Chp. 5 Review - St. Paul School
advertisement

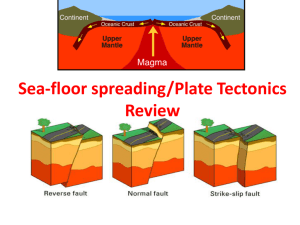
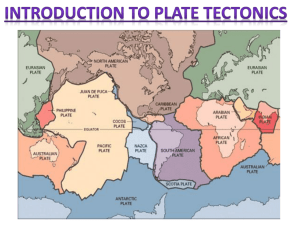
Chapter 5 Review Vocabulary All of the Earth’s landmasses were once joined in the supercontinent __________. Pangaea Vocabulary At the mid-ocean ridge, ______ occurs because of the welling up of molten material from the mantle. Sea-floor spreading Vocabulary A plate boundary where two plates come together is called a _________. Convergent boundary Vocabulary The process of one plate moving under another is ______. Subduction Vocabulary The theory of _______ states that the lithosphere of the Earth is divided into moving pieces. Plate tectonics Vocabulary Any plate boundary where the plates move away from each other is called a _________. Divergent boundary Vocabulary When a plate is subducted, a deep ocean valley, or ________, is formed. Trench Vocabulary A plate boundary where two plates slide past each other is a _________. Transform boundary What’s the Difference? Convergent Boundary vs. Divergent Boundary Convergent- when two plates come together. Divergent- when two plates move away from each other. What’s the Difference? Lithosphere vs. Tectonic Plate A tectonic plate is one of the pieces that make up the lithosphere. What’s the Difference? Subduction zone vs. Trench Subduction zone- the place where one plate is pushed down under another. Trench- and ocean valley that forms in a subduction zone. Check Your Knowledge How did scientists prove that sea-floor spreading occurs? Scientists found a patter of parallel magnetic stripes in the sea floor and found that the age of the crust increases the farther away you get from the ridge. Check Your Knowledge List the three ways in which plates can interact with one another. Plates can converge, diverge, or slide past one another. Check Your Knowledge How do the marks left by ancient glaciers provide evidence for continental drift? Glaciers always flow toward oceans, so the marks left in rocks by a glacier should point toward an ocean. Some glacial marks do not point toward present-day oceans, indicating that the landmasses were not always oriented as they are today. Check Your Knowledge Explain the two models proposed for how convection moves plates. One model says that the plates are simply floating on convection cells. The other model says that the plates are actually part of the convection cells. Check Your Knowledge What landforms can result when two plates meet at a convergent boundary? Trenches, volcanoes, and mountain ranges. Check Your Knowledge What is the theory of continental drift? The theory of continental drift states that the Earth’s landmasses were once connected, have moved apart, and are still moving. Check Your Knowledge How does the age of rocks found at the bottom of the ocean compare to the age of rocks found on the continents? Ocean rocks are younger than rocks from continents. Check Your Knowledge List the three kinds of convergent boundaries. Oceanic-oceanic, oceaniccontinental, and continentalcontinental. Check Your Knowledge What two continents were formed when Pangaea broke apart? During which era of geologic time did this occur? Laurasia and Gondwanaland. Mesozoic Era. True or False? The present-day continents of Africa, South America, Australia, India, and Antarctica were once joined as the continent Laurasia. False; Gondwanaland True or False? The mid-ocean ridges are all subduction boundaries. False; divergent True of False? Tectonic plates “float” on the lithosphere. False; asthenosphere True or False? The density of oceanic crust if greater than the density of continental crust. True Check Your Understanding Where is new crust created? Along a divergent boundary. Check Your Understanding How do continental plates differ from oceanic plates? Continental plates include both continental and oceanic crust. Check Your Understanding What happens to the rock material of a subducting plate? The rock material melts and is absorbed into the mantle. Check Your Understanding Where do we typically find ocean trenches? Associated with subduction zones. Check Your Understanding What kind of fault line is the San Andres Fault? A transform boundary Check Your Understanding What is another name for the Earth’s internal heat? Geothermal energy. Check Your Understanding What kind of boundary were the Himalayan Mountains formed at? A convergent boundary.