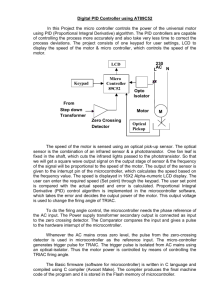
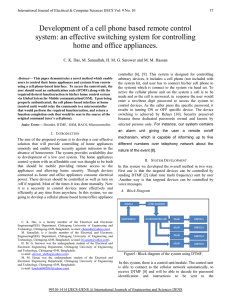
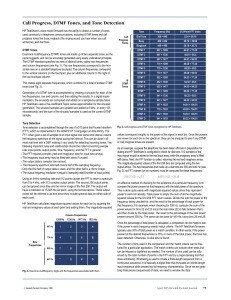
Click to PPT 1
advertisement

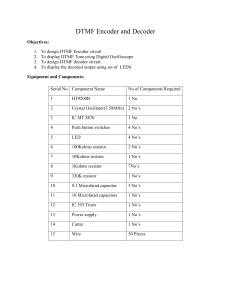
PROJECT PRESENTATION ON CELL PHONE OPERATED LAND ROVER ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION DEPARTMENT CONTENTS • • • • • • • • • • • • Introduction Basic block diagram of project Circuit diagram Technology used Components used Software used Algorithm Advantages and disadvantages Applications Future scope Conclusion References INTRODUCTION • Aim of the project is to use a mobile phone to control a robotic arm mounted on a land rover • Provides robust control, large working range and 16 controls. • Control of robot involves 4 different phases: a) b) c) d) Perception Processing Action Detection BASIC BLOCK DIAGRAM OF PROJECT MT 1.PERCEPTION • First part is to make a call to the mobile phone which is attached to the robot. • Next part is the decoding of DTMF tone generated by pressing a key in calling phone. • Audio signal output from receiving phone is fed to DTMF decoder chip. • Decoder chip converts DTMF tone into binary codes to be fed to microcontroller. • MT8870 IC used as DTMF decoder in our project. 2. PROCESSING • After perception stage, microcontroller processes the binary codes it receives. • Microcontroller is pre-programmed in “C” to perform specific task according to input bits. • Atmel’s ATmega16 is used for processing. 3. ACTION • Final stage is rotation of motors based on input given by the microcontroller. • Two DC motors of 30 rpm are used for the land rover and driven by motor driver IC L293D. 4. DETECTION • For obstacle detection, a pair of IR transmitter and receiver is used along with buzzer. • When the obstacle come near the robot, the IR transmitter will transmit the IR rays on the object and the object will reflect the IR rays to the IR receiver. • The IR receiver will receive the IR rays and it will activate the buzzer. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM OF MAIN PROJECT OBSTACLE DETECTION CIRCUIT DTMF SIGNALS AND DTMF DECODING CIRCUIT • • • • • DTMF “Dual Tone Multiple-Frequency”. Used in a telecommuncating signaling The 16-keys touch tone pad. DTMF assigns a unique ‘sound’ to each key. Keys are arranged in a matrix of 4 columns and 4 rows. GROUPING OF FREQUENCY • Signals generated by the superposition of two pure sinusoidal tones. •The DTMF signal generated is the sum of two sinusoidal tones. DTMF DECODER IC TRUTH TABLE FOR DTMF DECODER ATMEGA16 MICROCONTROLLER • Advanced-RISC architecture. • 16K bytes of In-System Programmable Flash Program memory. • Internal and external interrupts. • 32 general-purpose registers. • High-performance, Low-power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller. FEATURES OF ATMEGA16 • • • • • • • Widely used. Easily available. Cost effective. Speed of execution of instructions. Flexible instruction set. Vast documentation. Easily available support and development tools. DIAGRAM OF ATMEGA16 DC MOTOR CONTROLLER L293D • Microcontroller output is not sufficient to drive DC motors, so L293D is used. • L293D comes in 16-pin DIP. It can provide current upto 600mA at voltages from 4.5V to 36V. • It can be used to drive inductive loads such as relays, solenoids etc • In the project it is used for simultaneous bidirectional control of two DC motors. DC MOTOR CONTROL ACTION PERFORMED CORRESPONDING TO THE KEY PRESS SOFTWARE USED • The software is written in ‘C’ language • Hex code for Atmega 16 is generated by using Code Vision AVR ‘C’ compiler. • The next software we used is ‘EAGLE’ for circuit schematic design and layout design. ALGORITHM • • • • • • • • • • • STEP 1: START STEP 2: DECLARE VARIABLES STEP 3: SET PORT A AS I/P PORT STEP 4: SET PORT D AS O/P PORT STEP 5: ACCEPT INPUT IF I/P IS 0X02 THEN MOVE MOTOR IN FORWARD DIRECTION IF I/P IS 0X08 THEN MOVE MOTOR IN BACKWARD DIRECTION IF I/P IS 0X04 THEN MOVE MOTOR TO LEFT IF I/P IS 0X06 THEN MOVE MOTOR TO RIGHT IF I/P IS 0X05 THEN STOP MOVING MOTOR STEP 6: STOP ADVANTAGES • Wireless control • Surveillance System. • Takes in use of the mobile technology which is almost available everywhere. • This wireless device has no boundation of range and can be controlled as far as network of cell phone DISADVANTAGES • Cell phone bill. • Mobile batteries drain out early so charging problem. • Not flexible with all cell phones as only a particular cell phone whose earpiece is attached can only be used. APPLICATIONS • Scientific • Military and Law Enforcement • Search and Rescue • Recreation and Hobby FUTURE SCOPE • Password Protection • Alarm-Phone Dialer • Adding a Camera CONCLUSION • We have successfully implemented the entire circuit on the PCB with obstacle detection feature. • Since all we need is a mobile call establishment to instruct the robot due to the cell phone’s unending and cheap availability, this is highly feasible. • The level of sophistication is quite low and hence its working is user friendly. • Project can also be subjected to standardization and hence has a good future scope. REFERENCES [1] Schenker, L, "Pushbutton Calling with a Two-Group Voice- Frequency Code” The Bell system technical journal, vol 14,no. 2, Jan 2006. [2] M. Ali Yousuf, R. Montúfar Chaveznava, and V. de la Cueva Cueva Hernández, "Robotic projects to enhance student participation, motivation and learning", Hernández Current Developments in Technology-Assisted Education ,pp 922-952, July 2008. [3] Robert Siwy, "Generation and Recognition of DTMF Signals with the Microcontroller MSP430", Texas Instruments Deutschland, October 2005. [4] “Cell phone based land rover” Liu, Simon & Silverman, Mark. November 2009 [online] Available: http://www.instructables.com/id/Cellphone-operated-Robot/ [accessed:Jan 2013]. [5]http://www.datasheetcatalog.com/datasheets_pdf/M/T/8/8/MT8870.shtml [6]http://www.alldatasheet.com/datasheetpdf/pdf/STMICROELECTRONICS/L298.ht ml [8]http://robosapiensindia.com/robomart/index.php?product_id=218&page=shop