Imperialism
advertisement

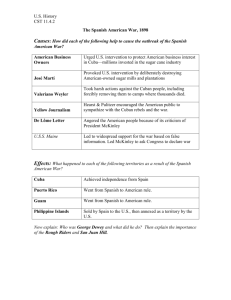
Imperialism Background • Late 19th century=hope + anxiety for U.S. • World’s leading industrial power • 1893-financial panic/depression • Potentially violent fault lines=debtors vs. creditors; labor vs. capital • European powers were scrambling for new colonies and influence in Africa, ME, and Asia (“The sun never sets on the British empire.”) • Threatened to exclude U.S. businesses from vital overseas markets Causes • • • • • • • • • Gather new resources Open up new markets/trade Military advantage/strategy Maintain a balance of power Closing of the frontier-provides new lands to conquer + adventure (manifest destiny) Duty to spread civilization-”white man’s burden” (superiority + humanitarian) Nationalism Social darwinism *economic, political, social and psychological Alfred Thayer Mahan • Military historian-very popular • “The influence of sea power upon history, 1660-1783” • Influence=control of the seas • 1900-U.S. had the 3rd largest navy • Roosevelt’s “great white fleet”-fleet of battleships painted white and ordered to sail around the world, an impressive sight Alaska • 1867 • Seward-Johnson’s Secretary of State • Resources: rich in oil, timber, fish, etc.; doubled the size • Purchased from Russia for 7.2 million • Wanted to get British Columbia down-have from AL. to WA. • “Seward’s Folly” Hawaii • Since 1790s-American merchant ships had stopped at Hawaii on their way to East Asia; est. Christian churches and schools + sugar cane plantations • 1891-king died and his sister, Liliuokalani ascended the throne • She wanted to eliminate the white control of govt. and land • 1893-American planters + U.S. Marines overthrow the queen • Annexation: Wealthy planter Dole asked U.S. to annex; majority of Hawaiians did not want it; American annexation sentiment remained strong and in 1898, Congress annexed it in Spanish-American War “Splendid Little War” Background • Spain controls: Philippines Cuba smaller islands: Guam, Puerto Rico Causes • Spanish atrocities: concentration camps, starvation, diseases, mutilations • Yellow press-exagerrations • DeLome Letter: private letter by the Spanish ambassador to D.C. to a friend in Cuba, intercepted by Cuban rebels and leaked to Hearst called the President weak and stupid: insult to President and national honor • USS Maine explosion: 1898-docked in Havana harbor as a courtesy call-blew up; 260 dead, “Remember the Maine” rallying cry (Spanish blamed: 1976 the real cause was noted: internal explosion triggered by fire in the coal bunker next to the magazines) Declaration of War • Roosevelt wanted war but McKinley and business leaders were a little timid • Spain, sensing U.S. militancy, announced a cease fire • McKinley started to ask for a declaration of war and blockaded Cuba’s northern coast • Blockade=act of war so Spain declared war on April 24 • U.S. declared on 4/25, but wanting to be first, made it retroactive to 4/21 Course of the War • • • • Philippines took 7 hours for Dewey to get there 3.5 months Dewey along with Emilio Aguinaldo (commanding the Filipino insurrectionists) entered into Manila • Spanish lost 381, U.S. 8 wounded Course of the War • Cuba • 17,000 troops engaged • 1st Volunteer Cavalry-Rough Riders (aka weary walkers)-under Teddy who was 2nd in command, landed at SE Cuba: didn’t think they could take the high ground, but took nearby Kettle Hill in 20 mins. and San Juan Hill one hour later (*became famous in the Wild West Show)-high points of the war • 474 Spanish killed/wounded vs. 1 U.S. killed and 1 wounded, 1750 prisoners End of the War • 114 days, approx. 4 months long • Over 60,000 Spanish dead of diseases or wounds vs. 6000 Americans (only 379 total in battle) • Emergence of U.S. as a world power Treaty of Paris 12/10/98 • Cuba • Independent, military govt. in 1898, 1900-their own constitution • 1901-Platt Amendment -will never sign a treaty with a foreign nation that impairs their independence -never build excessive debt -permit the U.S. to intervene in affairs to preserve independence and law and order -allow the U.S. to maintain a navy baseGuantanamo Bay • 1902-withdrawal by U.S. Treaty of Paris • Will agree to pay $20 million for P.R., Guam and Philippines • Guam Will be a U.S. protectorate • Puerto Rico U.S. protectorate est. a civil govt. not the same rights as a U.S. citizen, have their own constitution, but it can’t conflict with the U.S. Constitution Treaty of Paris • Philippines • Remain under U.S. control until the end of WWII • Commercial possibilities + mission work to “the little brown brother” • McKinley’s statement includes maintaining possession for national glory, commerce, racial superiority and altruism (selflessness, helping others) • Aguinaldo at this point leads the resistance • 2 year conquest • Massacres and tortures to those who resisted • 63,000 American troops, 4300 dead • Over 200,000 Filipinos dead China • Imperial powers (Britain, Japan, Germany, Russia, France, U.S.) wanted an equal opportunity to trade in China: Open Door Policy • 1900-Boxers oppose the foreign influences and lead a siege on foreign embassies • Boxer Rebellion vs. Imperial powers (to relieve the embassy issue) • Imperial powers win: approx. 6 weeks Panama • Initially under the control of Columbia • DeLesseps and the French started building the Panama Canal-abandoned the project (cost, diseases) • Columbians not letting the U.S. in; U.S. was outraged over quoted prices higher than that of the French • Panamanians wanting indep. Work with the U.S., who happens to send warships off the Panamanian coast • Panamanian rebellion-Columbia unable to reinforce or suppress the rebellion; relinquish control • Panamanians, owing the U.S., allow the U.S. in • They rent the land + build the canal starting in 1904 (costly$ + lives): finish it in 1914 Progressive Presidents and their approach to foreign affairs Foreign Policy Stance • Roosevelt: Big Stick Diplomacy-”Speak softly but carry a big stick”-military influence • Roosevelt Corollary: 1904: to strengthen the Monroe Doctrine-U.S. to intervene to forestall the actions of outsiders in Latin America as it pertained to economic issues (pay off loans) • Taft: Dollar Diplomacy: substituting dollars for bullets: increase investment in other countries to maintain and increase power • Wilson: Moral Diplomacy: support governments that are democratic and support U.S. interests