General forces
advertisement

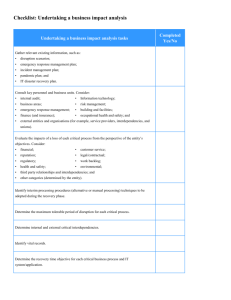
Organizational Theory The environment consists of specific and general forces. Specific forces directly affect an organization’s ability to obtain resources. General forces shape the specific environment and affect the ability of all organizations in a particular environment to obtain resources. 1 FIGURE 3-1 The Organizational Environment International Forces Demographic / Cultural Forces Political Forces Customers Suppliers Distributors Unions Organization Government Competitors Environmental Forces Technological Forces Economic Forces General Forces Specific Forces 2 Organizational Theory Environmental complexity is a function of the strength, number, and interconnectedness of the specific and general forces that an organization has to manage. As complexity increases, uncertainty about the environment increases. 3 “Struggling for New Role, AT&T to Stop Marketing to Consumers” AT&T, which for more than century has been synonymous w/ phone service in American home, announced in July 2004 that it would no longer market services to consumers Company struggling to find role in volatile and competitive telecommunications industry created from breakup of AT&T monopoly in 1984 In two decades since AT&T lost its exclusive franchise to sell phone service, Co has moved in and out of businesses at frenetic pace, trying everything from selling computers to providing cable and wireless services, often w/ dismal results Has maintained big business in long-distance calling, but collapse of telecommunications bubble in 2000 has hastened its decline as cost of phone calls has plummeted Consumers are more and more buying packages of phone, data,4 and video services from cable, satellite, and phone carriers “Struggling for New Role, AT&T to Stop Marketing to Consumers” AT&T continued to sell telephone and data services to corporate users Co wouldn’t turn away new consumers who asked for its service, but would stop trying to attract new customers or retain those who wish to defect Hoped to build up corporate business by using money generated by its consumer operations and spending less on advertising, direct marketing, and other costs associated w/ acquiring retail customers AT&T’s decision made it more likely that the four dominant local phone providers – Verizon, SBC, Bell South, and Qwest – can reassert their increasing market power Telecommunications Act of 1996 allowed ‘Baby Bells’ to enter long distance market and compete w/ former parent AT&T New York Times, 7/22/04 Stephen Colbert explains the whole AT&T thing 5 6 Organizational Theory Resource dependence theory argues that the goal of an organization is to: Minimize its dependence on other organizations for the supply of scarce resources AND To find ways of influencing these organizations to make resources available 7 Organizational Theory Symbiotic (Resource) interdependencies exist between an organization and its suppliers and distributors. Competitive interdependencies exist among organizations that compete for scarce inputs and outputs. 8 Organizational Theory Strategies for Symbiotic (Resource) Interdependencies (in order of increasing formality) Developing a good reputation—held in high regard and trusted by other firms Co-optation—a strategy that neutralizes problematic forces in the specific environment 9 Organizational Theory Strategies for Symbiotic (Resource) Interdependencies (in order of increasing formality) Strategic alliances—an agreement that commits two or more companies to share resources to develop joint business opportunities 10 Organizational Theory Strategies for Symbiotic (Resource) Interdependencies (in order of increasing formality) Strategic alliances—various types, presented in order of increasing formality: Long-term contracts Networks Minority ownership (keiretsu) Joint ventures 11 FIGURE 3-7 Interorganizational Strategies for Managing Competitive Interdependencies Informal Collusion and cartels Formal Third-party linkage mechanisms Strategic alliances Merger and takeover 12 13 14 Organizational Theory Transaction cost theory states that the goal of an organization is to minimize the costs of exchanging resources in the environment and the costs of managing exchanges inside the organization. Transaction costs are defined as the costs of negotiating, monitoring, and governing exchanges between people. 15 Organizational Theory Final report by Columbia Accident Investigation Board raised fundamental questions about NASA’s increasing dependence on Boeing and Lockheed Martin and other contractors. Suggested that while streamlining space program during push toward privatization in mid-90s, NASA abdicated much of its responsibility for overseeing safety. Crucial analysis about potential damage from debris conducted by team of inexperienced Boeing engineers who failed to seek assistance from more experienced colleagues. 16 Organizational Theory CAIB recommendations: Establish independent Technical Engineering Authority, funded from NASA HQ, to identify and analyze any possible hazards during shuttle’s life Would be sole waiver-granting authority for all technical standards and would independently determine launch readiness Give NASA HQ Office of Safety and Mission Assurance direct authority over entire safety of shuttle program, providing its resources independently Source: Wall Street Journal, 8/26/03 17