Unit 1 Vocabulary terms
advertisement

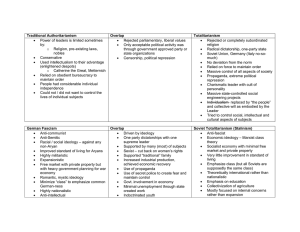
Unit 1 Vocabulary terms inflation fascism totalitarianism Gulag Unit 1 Vocabulary terms ideology nazism censorship collectivization Unit 1 Vocabulary terms Socialism communism politburo overproduction Unit 1 Vocabulary terms SS repression Aryan Dada Unit 1 Vocabulary terms Five-year Plans surrealism AntiSemitism Weimar Republic Unit 1 Vocabulary terms reichstag depression tariff Great Purge Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions inflation economic crisis that is characterized by the decreasing value of money (usually from increased supply in circulation) and sharp increase in prices. Fascism— Totalitarianism— Gulag— Political ideology of a government that asserts total control over every aspect of its citizens’ lives; dictatorship Russian prison with horrible conditions; used for many political prisoners during Great Purge and all of Stalin’s reign. Political ideology born in Italy under Benito Mussolini. Focuses on nationalism, industrialism and growth of empire. Complete obedience to state and leader are required. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Ideology— Nazism— A defined set of political, social and/or economic beliefs. A German brand of fascism. Same components as fascism with the added ingredient of AntiSemitism. Ideology developed by Adolf Hitler. Censorship— collectivization the process of organizing privately held lands into publicly owned land which the public may live and work on, as dictated by the government. a practice of editing or controlling information that is shared with the public. Usually a political tool to control the masses. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Socialism— Economic & political ideology defined by an economic system where the means of production are owned and run by the government Communism— politburo communist party’s committee that determined state policy (along party lines) overproduction Producing more goods than are purchased by consumers. Loss of profit follows since revenue does not make up for investment. Loss of profit usually leads to cutting back in costs, i.e. employees. Economic ideology where no government exists and the means of production are owned and operated by all people as an equal class. The Soviet & Chinese brand of communism was, in reality, socialism but called communism. Why? Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions SS— (schutzstaffeln) a repressive paramilitary group founded by Hitler in 1925 as a personal bodyguard. Later controlled secret & public police forces. During World War II, the SS was responsible for administering concentration camps. Aryan term used to describe people with the physical characteristics of white skin, blonde hair, blue eyes…to Hitler, these people represented the “master race.” repression using force to take away freedom; used by a government to suppress (keep down) the people. Dada French “nonsense” word that means hobbyhorse: it describes a post-war artistic movement that sharply differed from traditional artistic styles; irrational, meaningless, odd. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Five-year Plans economic plans created by Stalin to stimulate industrial growth & production in five year increments. These plans focused on products that didn’t serve people’s basic needs. Soviet industrial production skyrocketed at the cost of its people. Anti-Semitism racism, or hatred, targeted specifically at Jewish people. Surrealism a post-war artistic movement that is characterized by unrealistic and dreamlike subject matter. Weimar Republic short-lived democratic government of Germany created in 1918. Replaced by Hitler’s totalitarian regime. Unit 1 Vocabulary definitions Reichstag-the German parliament (reich means “empire” in German) depression an economic slump that is characterized by a decrease in production, increased poverty and rising unemployment. tariff a tax on imported goods Great Purge Stalin’s plan to rid the Soviet Union of any people who opposed him; included imprisonment, execution, forced labor and exile. Millions died during the 1930’s.