File
advertisement

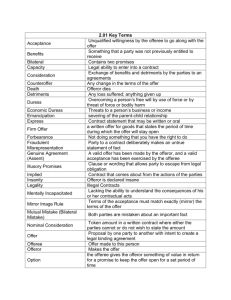
ES 2.00 UNDERSTAND CONTRACT LAW Obj. 2.01 Understand the elements and characteristics of a contract Elements of a Contract Offer Acceptance Genuine Agreement/Assent Consideration Capacity Legality All elements MUST be present to be an enforceable contract. Offer An offer is a proposal by one party to another intended to create a legally binding agreement. The offer must be made seriously, definite and certain and communicated to the offeree Offer Often a invitation to negotiate is confused with an offer. Invitations to negotiate are invitations to deal, trade, or make an offer. Sellers usually have limited merchandise to sell and cannot possible sell an advertised product to everyone who sees an ad. For this reason most advertisements are not treated as offers OFFER Proposal by one party to another with intent to create a legal binding agreement Offeror Makes the offer Offeree Offer made to this person Requirements of an Offer Serious Intent Must intend to make the offer Advertisements? Definite and Certain No serious intent Known as an invitation to negotiate Must use definite words Communicated to the Offeree Phone, fax, Internet, letter, etc Termination of Offer Revocation – Taking back of an offer by offeror Rejection – Refusal by the offeree Counteroffer – Any change in the terms of the offer Death – Offeror dies Insanity – Offeror is declared insane Expiration of Time – If the offeror puts a time limit on the offer and it has passed Destruction of the subject matter Options & Firm Offers Option – the offeree gives the offeror something of value in return for a promise to keep the offer open for a set period of time Firm Offer – a written offer for goods that states the period of time during which the offer will stay open No additional consideration is required Maximum period of time set by the UCC – 3 months Offeror must be a merchant who deals in related goods on a daily basis STOP HERE……WORK SHEET Acceptance An acceptance is the second party’s unqualified willingness to go along with the first party’s proposal. ACCEPTANCE • Mirror Image Rule • • Terms of the acceptance must match exactly (mirror) the terms of the offer Any change means there is no acceptance (counteroffer) Bilateral and unilateral contract A bilateral contract is a contract that contains two promises. Most are this way Unilateral contract is a contract that contains a promise by only one person to do something, if and when the other party performs some act Methods of Acceptance Bilateral Acceptance Offer is accepted by offeree through communication of the promise to the offeror Only requires giving a promise to perform, not performance itself Most offers are bilateral Unilateral Acceptance Offeror promises something in return for offeree’s performance and indicates that performance represents acceptance Silence as Acceptance Does not represent acceptance Offeror cannot word offer in a way that silence would be considered acceptance STOP HERE WROKSHEET Genuine Agreement Genuine Agreement means that an agreement is true and genuine: a valid offer is met by a valid acceptance. GENUINE AGREEMENT (ASSENT) • A valid offer has been made by the offeror, and a valid acceptance has been exercised by the offeree Several causes for genuine agreement to be lacking in a contract • • • • • Duress Undue Influence Unilateral or Mutual Mistake Innocent Misrepresentation Fraudulent Misrepresentation Duress Overcoming a person’s free will by use of force or by threat of force or bodily harm Threats of Illegal Conduct Threats to Report Crimes Threats to Sue Threats to sue made for purpose unrelated to the suit Economic Duress Threats to a person’s business or income Undue Influence Unfair and improper persuasive pressure within a relationship of trust Must be able to prove: Relationship of trust, confidence or authority Unfair persuasion Unilateral Mistake An error on the part of one of the parties Usually a person cannot get out of a contract just because of a mistake. Does not affect validity of the contract Cannot get out of contract Nature of the Agreement Signing a contract you don’t understand or have not read Signing a contract in a language you don’t understand Mutual Mistake (Bilateral Mistake) Both parties are mistaken about an important fact. Often when the mistake is bilateral, etiher one of the parties can get out of the contract. Impossibility of Performance Contract is impossible to perform Contract is void Subject Matter Either party can void contract Existing Law Contract is valid Parties are expected to know the law Innocent Misrepresentation Innocent statement of supposed fact that turns out to be false Statement must be one of fact Statement must be material Statement must be relied upon Injured party has the right to rescind (take back) the offer No rights to damages Fraudulent Misrepresentation Party to a contract deliberately makes an untrue statement of fact Deliberate: Done with or marked by full consciousness of