Science Curriculum Outline - Weald Community Primary School
advertisement

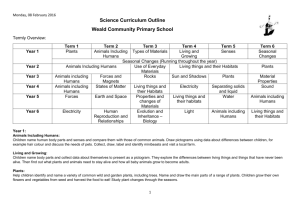
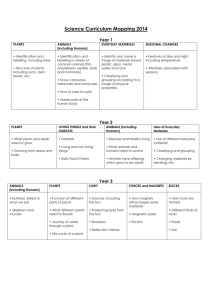
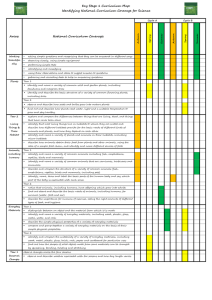
Friday, 18 March 2016 AH and JC Science Curriculum Outline Weald Community Primary School Termly Overview: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Term 1 Plants Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Term 5 Animals Including Types of Materials Living and Senses Humans Growing Seasonal Changes (Running throughout the year) Animals Including Humans Use of Everyday Living things and their Habitats Materials Animals including Forces and Rocks Sun and Shadows Plants Humans Magnets Animals including States of Matter Living things and Electricity Separating solids Humans their Habitats and liquid Forces Earth and Space Properties and Living things and Water changes of their habitats Materials Electricity Human Evolution and Light Animals including Reproduction and Inheritance – Humans Relationships Biology Term 6 Seasonal Changes Plants Material Properties Sound Animals including Humans Living things and their Habitats Year 1: Animals Including Humans: Children name human body parts and senses and compare them with those of common animals. Draw pictograms using data about differences between children, for example hair colour and discuss the needs of pets. Collect, draw, label and identify minibeasts and visit a local farm. Living and Growing: Children name body parts and collect data about themselves to present as a pictogram. They explore the differences between living things and things that have never been alive. Then find out what plants and animals need to stay alive and how all baby animals grow to become adults. Plants: Help children identify and name a variety of common wild and garden plants, including trees. Name and draw the main parts of a range of plants. Children grow their own flowers and vegetables from seed and harvest the food to eat! Study plant changes through the seasons. 1 Friday, 18 March 2016 AH and JC Seasonal Changes: Children find out facts about the Sun and observe its apparent movement across the sky. They investigate how shadows change during the day. Discuss the 4 seasons and varied day length. Describe the weather associated with each season and the changes this brings Senses: Children have lots of hands-on experience to investigate the five senses of touch, sight, hearing, taste and smell. Discuss how animals can use their senses to help us or to show their feelings, and how some people deal with losing one of their senses. Types of Materials: Explore materials commonly found in the classroom, sorting them into plastic and not plastic. Discover objects that float and sink before carrying out related investigations. Use the Three Little Pigs to study building materials before looking at magnets. Year 2: Animals Including Humans: Discuss how animals have offspring that grow into adults and think about how children have changed since they were babies. Look at various life cycles and find out what animals need to survive. Study balanced diets and exercise, which help keep humans fit and healthy. Use of Everyday Materials: Children identify and compare the suitability of some everyday materials for particular uses. Plastic and fabrics are looked at in detail. Find out how the shapes of solid objects made from some materials can be changed. Think about new uses for materials. Living things and their Habitats: Children develop an understanding that materials have different properties and therefore different uses. Discuss natural / man-made materials. Children find that materials, e.g. water, often change when heated or cooled and that forces can change the shape of materials. Plants: Children observe inside seeds and bulbs and describe how they grow into mature plants. They find out and describe how plants need water, light and a suitable temperature to grow and stay healthy. Find seeds in the local environment. Year 3: Animals Including Humans (New Curriculum) Find out about food groups and healthy balanced diets. Study the human digestive system and how food is transported around the body. Investigate skeletons and look closely at bones, joints and muscles and compare with animal skeletons. Discover effects of exercise. Forces and Magnets: Identify pushes and pulls as forces and explore how things move on different surfaces. Find out about attraction and repulsion by magnetic forces and which materials are magnetic. Look at compasses and uses of magnets. Carry out some enquiries using magnets. 2 Friday, 18 March 2016 AH and JC Plants: Study the parts of flowering plants and their functions, the conditions affecting plant growth and plants as living things. Investigate how water is transported in plants. Describe plant life cycles, in particular how seeds are formed, dispersed and germinate. Rocks: What is under our feet? Children are always fascinated by rocks, they describe rocks and compare their properties after tackling exciting activities. Children hear how fossils are formed in sedimentary rocks. Discover soil facts and consider different soil types. Sun and Shadows: Discover fascinating facts about the Sun. Explore the Earth’s movement to give seasons and day and night. Investigate shadows and sundials. Discuss safety in the Sun and solar energy. Children also find out about transparent, opaque and translucent materials. Material Properties: Children compare