Chapter 7 On-Line Study Guide
advertisement

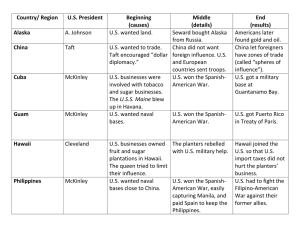
Chapter 7 On-Line Study Guide American History Mr. Maxa & Mr. Bellisario Protectorate • The imperial power allowed the local rulers to stay in control and protected them against rebellion and invasion. • In exchange, the local rulers usually had to accept advice from the Europeans on how to govern their countries. Anglo-Saxonism • The ideas that English speaking nations had superior characteristics, ideas, and systems of government. Reverend Josiah Strong • Supporter of Anglo-Saxonism. • Strongly linked Anglo-Saxonism to Christian ministry ideas. Alfred T. Mahan • Wrote, The Influence of Sea Power Upon History, 1660-1783. • Mahan argued that prosperous people in the past (e.g., British and Dutch) had built large fleets of merchant ships, thus a navy was needed to protect the merchant fleet and defend its right to trade with other countries. Trade with Japan (265) • American business leaders wanted to trade with Japan and China. • Until the 1850s, Japan was a closed society, only trading with Chinese and Dutch merchants. • Congress sent petitions to President Millard Fillmore asking him to force Japan to trade with the United States. Commodore Matthew Perry (265) • Ordered by President Millard Fillmore to go to Japan with four warships. • Arrived on July 8, 1853. • Had the Japanese sign the Treaty of Kanagawa. Treaty of Kanagawa (265) • The treaty gave the US: – Trade rights in two Japanese ports. – Peace between the two countries. – Promised help for any American ships, shipwrecked off the Japanese cost. – Gave American ship permission to buy supplies such as wood, water, food and coal in Japanese ports. Why did people go to Hawaii • Whaling and merchant ships would stop in Hawaii to rest and restock their supplies. What did Hawaii offer • Good soil, sugarcane grows very good. • By the mid-1800s, many Plantation were set-up on the islands. Queen Liliuokalani • Disliked the influence American settlers had gained. • 1893, she tried to impose a new constitution reasserting her authority. • The planter responded by trying to have her overthrown (she was forced to step down). Hawaii Annexation • President Cleveland did not support imperialism. • When Queen Liliuokalani was forced to step down, he tried to have her restored to power but it failed. • Planters waited until after President Cleveland left office to have Hawaii annexed. Cuban Rebel Against Spanish Rule • 1868 rebels declare independence (it fails). • Jose Marti, rebel leader flees to US to raise support. • Cuban rebellion successful in 1895. • U.S. officially neutral but American public sided with Cubans. American Investments in Cuba • U.S. and Cuba closely linked economically. • U.S. had about $50 Million in investments (sugarcane, mines, and railroads). Yellow Journalism • Exaggerated stories to sell newspapers (usually negative). William Randolph Hearst & Joseph Pulitzer • Two New York newspaper owners who competed against each other to sell newspapers. • Both wrote about the atrocities of the Spanish. Valerian “the Butcher” Weyler • Spain sent 200,000 men to round up the rebels and put them into concentration camps, over 10,000 people died. • Weyler acquired the nickname, “the Butcher”. U.S. Calls for Intervention • President William McKinley did not want to go to war with Spain, fearing the war would cost too many lives and hurt the economy. • He told the Spanish if they did not resolve the conflict soon, the US might intervene. USS Maine Explosion • The USS Maine was sent to Cuba to protect Americans and American businesses. • An accidental explosion kills 260 sailors. • Newspapers claim the Spanish caused the explosion. Jingoism • Aggressive nationalism, U.S. asked Spin to leave Cuba. Battle of Manila Bay • On May 1, 1898, Commodore George Dewey with four ships, destroyed eight Spanish ships in one day. Teddy Roosevelt & the Rough Riders • The Rough Riders were a voluntary group made up of cowboys, farmers, and athletes. • Roosevelt was second-in-command of the Rough Riders. • The Rough Riders captured Kettle Hill. American Acquisitions After the War • When Spain surrenders, Cuba is given their independence (with a condition), • U.S. also received Guam, Puerto Rico, and Philippines. Guam, Puerto Rico, Philippines • Guam and Puerto Rico were annexed by U.S. • Philippines was annexed because President McKinley thought they needed to be “Christianized”. Anti-Imperialists • a group of Americans who did not support annexation. • The group included William Jennings Bryant, Andrew Carnegie, Jane Adams, and Mark Twain. Cuban Independence Platt Amendment • Attached to new Cuban constitution: – Cuba could not make any treaty with another nation that would weaken its independence. – Allowed U.S. buy or lease a Naval base (Guantanamo Bay). – U.S. would have the right to intervene in Cuba. Guantanamo Bay • U.S. naval base in Cuba, written into the Platt Amendment. Puerto Rico • In 1900 Congress passed the Foraker Act, establishing a civil government for the island. • Basically, Puerto Rico becomes a U.S. territory. Philippines Insurrection • Emilio Aguinaldo called for war against the U.S. • Insurrection lasted for thee years. • U.S. set up concentration camps against rebels. William Howard Taft • William Howard Taft sent to the Philippines to set up schools, roads, and health care. Sphere of Influence in China • In China, foreign government would “lease” land, the land would still belong to China but they would lose control of the leased area. • British, French, Japanese, Russians, and Germans all had a sphere of influence in China. • These leased areas were the center of economic development including railroads and mining. Open Door Policy • Americans wanted to trade in China but were unsure if countries that had a sphere of influence in an area would discriminate against other foreign nations wanting to do business in their sphere. • U.S. Secretary of State asked each foreign power with a sphere of influence if they would discriminate, they all agreed not to discriminate. Boxer Rebellion • A secret Chinese society organized to fight against foreign control. • The society of Harmonious fists (a.k. a. the Boxers). • The group decided to destroy both the “foreign devils” and their Chinese Christian converts. • Eight nations joined together with 50,000 troops to defeat the Boxers. President McKinley vs. William J. Bryant in 1900 • The election of 1900 pitted McKinley versus Bryant…again. • Bryant attacked McKinley for support of imperialism in Asia. • McKinley picked war-hero Theodore Roosevelt and ran on the slogan, “Four years more of the full dinner pail”. President McKinley Assassinated • While in Buffalo, NY, President McKinley is shot by an anarchist and dies a few days later. Acquiring the Canal Zone in Latin American • The U.S. was looking at two locations to build the canal (Panama & Nicaragua). • A French company offered to sell the U.S. their rights and property in Panama. • Panama at the time belonged to Colombia. • U.S. offered Columbia ten million and yearly rent of $250,000 to build the Canal. – Columbia refused the U.S. offer. “speak softly but carry a big stick” • West African saying • Roosevelt believed in a strong global military presence. • Displaying American power to the world would make nations think twice about fighting and help promote peace. Panamanian Revolution • Panama had opposed Columbia rule. • The French company that was going to sell their rights and property arranged for a small army to staged an uprising with ten U.S. warships off the coast. Building the Panama Canal • It took the U.S. ten years to build. • Disease and mudslides killed workers. Roosevelt Corollary (to the Monroe Doctrine) • President Roosevelt made a speech to congress that stated that the U.S. would intervene in Latin American affairs when necessary to maintain economic and political stability in the Western Hemisphere.