the nature and effects; intentional Deception: The fact or state of being deceived Gain: To secure as profit or reward In order to prove fraud, you must prove the above 3 definitions Proving Fraudulent Misrepresentation Untrue statement of fact (failing to disclose that a car had been damaged in a flood) Must be one of fact, not opinion Active concealment Silence – may stay silent about defects except when: statement is about material facts True statement is made false by subsequent events One party knows the other party has made a basic mistaken assumption Materiality Statement would cause reasonable person to contract If one party knows the other party would rely on the statement If one party knows the statement is false Proving Fraudulent Misrepresentation Reasonable One Reliance party must reasonable rely on statement Intentional or reckless One party deliberately lies or conceals a material fact One party recklessly makes a false statement of fact, without knowing whether it is true or false Statement must be intended to induce party to enter into contract Resulting Must Loss cause an injury STOP HERE WORK SHEET AGREEMENT CAPACITY Legal ability to enter into a contract The following have the right to get out of a contract….. • • • Minors Mentally Incapacitated Intoxicated A person serving a prison sentence lacks capacity. Minors Minor – not yet reached legal age (age of majority) NC Age of Majority – 18 years old The law allows minors to get out of contracts. It considers them too inexperienced, immature unknowledgeable or naïve. Minors Emancipated minors are responsible for their own contracts. Emancipation - severing of the parent-child relationship Emancipated minors are responsible for their own contract. Minors are automatically emancipated when they get married or set up their own household. Formal – court decree Informal – arises from the conduct of the minor and the parent Parent and minor agree that parent will end support Minor gets married Minor moves out of family home Minor joins armed forces Minor gives birth Minor takes on full-time employment Minors Ratification – the act of agreeing to be bound by a contract that could be avoided If a minor makes a payment on a contract that is due after becoming an adult, that minor has ratified the contract Contracts made by minors are voidable; minors may disaffirm (or avoid being bound by) contracts Mentally Incapacitated Lacking the ability to understand the consequences of his or her contractual acts Severe mental illness Severe mental retardation Severe senility Contracts made by mentally incapacitated are usually void unless involving necessaries. Intoxicated People under the influence of drugs or alcohol Intoxication is a voluntary act. Most courts are reluctant to consider contracts entered into by intoxicated individuals as voidable. Must be so intoxicated that the person did not know they were contracting. This decision is made by a judge. Stop WORK SHEET CAPACITY CONSIDERATION Exchange of benefits and detriments by the parties to an agreements Requirements of consideration: Benefits Something that a party was not previously entitled to receive Detriments Must involve a bargained-for exchange (promise made in return for another promise) Must involve something of value Benefits and detriments must be legal Any loss suffered; anything given up Forbearance Not doing something that you have the right to do Adequacy of Consideration Courts don’t look at adequacy or value of an agreement unless it is “unconscionable” Unconscionable So grossly unfair or oppressive that it would shock the conscience of the court So lop-sided that the average person would not agree to terms Nominal Consideration Token amount in a written contract where either the parties cannot or do not wish to state the amount Agreements without Consideration Promise to make a gift Gifts have no consideration Cannot be enforced Gift that has been given Doesn’t have to be returned Donor – Gives the gift Donee – Accepts the gift What happens when the engagement is off? Your fiance recently ended the engagement and you spent $3000 on an engagement ring. She refuses to give the ring back. Are you entitled to the ring according to the law? What happened if you are the one who bought the ring and also broke the engagement, do you still get the ring back? Illusory Promises Clause or wording that allows party to escape from legal obligation. A promise that is unenforceable due to indefiniteness or lack of mutuality, where only one side is bound to perform. Ex. The seller agrees to sell all of the icecream he wants to , to the buyer. Termination clause Output Contracts Agreement to purchase all of a specific producer’s product Requirements Contracts Illusory – clause to allow termination of contract for any reason Not illusory – termination only allowed after a change in defined circumstances Agreement to supply all of the needs of a specific buyer Output & Requirements contracts are recognized by the courts as having consideration by