Topic 2 The Ecosystem
advertisement

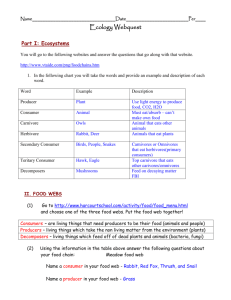
2.4 Biomes Assessment Statements 2.4.1 Define the term biome 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome 2.4.1 Define the term biome A collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions. BIOME is the collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions. Cell 3 North Cold, dry air falls Model of global air circulation and biomes. The direction of air flow and the ascent and descent of air masses in convection cells determine the earth’s climatic zones. Moist air rises — rain Polar cap Arctic tundra Evergreen coniferous forest 60° Temperate deciduous forest and grassland Desert 30° Cell 2 North Cool, dry air falls Cell 1 North Moist air rises, cools, and releases moisture as rain Tropical deciduous forest 0° Equator Tropical rain forest Tropical deciduous forest 30° 60° Desert Temperate deciduous forest and grassland Cell 1 South Cool, dry air falls Cell 2 South Polar cap Cold, dry air falls Moist air rises — rain Cell 3 South Uneven Solar Heating and Latitude Earth as a whole is in thermal equilibrium, but different latitudes are not. Moving masses of air and ocean currents transport energy from locations with a surplus to those with a deficit. 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome Tropical Rainforest Temperature: 26 C Rainfall: Over 2500 mm/yr Insolation (Light Level): High Distribution: Between the tropics of cancer and capricorn Structure: Highly stratified (Emergent, Canopy, Understory, Immature, and Herb layers) Productivity: High 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome Desert Temperature: 45 C Rainfall: Under 250 mm/yr Insolation (Light Level): High Distribution: 30 o N and S Structure: Little vegetation, organisms highly adapted to low water and fluctuating temperatures Productivity: Very low 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome Tundra Temperature: Low down to -50 C Rainfall: Low Insolation (Light Level): Low Distribution: High Latitudes Structure: Plants with leathery leaves or underground storage organs, larger animals with fur Productivity: Low 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome Temperate forest Temperature: cold winters, hot summers Rainfall: 500-1500 mm/yr Insolation (Light Level): varies through year Distribution: 40 to 60 o N Structure: Dominated by one species of tree (evergreen or deciduous) bigger shrub layer due to less dense canopy Productivity: Relatively high 2.4.2 Explain the distribution, structure, and relative productivity of tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and any other biome Grasslands Temperature: cold winters, hot summers, fluctuate wildly if removed from the sea Rainfall: 250-500 mm/yr Insolation (Light Level): varies through year Distribution: Almost every continent 16% of the earth’s surface Structure: Diverse grasses, with a mat of slowly decomposing vegetation Productivity: Relatively low AQUATIC BIOMES Ocean Lakes Coral reefs Mangroves Rivers High tide Low tide Sun Sea level 50 Euphotic Zone 100 Estuarine Zone Continental shelf Photosynthesis 0 500 Bathyal Zone 1,000 Twilight 200 1,500 Abyssal Zone 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 10,000 Darkness Coastal Zone Open Sea Depth in meters Aquatic Ecosystems Environmental Factors Temperature Aquatic Ecosystems Environmental Factors Light Aquatic Ecosystems Environmental Factors Salinity The Black Sea 16 PPT Baltic Sea 5-15 PPT Lake Michigan 0.5 PPT The Dead Sea 332 PPT Pacific Ocean 36 PPT The Red Sea & The Persian Gulf 40 PPT Aquatic Ecosystems Environmental Factors Currents Aquatic Ecosystems Environmental Factors Dissolved Oxygen Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) Temperature Temperature (ºC) Depth (m) Depth (m) Dissolved Oxygen Aquatic Ecosystems Zonation Aquatic Ecosystems Human Impacts Waterways across the United States are contaminated by a medicine chest of antibiotics, hormones, caffeine, painkillers and other drugs Agricultural runoff can carry fertilizers, including traces of antibiotics and hormones, into waterways