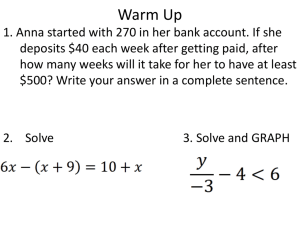The Pythagorean Theorem
advertisement

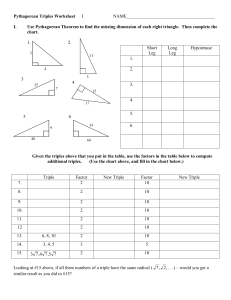
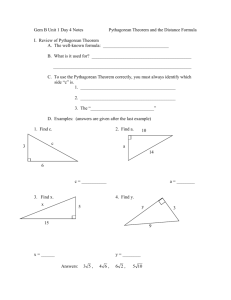
The Pythagorean Theorem Section 8-1 Use the Pythagorean Theorem. Key Vocabulary • • • • Leg Hypotenuse Pythagorean Theorem Pythagorean Triple Parts of a Right Triangle • Longest side is the hypotenuse, side c (opposite the 90o angle). • The other two sides are the legs, sides a and b. • Pythagoras developed a formula for finding the length of the sides of any right triangle. Theorem 4.7 - The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem In a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs. Example: (hypotenuse)2=(leg)2+(leg)2 Example 1 Find the length of the hypotenuse. SOLUTION (hypotenuse)2 = (leg)2 + (leg)2 c2 = 52 + 122 c2 = 25 + 144 c2 = 169 c2 = 169 c = 13 ANSWER Pythagorean Theorem Substitute. Multiply. Add. Find the positive square root. Solve for c. The length of the hypotenuse is 13. Example 2 Find the unknown side length. SOLUTION (hypotenuse)2 = (leg)2 + (leg)2 142 = 72 + b2 196 = 49 + b2 196 – 49 = 49 + b2 – 49 147 = b2 147 = b2 12.1 ≈ b ANSWER Pythagorean Theorem Substitute. Multiply. Subtract 49 from each side. Simplify. Find the positive square root. Approximate with a calculator. The side length is about 12.1. Your Turn: Find the unknown side length. 1. ANSWER 8 ANSWER 8 ANSWER about 10.6 2. 3. Example 3a A. Find x. The side opposite the right angle is the hypotenuse, so c = x. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem 42 + 72 = c2 a = 4 and b = 7 Example 3a 65 = c2 Simplify. Take the positive square root of each side. Answer: Example 3b B. Find x. The hypotenuse is 12, so c = 12. a2 + b2 = c2 Pythagorean Theorem x2 + 82 = 122 b = 8 and c = 12 Example 3b x2 + 64 = 144 x2 = 80 Simplify. Subtract 64 from each side. Take the positive square root of each side and simplify. Answer: Your Turn: A. Find x. A. B. C. D. Your Turn: B. Find x. A. B. C. D. More Examples: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) A=8, C =10 , Find B A=15, C=17 , Find B B =10, C=26 , Find A A=15, B=20, Find C A =12, C=16, Find B B =5, C=10, Find A A =6, B =8, Find C A=11, C=21, Find B B=6 B=8 A = 24 C = 25 B = 10.6 A = 8.7 C = 10 B = 17.9 C A B Pythagorean Triples Three whole numbers that work in the Pythagorean formulas are called Pythagorean Triples. The largest number in each triple is the length of the hypotenuse. Pythagorean triples are not the only possible side lengths for a right triangle. They give the triangles where all the lengths are whole numbers, but the side lengths could be any real numbers. Pythagorean Multiples If you multiply the lengths of all three sides of any right triangle by the same number, then the resulting triangle is a right triangle. In other words, if a2 + b2 = c2, then (an)2 + (bn)2 = (cn)2. Therefore, additional pythagorean triples can be found by multiplying each number in a known triple by the same factor. Pythagorean Triples Multiples Primitive Pythagorean Triples A set of Pythagorean triples is considered a primitive Pythagorean triple if the numbers are relatively prime; that is, if they have no common factors other than 1. 3-4-5 5-12-13 7-24-25 8-15-17 9-40-41 11-60-61 12-35-37 13-84-85 16-63-65 20-21-29 28-45-53 33-56-65 36-77-85 39-80-89 48-55-73 65-72-97 You need know the first 4 primitives: 3-4-5, 5-12-13, 7-24-25, 8-15-17. Example 4 Use a Pythagorean triple to find x. Explain your reasoning. Example 4 Notice that 24 and 26 are multiples of 2 : 24 = 2 ● 12 and 26 = 2 ● 13. Since 5, 12, 13 is a Pythagorean triple, the missing leg length x is 2 ● 5 or 10. Answer: x = 10 Check: 242 + 102 =? 262 676 = 676 Pythagorean Theorem Simplify. Your Turn: Use a Pythagorean triple to find x. A. 10 B. 15 C. 18 D. 24 More Practice Use Pythagorean Triples to find each missing side length. Primitive: 5-12-13 X=26 Primitive: 7-24-25 X=50 Primitive: 3-4-5 X=15