Foundational Philosophies in Education
advertisement

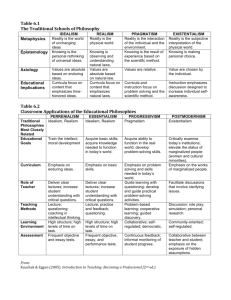
Foundational Philosophies in Education Idealism - mind Realism - fact Scholasticism - tradition Thomism – combination of faith & reason Pragmatism – growth in efficiency Existentialism – Intensity of feeling Post-modernism – Ending domination/cultural assertion Foundational Philosophies in Education Traditional Philosophies Idealism, Scholasticism, Thomism, Realism Absolute Truths – permanent, universally relevant Required Subjects Relativistic Philosophies Pragmatism, Existentialism, Post-modernism Relative Truths No Fixed Curriculums Idealism Idealist - Anytime someone puts more emphasis on the mind, or the mental side, than anything else. Idealism Extreme Idealism Mind, Thinking Body,Feeling, Matter, Subconscious, Instinct, etc. Idealism Plato The Circle Descartes Doubting = Thinking (If I think, then I am) Move beyond the learner, turn to ways of thinking (Blooms Taxonomy) Lecture > Dialectic >Think Realism Realist – Best type of knowledge is those of physical fact. Beginning of Realism Scientific Realism Physical Fact Mind, Feeling, Subconscious, etc. Realism Levels of Certainty: 1. 2. 3. 4. Physical Science Social Science Philosophical Knowledge - Speculation Religious Knowledge – Proof? Low Agreement Behaviorism – Conditioning Aristotle Scholasticism The main focus here is Tradition. Truth is found in the physical, mental and emotional things that have endured over time and is still relevant. The world was here before we were born and we must be a part of this world. Liberal Education Thomism God exists and can be known through faith and reason. Since both physical objects and human beings, including minds and ideas, are created by God, faith has nothing to fear from idealism and rationalism. Aquinas & Aristotle (Faith & Reason) Pragmatism Everything is subject to change. (Relevance?) Saber-Tooth Curriculum Certainty is only at a practical level – that which brings the most practical results to the most people. Focus: learning the scientific method and problemsolving. working cooperatively with others Existentialism Truth is Subjective Existence precedes essence. 55 mph? (Our we committed to this?) Students should be given the opportunity to choose to learn and what to learn (responsibility) (Spiderman) Reality is only determined by our choices. The only authority is the authority of self. (knowledge & values) Pragmatists – success is important. Existentialists – success is of no value, be true to yourself. Post-Modernism Truth is found in the interaction of different cultures. There should no be an ever dominant group. This hinders certainty and rightness. New creations of truth can and should arise when all groups are equal and interact. Multicultural Education Curriculum and Instruction