Coriolis Effect and Wind Pattern Notes
advertisement
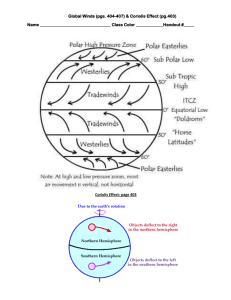
Coriolis Effect and Wind Patterns 3rd factor that affects weather (Wind Speed and Direction) Wind • What is wind? • Wind is moving air. It moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. • What is the main source that drives the winds? • The SUN!!! What causes wind? • Winds are caused by the uneven heating and cooling of the earth. When warm air rises, cooler air flows underneath creating a convection current, thus causing wind! Coriolis Effect • The results from the earth’s rotation causing freely moving objects (such as airplanes) to veer toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. • Affects things like wind, ocean currents, airplanes, and missiles. http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_scien ce/terc/content/visualizations/es1904/es1904 page01.cfm • Another example of the Coriolis Effect is a merrygo-round. • If you tried to pass a ball across to someone on the other side, the ball would be deflected instead of moving in a straight line. • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/ fw/gifs/coriolis.mov • Without the Coriolis Effect, wind and weather patterns would be more stabilized because they would move in a straight line instead of “deflecting” to the right or left. This means there would be fewer changes in the atmosphere (weather patterns)—this would be boring! Global Winds • Wind patterns on Earth. • Helped early sailors navigate the oceans • 4 Types of Global Winds: 1. 2. 3. 4. Polar Easterlies Westerlies Trade Winds Doldrums Polar Easterlies • In the far north and south poles • Cold, dense air sinks and moves away from the poles. Westerlies • Above the subtropical highs in the Northern Hemisphere and below the subtropical highs in the Southern Hemisphere, winds blow from the West towards the East. Trade Winds • Air movements toward the equator. • Warm, steady breezes that blow almost continuously. • The Coriolis Effect makes the trade winds appear to be curving to the west, whether they are traveling to the equator from the south or north. Doldrums • Area of calm weather near the equator • Converging trade winds produce general upward winds as they are heated, so there are no steady surface winds. • Cloudy, rainy weather develops most afternoons (tropical rainforests) GGlobal Winds