differences between variable, fixed and mixes costs
advertisement

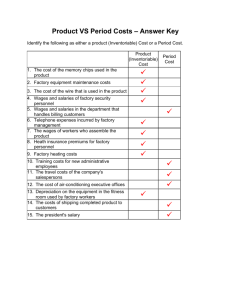
KENNETH C HOLMES APPLIED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING PROFESSOR: JASON CADE JANUARY 15, 2015 PHASE 2: DISCUSSION BOARD VARIABLE, FIXED AND MIXED COSTS Variable Costs: Costs that change with changes in level of activity, they are driven by activity. Examples: selling expenses (commissions), administrative expenses, supplies, raw materials, direct labor (hourly), indirect labor (hourly), and inventory. Fixed Costs: Costs that do not change with the level of activity that fall within relevant range. Examples: monthly cell phone contract fee, wages for salaried employees, depreciation on building and equipment, real estate taxed on factory or office property, R & D, rent, insurance, taxes, and long-term debt. Mixed Costs (Semi-Variable Costs): Costs that have characteristics of both variable and fixed costs. Examples: land, plant and equipment, utility costs and cell phone bill. Cost Drivers: the factors that affect change in variable cost. Example: units produced, machine hours, miles driven on distribution truck, labor hours, raw materials, minutes on phone service or miles on lease vehicle used beyond contract agreement. Cost behavior: How a cost reacts to changes in the level of activity within the relevant range. Unit fixed cost: falls when volume rises because the costs are spread over more units, and increases when volume falls because the costs are spread over fewer units, when within the relevant range. Increased production beyond the relevant range will reduce unit fixed cost. Unit variable cost: remains constant irregardless of sales activity. Total fixed cost: are not affected by level of sales when in the relevant range, because they are ongoing cost, and include: rent, monthly equipment fees, cost of salaried employees and loan payments. Total variable cost: increases as activity rises, and decreases as activity decreases. Edison Electronic Company variable, fixed and mixed costs: Variable costs include: selling expenses, administrative expenses, supplies factory, indirect labor, maintenance expense factory, purchase of raw materials, direct labor factory, bad debt expense, accounts payable, and income tax rate. Fixed costs include: insurance factory, factory salaries, factory property tax, depreciation expense factory, interest expense, notes payable, and bonds payable. Mixed costs include: utilities factory, land, plant, equipment, and prepaid expenses. REFERENCES Cade, J. (2015, January 9). Applied Managerial Accounting, Phase 2 DB Chat and Power Point. Retrieved from www.ctuonline.edu Lister, J. (2015). What effects Does Total Unit Cost & Total Fixed Cost have on a Company? Retrieved from www.smallbusiness.chron.com>money & debt small business