 1 + .04 (Borrow-Sell4 Invest) Therefore, Present Inflow = $594,059 × Rs.60.45/$ = Rs.35,910,867 And, Total Inflow = Rs. 35,910,867 ( 1 + 0.1 ) = Rs.36,808,639 4 Forward Cover Future Cover Option Inflow on 12th March = Total $ Receivable × Forward Rate $600,000 × Rs.60.62/$ = 36,372,000 Profit on Squaring Future on 12th March = ( Rs.60.74/$ - Rs.60.65/$ ) × $600,000 = Rs.54,000 On 12th March $ Purchase at $600,000 × Rs.60.7/$ = Rs. 36,420,000 Therefore, Total Inflow under Future = Rs. 36,420,000 + Rs.54,000 = Rs.36,474,000 FV of Premium Outflow on P+ = ( $600,000 × 0.5p ) × ( 1 + 0.1 ) = Rs. 307,500 4 Put not exercised as Spot Price > E, therefore Buy $ at $600,000 × Rs.40.7/$ = Rs. 36,420,000 Total Inflow on 12th March = Rs. 36,420,000 - Rs.307,500 = Rs.36,112,500. Interest Rate Derivatives Over-the-counter (OTC) interest rate derivatives include instruments such as • Forward Rate Agreements(FRAS): A Forward Rate Agreement (FRA) is a financial contract between two parties to exchange interest payments for a 'notional principal' amount on settlement date, for a specified period from start date to maturity date. • Interest Rate Swaps (IRS):provide for the exchange of payments based on differences between two different interest rates. • Caps, Floors, And Collars: are option-like agreements that require one party to make payments to the other when a stipulated interest rate, most often a specified maturity of LIBOR, moves outside of some predetermined range. Settlement under FRA HDFC Bank quotes on 15 march its 6×9 FRA at (MIBOR) 5.35 – 5.45. ABC barrows Rs. 5 crores under FRA. MIBOR on 13th September is 6%. The following formula applied in calculating the compensation payable under FRA: Compensation = (L-R) or (R-L) × D × A (B × 100) + D × L Where, L = Settlement Rate (LIBOR, MIBOR, etc.) i.e. 6% R = Contract reference rate i.e. 5.45% D = No. of days in contract period i.e. 91 days B = Days basis that is, 360 or 365 days in a year A = Notional principal amount i.e. Rs.50,000,000 Compensation = (6 - 5.45) × 91 × 50,000,000 = Rs.67551.15 (365 × 100) + 91 × 6 SWAP SWAP Currency Swaps A Plain Vanilla Swap A Basis Swap rate An Amortizing Swap Interest Rate Swap Step up Swap Cross Currencies Interest Rate Swap Extendable Swap Delayed Start Swaps/ Forward Swap Differential Swap Interest Rate Swap Structure Companies A and B faces the following Interest Rates: A B U.S. Dollars (Floating Rate) LIBOR + 0.5% LIBOR + 1% Canadian (Fixed Rate) 5% 6.5% Assume that A wants to borrow U.S. Dollars at a floating rate of interest and B wants to borrow Canadian dollars at a fixed rate of interest. A Bank is planning to arrange a swap and requires 50 basis point spread. If swap is equally attractive to A and B, what interest rate will A and B end up paying? SWAP STRUCTURE L + 0.25% Bank L + 1% 5% B A 5% L + 0.25% 6.25% Spread = 0.5% L + 1% 6.25% Interest Rate Option • Allows the buyer of the option to borrow or lend the specified amount of a specified currency at a specified future date at a specified rate of interest without any obligation to do so. • A buy call option means a buyer with right to borrow • A buy put option mean right to invest. • Interest Rate Cap enforce an upper limit on the floating rate payment and the risk of higher interest rates is crystallized into a single payment to be made upfront, without sacrificing downside risk. • Interest Rate Floor is a series of put option meant to protect the lender against drop in interest below a specified rate in a floating rate asset. Collar: Interest Rate Risk Hedging Strategy Index USD 6 months LIBOR Notional USD 10 Million Tenor 5 years Cap strike 3.75% Floor strike 2.50% Bank will charge 225 bps Here the interest coupon is floored at 2.50% + 2.25% = 4.75% and cap at 3.75% + 2.25% = 6% LIBOR On ECB / FCY loan Pay On collar (Floor at 2.50%, Cap at 3.75%) 2.25% 4.50% Receive from/ Pay out Pays 0 3.25% 5.50% - 4.25% 6.50% 4.75% 7.00% Receive Net Pays Pays 0.25% 4.75% 0 0 5.50% Receive 0.50% 0 6.00% Receive 1.00% 0 6.00% Seagull: Interest Rate Risk Hedging Strategy Index USD 6 months LIBOR Notional USD 10 Million Tenor 5 years Cap 1 strike 3.75% Cap 2 strike 4.50% Floor strike 1.75% Bank will charge 225 bps. In the above illustration contract holder sell two deep out of money floor at interest coupon of 4% and cap 2 at interest coupon of 6.75%. Buy single cap 1 which is relatively less out of the money at interest coupon of 6%. LIBOR On ECB / FCY loan Pay 1.00% 2.50% 3.50% 4.50% 5.50% 3.25% 4.75% 5.75% 6.75% 7.75% On collar (Floor at 1.75%, Cap 1 at 3.75% and Cap 2 at 4.50%) Receive from/ Pay out Pays Receive Receive Net Receive Pays Pays 0 0 0 0.75% 0.75% 0.75% 0 0 0 0 4.00% 4.75% 5.75% 6.00% 7.00% Thank You