BBA - 01 Overview of Financial management
advertisement

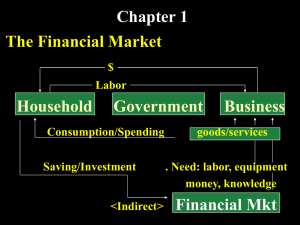
An Overview of Financial Management Class Objectives Read, interpret, and analyze financial reports Manage working capital and profits Understand the importance of growth Know how to finance growth Class Objectives cont. Sources, types, and costs of capital Risk, reward, and value creation Investment analysis Structure and negotiate a new hospitality venture Hospitality Financial Challenges A multi-faceted industry Low profitability Fluctuating sales volume Labor intensive Capital intensive Reliance on discretionary incomes What is Finance? money or other liquid resources of a government, business, group, or individual the system that includes the circulation of money, the granting of credit, the making of investments, and the provision of banking facilities What is Finance? the science or study of the management of funds the obtaining of funds or capital Areas in Finance Markets and institutions – Money market & Capital market – Financial institutions; Banks, Insurance company, Finance company etc. Investment – Decision making of investors Financial management – Maintenance and creation of economic value or wealth Financial Management Issues Use of computers and electronic transfers of information The globalization of business Responsibilities of the Financial Staff Forecasting and planning Investment and financing decisions Coordination and control Transactions in the financial markets Risk management Alternative Forms of Business Organization Sole proprietorship Partnership Corporation Sole Proprietorship Advantages: – Ease of formation – Subject to few regulations – No corporate income taxes Disadvantages: – Limited life – Unlimited liability – Difficult to raise capital Partnership A partnership has roughly the same advantages and disadvantages as a sole proprietorship. Corporation Advantages: – Unlimited life – Easy transfer of ownership – Limited liability – Ease of raising capital Disadvantages: – Double taxation – Cost of set-up and report filing Goals of the Firm The primary goal is shareholder wealth maximization, which translates to maximizing stock price. Do firms have any responsibilities to society at large? Is stock price maximization good or bad for society? Should firms behave ethically? Possible financial Goals Survive Avoid financial distress and bankruptcy Beat the competition Maximize sales or market share Minimize costs Maximize profits Maintain steady earnings growth The Goal of financial management is to maximize the current value per share of the existing stock Because we consider stockholders of the firm are true owner. Factors Influenced by Managers that Affect Stock Price Projected earnings per share Timing of the earnings stream Riskiness of the earnings stream Use of debt (capital structure) Dividend policy Ten Axioms that Form the Basics of Financial Management 1. The Risk- Return Tradeoff: We won’t take on additional risk unless we expect to be compensated with additional return 2. The time value of money: A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future. 3. Cash-not profits- is King. 4. Incremental cash flow: It’s only what changes that counts. Ten Axioms that Form the Basics of Financial Management 5. The curse of competitive markets: Why it’s hard to find exceptionally profitable projects. – Differentiate products – Minimize cost 6. Efficient capital market: The markets are Quick and the prices are right. 7. The Agency problem: Managers won’t work for the owners unless it’s in their best interest. Ten Axioms that Form the Basics of Financial Management 8. Tax bias business decisions 9. All risk is not equal: Some risk can be diversified away, and some can not. 10.Ethical behavior is doing the right thing, and Ethical dilemmas are everywhere in finance. Business Ethics Bribery Personal gain Insider information Product safety Employee practices Agency Relationships An agency relationship exists whenever a principal hires an agent to act on his or her behalf. Within a corporation, agency relationships exist between: – Shareholders and managers – Shareholders and creditors Shareholders versus Managers Managers are naturally inclined to act in their own best interests. But the following factors affect managerial behavior: – – – – Managerial compensation plans Direct intervention by shareholders The threat of firing The threat of takeover Shareholders versus Creditors Shareholders (through managers) could take actions to maximize stock price -high risk project for higher returns- that are detrimental to creditors. Creditors has bankruptcy threat. In the long run, such actions will raise the cost of debt(when a company takes part in more risky business) and ultimately lower stock price (while risk has been increased dramatically).