implying fair dealing. Existing Duty Existing Public Duty You cut my hair, I give you $25.00. No detriment Obligation to obey the law Existing Private Duty If a person is already under legal duty to do something, another promise to do that same thing does not furnish consideration for a new contract. Past Performance An act that has already been performed cannot be consideration in a contract. Exceptions to Consideration Promises to charitable organizations Gift or Pledge for future contribution Enforceable as consideration if organization identifies the pledge for a specific use and acts in reliance on the pledge Promises covered by the UCC Firm offers Good faith modification of contract Promises discharged in bankruptcy Exceptions to Consideration Promises barred from collection Promissory Estoppel Is the principle that a promise made without consideration may nonetheless be enforced to prevent injustice Rely on what a person said Elements: Promise must bring action or forbearance One who gave no consideration must have relied on the promise Injustice can be avoided onlyby enforcing the promise Example of Promissory Estoppel You are the principal of a small high school. A musician approaches you to discuss implementing a music program on campus. Excited you begin planning for the program. You order construction of anew building complete with soundproofing and a stage. Next new furniture and fixtures, drums etc. You hire a new staff, then in one fell swoop the promise is retracted. The musician simply changes his mind. The doctrice of Promissory Estoppel can help you recover your losses. It states that you can recover losses if they were the result of a promise made by a promisor and the promise was significant enough to move the promisee to act on it. LEGALITY Illegal Contracts Civil & Criminal Usury State sets a max interest rate Interest – fee the borrower pays to the lender for using the money Usury - charging too high of an interest rate Gambling Agreements to commit a crime/tort are illegal Legal gambling varies from state to state Licensing States require that persons in certain occupations obtain a license to practice that occupation Doctors, plumbers, barbers, lawyers, funeral directors Illegal Contracts Public policy no one should be allowed to something that harms the public. Agreements that unreasonably restrain trade, the law protects the right to make a living ex. Agreements not to compete Takes away the ability to do business with others Restrictive covenant - agreement not to compete in a region for a period of time with the seller of the business you just bought. Only legal for a short period of time and small geographic region Agreements for price fixing Price Fixing - competitors agree on certain price ranges within which they will sell their products Illegal Contracts Public policy (continued) Agreements to eliminate competitive bidding (or bid rigging) Bid - offer to buy or sell goods or services at a stated price Bid rigging – competitors agree that one bidder will have low bid for a certain job….low bidder sets bid higher than would if real competition Agreements to obstruct justice Agreements to induce breach of duty or fraud Anything that delays or prevents justice Influencing persons who hold positions of high trust for private gain Agreements to interfere with marriage Damage, destroy, or discourage good family relationships Statute of Frauds Requires that certain contracts be in writing to be enforceable Contracts to buy and sell goods for a price of $500 or more Contracts to buy and sell real property Contracts that require more than one year to complete Promises to pay the debt of another Promises to give something of value in return for marriage Stop here Worksheet Legality CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTRACT Valid, void, voidable, unenforceable Express or implied Bilateral or unilateral Oral or written Valid, Void, Voidable, Unenforceable Valid contract Void contract Includes all elements recognized by the courts Legally binding Without legal effect Contracts missing one or more elements Voidable contract One or more parties can get out of contract for some legal reason Contract lacks genuine assent, contracts with minors Unenforceable contract Contract that court will not uphold, usually because of some rule of law Statute of limitations has expired Express or implied Express Contract statement that may be written or oral Implied Contract parties that comes about from the actions of the Bilateral or Unilateral Bilateral Contains two promises Most contracts are bilateral Unilateral Contains a promise by only one person to do something if, and when, the other party performs a certain act Reward offer is most common unilateral contract Oral or written Oral Created by two or more people speaking to each other Written contract terms are written so that both parties know the exact terms Provides proof of existence for the contract Certain contract are required by the Statute of Frauds to be in writing