File
advertisement

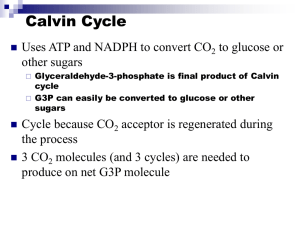
AP ? Of the Day 1. 2. 3. 4. Which of the following has the least amount of stored energy per molecule? ATP Pyruvic Acid NADH CO2 Think about their relationships An ATP molecule contains less energy than an NADH because 1 NADH supports the synthesis of 3 ATP during electron transport. NADH contains less free energy than pyruvate, because the oxidation of pyruvate produces 4 NADH (plus 1 FADH2 and 1 ATP). Carbon dioxide contains the lowest amount of free energy in this list, because it has only 1 carbon atom, and the others all have more than 1. Today… Notes on the Calvin Cycle Finish POGIL Pre-lab, design your experiment for Friday/Monday Photosynthesis II Dark Reactions or more appropriately, Light Independent Rxns. AKA – Calvin Cycle. I love science. Recap. . . H2O + CO2 + Light glucose + O2 Light reactions thylakoid membrane Produce ATP & NADPH What for? To power Calvin Cycle How produce ATP? chemiosmosis Light Independent Rxn Calvin Cycle Where? Stroma Use ATP & NADPH from light reactions What is left in the equation? CO2 Purpose: produce glucose Calvin Cycle Carbon Fixation Add 3CO2 to 3 RuBP (5C) molecules 6 PGA (3C) Reverse of glycolysis Add 6 ATP & 6 NADPH reduce PGA into 6 G3P (3C) (G3P) molecules 1 G3P molecule leaves glucose Reform RuBP Change G3P RuBP by adding 3 ATP G3P (3C) RuBP (5C) (starts cycle) Photorespiration In the presence of O2, Rubisco (enzyme) releases CO2 Undoes the Calvin cycle 20% of fixed carbon is lost to photorespiration As temp increases more photorespiration occurs C3 vs C4 vs CAM C4 Photosynthesis Use PEP carboxylase instead of Rubisco NO PHOTORESPIRATION C4 molecule is modified & releases a CO2 This CO2 is captured by Rubisco Calvin cycle Adaptation for plants in warmer climates C4 Pathway C4 photosynthesis in mesophyll cells Calvin Cycle in bundle sheath cells Creates high local levels of CO2 for rubisco in the Calvin cycle Oxaloacetate maltate bundle sheath cell Releases a CO2 Calvin cycle (pyruvate) CAM Pathway Crassulacean Acid Succulent plants Stomata open at night & closed in day Reverse of most plants Fix CO2 using C4 pathway Fixed & stored at night decarboxylized during day High CO2 drives the Calvin cycle & reduces photorespiration Comparison of C4 & CAM Photosynthesis