Unit 4: Water World
advertisement

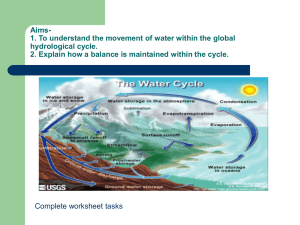
Topic 4: Water World Revision The Hydrological Cycle Watch this clip Water on planet Earth • All water: 97% salt water, 3% freshwater • Freshwater: 75% glacier ice, 24% groundwater & 1% surface water • Surface water : 81% soil moisture, 16% lakes, 2% rivers & 1% biomass The hydrological cycle is a system • What do we mean by a system? • How can systems be closed/open? A system has inputs, stores, flows (transfers) and outputs The hydrological system is a closed system – water goes around and around, no water is lost or added Define: Evaporation Condensation Precipitation Infiltration Transpiration Percolation Groundwater flow Through flow The Hydrological Cycle Energy from the sun __________ water from the sea and land. The v__________ rises, cools and condenses to form __________ which are blown by the wind. The water falls back to the ground as _______, hail or snow. The water either travels over the land in _________ or sinks into the ground. Eventually most water will return to the sea. Click on the photos to complete the key terms Key terms • Inputs – goes into the cycle • Flows – transfers water from one source to the other • Stores – holds water • Outputs – water goes back into the atmosphere What examples can you think of? Exam question Explain why the biosphere and lithosphere are important to the hydrological cycle (4) Discuss in pairs: More than likely there will be ‘Water Wars’ in the future Explain how water is being used unsustainably Population increase electricity industrialisation tourism Climate change urbanisation Many parts of the world are experiencing water stress Many lakes, rivers and groundwater supplies are drying up due to overuse. Describe the distribution of physical water scarcity(3) The Sahel lies in which countries? Lack of rainfall has resulted in desertification. Watch this clip: What is desertification? Try to come up with your own definition Desertification – the spread of desert-like conditions Desertification and Degradation Desertification is the persistent degradation of dry land ecosystems so land conditions turn to deserts. Degradation is primarily driven by land management (human causes). It is the spread of desert conditions caused by pressures put on the land by human activity. What is the Sahel like? • • • • Semi-arid area Periods of rainfall and drought Supports small bushes Windbattered trees Case study Describe how water shortage might affect people (4) How do we damage water supplies? • • • • Domestic Agricultural Industrial Transport Sewage disposal (MEDCs and LEDCs) Industrial pollution (could use China) Intensive agriculture Deforestation (Cutting down trees) (Taking too much Over abstraction water out) Building dams/reservoirs Exam Style Question Using examples, show how different water uses can have unintended effects (4 marks) Explain how water usage can be unsustainable (6) Large-scale water management projects The Three Gorges Dam, China Copy and complete: Advantages Social Economic Environmental Disadvantages Describe the economic impacts of a named large scale water management scheme (6) Small scale water management schemes Rainwater harvester Rope pump WaterAid uses appropriate/intermediate technology Development schemes which meet the needs of local people and the environment in which they live How are the schemes SUSTAINABLE? • • • • • • • The needs of the community Available water sources Local financial conditions Local geographical conditions Local availability of materials for construction Local availability of labour for construction Local availability of spare parts A water pump must be sustainable, which means it must be able to be fixed locally, cheaply and quickly. A rope pump is a simple technology that can be constructed from recycled parts like bicycle wheels, scrap metal and plastic. WaterAid’s partners train and support local people to maintain the pumps and in some cases manufacture them. Rainwater harvesting Using named examples, describe and explain how SMALL SCALE management schemes are often sustainable (6) Exam Practice Read the question carefully. WHAT is it asking you? How many marks are available? What is the key point you want to get across? Does it relate to the question? 2+2 3+1 3+3 Using examples, explain how water use could be made more sustainable (4)