File
advertisement

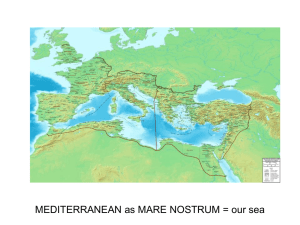
Review Outline Early European 29-526 CE edited October 13, 2015 2014-2015 Enduring Understanding Art of this period studied in chronological order and divided into geographical regions, governing cultures, identifiable styles with considerable overlap in time, geography, heritage of art Numerous religions (Jewish, Christian, Islamic) and languages (Greek, Latin, Arabic) have created a fragmentation of Early European (Medieval) art Essential Knowledge Influence of Roman art and tribes of Eastern Europe, West Asia, Scandanavia Architecture is primarily religious in nature Figure work was primarily religious, avoided naturalism and incorporated text until later medieval period Contextual information comes primarily from literary, theological (secular and religious) records. Overall, in Mediterranean region Christian themes proliferated after Constantine converted the empire leading to established standards of imagery (Christ) and building (basilica church). Classical style was rejected in favor of non-naturalistic style with hieratical images that brought focus on the spiritual as opposed to natural worlds Geographic/Cultural Context Geography, Politics, Religion Geography Empire divides east (Byzantium) and west (Rome) Politics Decline of Roman empire o Invasion from north Europe-Germanic tribes Rome sacked twice 410, 455 o Plague from east o General civil conflict within the empire Military, economic, political o Gradual shift east Religion Polytheism to monotheism o Rise of Christianity Edict of Milan – 313 CE Religious tolerance Council of Nicea -325 CE Formalizing of Christianity in Roman Empire Constantine moves capital from Rome to Byzantium -330 Constantine’s conversion 337 o Judaism Emergence of eastern and western churches o east (Byzantium-Orthodox) and west (Rome-Catholic) Art Context Christian imagery, Architecture, Mediums Christian imagery Shift in view/presentation of the figure o Naturalism to symbolism (spiritual) Blurred pagan imagery with classical Perceptual to conceptual o Became more standardized Two periods-pre 313 and post 313 o Pre more discreet; post more public Architecture Development of Christian church designs o Basilica plan o Central plan Catacombs-burial chambers o Primary source of Christian imagery o In Rome Artistic mediums Mosaic Fresco Manuscript illumination Marble o sarcophagi Key art images-with star in slide show Vocabulary words Catacombs-subterranean networks of rock-cut galleries and chambers designed as cemeteries for the burial of the dead Syncretism-assimilation by artists of images from other religious traditions; creation of new meanings assigned Orant-figures that take pose of outstretched arms in prayer Clerestory - the topmost zone of a wall with windows in a basilica extending above the aisle roofs. Provides direct sunlight into the central interior space (nave) Mosaic-images made using small pieces of stone or glass embedded in cement; usually on walls or floors