COASTAL LANDFORMS - 2015-Sec3-Geog
advertisement

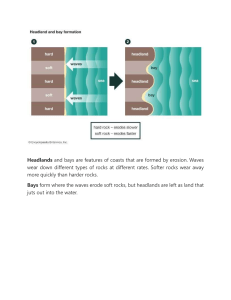
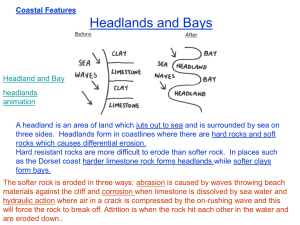
COASTAL LANDFORMS CLIFFS SHORE PLATFORMS TOMBOLOS LANDFORMS HEADLANDS SPITS BEACHES BAYS Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps CLIFF It refers to a high, steep rock face along a coast. Cliff: Formation Waves pound repeatedly against a rocky coast. This weakens the rock and causes lines of weaknesses to form in the rock. Over time, the waves erode the coast to cut a notch along the lines of weaknesses Cliff: Formation The notch may be further eroded to form a cave. The overhanging part of the cave or notch eventually collapses. The part of the coast that is left forms a cliff. SHORE PLATFORM It refers to a gently sloping, coastal land surface with a cliff behind it. Platform Formation Due to constant erosion, the cliff retreats inland. Over time, a gently sloping surface develops at the base of the cliff. Rock fragments from the receding cliff are deposited in this surface known as a shore platform. Draw: Cliff & Shore Platform Formation HEADLAND It refers to a high steep faced cliff that protrudes into the sea. BAY It refers to a wide, inward curve of the coastline. Formation The coastline consists of parallel bands of hard and soft rock (perpendicular to the sea). Formation Due to differential erosion, the less resistant rocks are eroded faster than the more resistant rocks. Formation The less resistant rocks will curve inwards to form bays. The more resistant rocks will protrude from the coastline to form headlands. Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps Formation As waves approach the headland, the waves gets refracted towards the headland. waves erode the headland along lines of weaknessess (e.g. joints, faults and bedding planes) Two back-to-back caves first form on each side of a headland. Continuous erosion causes these back-toback caves to extends backward till the sea caves meet and a natural tunnel is produced. The top portion of the sea caves becomes an arch, linking the tip of the headland with the mainland. When the arch collapses , the sea ward pillar is left standing and becomes a stack. Continual wave erosion eventually reduces the stack into a stump. BEACH It refers to an accumulation of sediments on the coast. Formation Materials eroded from the headlands, together with other material carried by the waves is deposited at the bay. Fine materials form gently sloping beaches while coarse materials form beaches of steep gradient. It refers to a long, narrow, ridge of sand with one end connected to the land and the other extends into the open sea. SPIT Formation Longshore currents encounter a bay or bend in a coast with shallow sheltered water. The materials the currents carry will be deposited in the direction of the longshore drift. Formation Over time, the accumulation of materials will result in a long narrow ridge of sand. One end of the ridge will be attached to the mainland and the other extends into the open sea. This coastal feature is known as a spit. TOMBOLO It refers to a long, narrow, ridge of sand linking the mainland to an island. Formation Tombolo is formed when a spit increased in length until it joins a nearby island. It can also be formed when two spits, facing each other grow and eventually meet. CLIFFS SHORE PLATFORMS TOMBOLOS LANDFORMS HEADLANDS SPITS BEACHES BAYS Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps THE END