the properties of everyday materials and relate them to everyday uses of the materials. Investigate plastic, safe floor surfaces for babies and their own questions about paper. Finally children research one material in detail to create a book. Year 4: Animals Including Humans: Find out about food groups and healthy balanced diets. Study the human digestive system and how food is transported around the body. Compare diets of herbivores, carnivores and omnivores. Investigate teeth and what causes decay. Look closely at food chains/webs. Electricity: Children construct simple circuits and draw them. They find which materials are the best electrical conductors and use this information to make switches. Children wire plugs and find what happens to a bulb’s brightness when circuits are changed. They research scientists. Living Things and their Habitats: Remind children of the characteristics of living things and the basic needs their habitats supply. Establish why classification of plants and animals is important and classify minibeasts. Read and construct food chains and webs. Recognise that environments can change. Sound: Show that sounds are made when objects vibrate and that sounds travel through solids, liquids and gases. Children investigate how well sound travels through different materials and discover how instruments make sounds. Suggest how to change the pitch and loudness. States of Matter: Find out about the properties of the three different states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Learn how to use thermometers. Set up enquiries about matter changing from one state to another. Study the water cycle. Investigate air as an example of a gas. 3 Friday, 18 March 2016 AH and JC Separating Solids and Liquids: Children reinforce their understanding of solids and liquids and states of matter. They find out how solids and liquids can be separated when they become mixed and explore reversible changes. They create their own sorting machines and learn how to filter a solution. Year 5: Animals Including Humans: Discuss why living things need to reproduce and begin to look at human life cycle, comparing with other animals. Study emotional changes at puberty. Research rites of passage throughout human life cycle. Earth and Space: Children find fascinating facts about the Sun, Moon and Earth and develop an understanding of day and night, the four seasons and the Moon’s phases. The Sun and the planets making up our Solar System are investigated, along with the other stars in their constellation. Forces: Look at a range of different forces: gravity, air resistance, water resistance and friction. Develop an understanding of balanced and unbalanced forces and their effects. Investigate how mechanisms, like levers, pulleys and gears, help us to use smaller forces. Properties and Changes of Materials: Revise the three states of matter and properties of materials. Introduce further properties: solubility and thermal conductivity. Separate materials using a range of methods and understand that some changes are irreversible. Discuss the formation of new materials. Water: Water exists as solid, liquid and gas in everyday conditions. Children investigate the properties of these different states of matter and how they change from one to the other. They apply this to the water cycle and consider the importance of water to daily life. Living things and their habitats: Children revise the parts of plants and their functions, the conditions affecting plant growth and plants as living things. Investigations into seed dispersal and germination are carried out and children develop an understanding that plants are a vital part of human life. Year 6: Animals Including Humans: Explore the structure of the heart and lungs. The double circulation through the lungs and the rest of the body is explained and children learn more about blood! How does exercise affect pulse rate? Why exercise is good for us and what can harm the heart and lungs? Electricity: Begin with revision of simple circuits and then lots of hands on experience with symbols, diagrams and incomplete circuits. Two enquiries about the length of wire in a circuit and the use of cells. Compare series and parallel circuits then face some challenges! 4 Friday, 18 March 2016 AH and JC Evolution and Inheritance – Biology: Discuss fossils as evidence of life millions of years ago and study the life of Mary Anning. Compare offspring with parents and see how plants/animals are adapted to habitats. Look at Darwin, Wallace and Mendel’s contributions to our understanding of evolution. Light: Identify sources of light and revise facts that light travels in straight lines and opaque objects form shadows. Understand that to see, light needs to enter the eye. Investigate light reflection and refraction, white light made of many colours and the speed of light. Living things and their Habitats: Look at the history of classification of living things from Aristotle to the present day. Study the binomial system introduced by Linnaeus and the 7 levels of classification used today. Understand why classification is important and use and create classification keys. Human Reproduction and Relationships: Review why living things need to reproduce and look in detail at human life cycle, comparing it to other animals. Study in detail changes at puberty. Research rites of passage in different cultures. Look at sexually transmitted diseases (particularly HIV / Aids). Review July 2016 5