Rapid Cycle Quality Improvement
advertisement

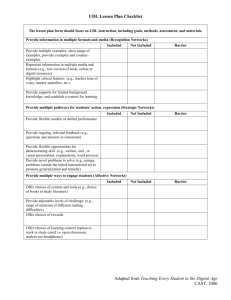
Rapid Cycle Quality Improvement Course Outline The Quality Journey Rapid Cycle Improvement Model Change Concepts Teams Tools Barrier Busters 1 Group’s Prior Experience with Quality Improvement Participant Survey Results Very Little 1-2 yrs 3-5 yrs 5-10 yrs 10+yrs 2 What is Quality? Quality is a never-ending cycle of continuous improvement. -Deming 3 Quality Alphabet Soup CQ I PI PD SA QA M Q T P QI R CQ IO A C PD I 4 Group’s Tools for Quality Improvement Participant Survey Results 5 Quality Improvement Program Vision, Goals, Objectives Quality Indicators – Monitoring Quality Project Continuous Improvements Solve Problems Change Systems Sentinel Events 6 The Quality Journey Quality Assurance Quality Improvement Rapid Cycle Quality Improvement 7 QA vs. QI Quality Assurance Conform to standards Relies on inspection Focus on items Quality is separate function Departmental function Quality Improvement Improved performance Monitor over time System orientation Quality integrated in organization Interdisciplinary function 8 Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award Patient / Customer and Health Care Market Focused Strategy and Action Plans 2 5 Strategic Planning Staff Focus 1 7 Organizational Performance Results Leadership 3 6 Focus on Patients, Other Customers, and Markets Process Management 4 Information and Analysis 9 PDSA Cycle 10 AIM Statement What are we trying to accomplish? The Aim Statement articulates the goals, guides the improvement effort, and keeps the team focused. Specific Measurable Challenging 11 Measurement How will we know that a change is an improvement? What to measure - what will be different? What are the guidelines 12 Cycles of Improvement What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? It’s your opportunity to brainstorm: Possible changes People that are needed Required resources Potential for collaboration Necessary leadership support 13 Cycles of Improvement Continuous improvements of multiple changes. PD PD PD PD SA SA Change 1 SA SA PD PD PD PD SA SA Change 2 SA SA PD PD PD PD SA SA SA SA Change 3 14 Rapid Cycle Improvement Model What are we trying to accomplish? How will we know that a change is an improvement? What changes can we make that will result in an improvement? Cycle 1 Cycle 2 Cycle 3 15 Potential EMSC Monitors: Timely management Wait time to see an MD in the ER Time to initiate antibiotics in fever management Use of an intraosseous line when needed Transfer within 2 hours when appropriate Use of the Broselow, or similar, system Pain management in the non verbal child Asthma management Obtaining a patient height Peak flow measurement Abuse recognition Provision of injury prevention education 16 What Quality Improvement activities are you working on at your hospital? Participant Survey Results 17 An Example of Rapid Cycle Planning Where do we begin? 18 Change Concepts Change concepts are generic ideas that can be applied to your situation to spark an idea for a specific change in your situation Not all change concepts apply to all aims Brainstorm ways to apply these concepts to the problem at hand 19 Change Concepts Enhance the Producer /Customer relationship Listen to patients Coach customers to use product/service Reach agreement on expectations Mass customize services to patient 20 Change Concepts Change the work environment Reduce demotivating aspects Implement cross training Clarify roles & expectations Improve work flow Synchronize Find and remove bottlenecks Do tasks in parallel Adjust to peak demand 21 Change Concepts Manage Time Reduce the setup or startup time Optimize maintenance Reduce wait time Manage Variation Eliminate waste Reduce or eliminate overkill Recycle or reuse 22 Change Concepts Optimize inventory Match inventory to demand Use pull systems - proactive Reduce multiple brands Design systems to avoid mistakes Use reminders Use differentiation Use constraints Minimize handoffs 23 Team Composition Sponsor Leader Team member(s) Helpful hints Be Multidisciplinary Assure available leadership Include hands-on expertise & variety of skills, e.g. computer skills Recognize progress Clarify roles & responsibilities Handle conflict constructively Maintain core group for consistency 24 Essential Tools Meeting Agenda (every meeting) Meeting Summary (every meeting) Project Work plan (create 1, post & update) Project Report Form (Internal - External) 25 Other Helpful Tools Brainstorming Run Charts Flow Charts Cause & Effect Diagram Pareto Diagram Nominal Group Technique Force Field Analysis Refer to Section 12 - Tab “QI Tools & Techniques” 26 Example – Run Chart Self Administered Med Project DRG 372 & 373 Percent of Pts Receiving Medication 50.0% 46% 45.0% 40.0% 44% 42% 41% 38% Percent of Pts 35.0% 37% 35% 34% 33% 34% 32% 30.0% 30% 29% 26% 25.0% 23% 22% 20.0% 22% 22% 21% 21% 24% 25% 19% 16% 17% 15.0% 15% 15% 15% 13% 13% 12% 10.0% 11% 11% 10% 8% 8% 5.0% 24% 23% 6% 5% 7% 7% 7% 6% 5% 5% 5% 3% 2% 7% 5% 6% 6% 3% 0.0% Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan- Feb- Mar- Apr- May- Jun99 99 99 99 99 99 00 00 00 00 00 00 Jul- Aug- Sep- Oct- Nov- Dec- Jan- Feb- Mar- Apr- May- Jun00 00 00 00 00 00 01 01 01 01 01 01 Jul- Aug- Sep01 01 01 Month % Pts Rec'd Darvocet % Pts Rec'd Tylenol 3 27 Example – Control Chart Self Administered Med Project DRG 372 & 373 Percent of Pts Receiving Darvocet Pre Project Project Implemented 60% Percent of Pts Mean: 39.4% 40% Mean: 23.8% 20% 0% 28 Barrier Busters Barrier - Problems with Setting an Aim Is there sponsorship for the project? Does project fit with organizational mission? Does project conflict with our values? Is Aim Statement clear and precise? 29 Barrier Busters Barrier - Problems with Teams Is your leader available and empowered? Are you meeting weekly? Does everyone know their responsibilities? If you have conflicts, who can you request to facilitate your team? 30 Barrier Busters Barrier - Problems with Resources Suggestions: Keep your team small at first Use volunteers and champions Collect just enough data Set a dedicated meeting time Huddle if needed (15 minutes is all you need!) Involve senior leadership if resources are a problem 31 Barrier Busters Barrier - Resistance : “No one thinks there is a problem” Take the high ground... “We are different” Share information and challenge assumptions... “It’s too difficult” Look at others (internally & externally) that have successfully made a change Break ideas for change into small components Present changes as a “test” - that can be accepted, refined, or abandoned Use just enough data Post results of the small test from the outset as proof that it can happen Engage senior leadership - it is a must 32 Resistance – How people respond to change… – 2.5% Early Adopters – 13.5% Early Majority – 34% Late Majority – 34% Laggards – 15% Innovators 33 Barrier Busters Barrier - Problems with Ownership Be sure to include all impacted areas Collaborate with staff at all levels Involve the people that DO the work Find champions in several disciplines Keep sponsors informed and involved 34 Next Steps: Action List What is one problem in your work setting where you think Rapid Cycle Quality Improvement would help you? What is one thing that you can do by next Tuesday? 35