Water And The Body Fluids
advertisement
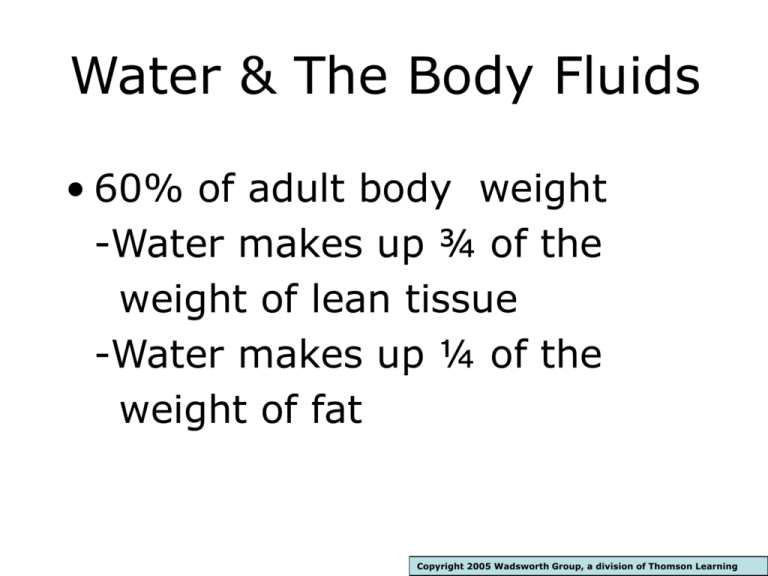
Water & The Body Fluids • 60% of adult body weight -Water makes up ¾ of the weight of lean tissue -Water makes up ¼ of the weight of fat Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Water & Body Fluids • Functions of water: –Transport –Structural support for molecules –Participates in metabolic reactions –Solvent –Lubricant & shock absorber –Body temperature regulation –Maintains blood volume & blood pressure Water & The Body Fluids • Water balance –Intracellular fluid-within the cells –Extracellular fluid-outside the cells •Interstitial fluid •Plasma Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning One Cell And Its Associated Fluids Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Water & Body Fluids • Water Balance -Intake/output = 2.5 liters/day -Regulated by hypothalamus & kidneys -Carefully controlled by: 1. Intake (liquid, foods, metabolic water) affected by thirst & satiety 2. Output (losses via kidneys, skin, lungs, feces) affected by blood salts, volume & blood pressure How The Body Regulates Blood Volume Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Water & Body Fluids • Recommendations: -Needs vary according to type of food eaten, temperature, humidity, activity level, etc. -General rule: 1–1.5 ml/kcal expended Example: if 2000 kcal “burned” then 2-3 liters suggested; >8 cups from fluids and the rest comes from food & metabolic water -Urine should be pale yellow -Caffeine & alcohol act as diuretics so not good water substitutes Fluid & Electrolyte Balance • Electrolytes – salts that dissolve in water, forming ions • Dissociation of salt in water –Ions •Cations- + charged particles •Anions- - charged particles –Electrolyte solution Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Water Dissolves Salts And Follows Electrolytes Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Fluid & Electrolyte Balance • Electrolytes attract water - affects fluid distribution in the body by osmosis • Water follows electrolytes – Solutes – Osmosis – Osmotic pressure • Electrolyte concentration regulated by kidneys • Electrolytes & proteins act as buffers to maintain the pH of body fluids – acid/base balance Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Acid-Base Balance • pH • Regulation by the buffers –Bicarbonate –Carbonic acid • Regulation by the kidneys • Regulation by the lungs Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalance • Replacing lost fluids and electrolytes –Oral rehydration therapy (ORT)a simple solution of sugar, salt and water Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalance • Sodium and chloride most easily lost • Different solutes lost by different routes • Rapid fluid/electrolyte loss, i.e. vomiting, diarrhea, heavy sweating, fever, burns, wounds = medical emergency Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning