Islam Notes - Stjohns

By: Ms. Susan M. Pojer
Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
Islam
An Abrahamic
Religion
Muslims are strict monotheists.
They believe in the Judeo-
Christian God, which they call
Allah .
Muslims believe that the Torah and the Bible, like the Qur is the word of God.
’ an ,
Peoples of the Book
Abraham ’ s Genealogy
HAGAR
Ishmael
ABRAHAM
Isaac
SARAH
12 Arabian
Tribes
Jacob Esau
12 Tribes of
Israel
The Prophetic Tradition
Adam
Noah
Abraham
Moses
Jesus
Muhammad
The Origins of the
Qur
’
an
Muhammad received his first revelation from the angel
Gabriel in the Cave of Hira in 610.
622 Hijrah Muhammed fled Mecca for Medina.
* The beginning of the
Muslim calendar ( 1 A.H.
)
Muhammad ’ s revelations were compiled into the Qur his death.
’ an after
The
Qur
’
an
Muslims believe it contains the word of God.
114 suras (chapters).
In the name of Allah, the compassionate, the merciful.
Written in Arabic.
1. The Shahada
The testimony.
The declaration of faith:
There is no god worthy of worship except God, and
Muhammad is His
Messenger [or Prophet].
1
2. The Salat
The mandatory prayers performed 5 times a day:
* dawn
* noon
* late afternoon
* sunset
* before going to bed
Wash before praying.
Face Mecca and use a prayer rug.
2
2. The Salat
The call to prayer by the muezzin in the minaret .
Example of one or two
Pray in the mosque on Friday.
2
3. The Zakat
Almsgiving (charitable donations).
Muslims believe that all things belong to God.
Zakat means both “ purification ” and “ growth.
”
About 2.5% of your income.
3
4. The Sawm
Fasting during the holy month of Ramadan .
Considered a method of selfpurification.
No eating or drinking from sunrise to sunset during
Ramadan.
4
Eid Mubarak
End of the Ramadan holiday.
5. The Hajj
The pilgrimage to Mecca.
Must be done at least once in a
Muslim ’ s lifetime.
2-3 million Muslims make the pilgrimage every year.
5
5. The Hajj
Those who complete the pilgrimage can add the title hajji to their name.
5
The Dar al-Islam
The World of Islam
1 2 3 4 5
Pop-Quiz
• What are the five pillars of Islam?
• What do “ Muslim ” and “ Islam ” mean?
• In what city did Muhammad die?
Ascend to heaven?
• To what city did Muhammad leave on the Hijrah?
• What is the Qur’an?
The Mosque
The Muslim place of worship.
The Dome of the Rock
Mosque in Jerusalem
Mount Moriah Rock where Muhammad ascended into heaven.
Muezzin
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-
QTkC-TTzZc
• http://www.videospider.tv/Videos/De tail/857371539.aspx
Adhan
• Sunni Text of the adhan : God is The
Greatest; I bear witness that there is no lord except God; I bear witness that Muhammad is the Messenger of
God; Make haste towards prayer;
Make haste towards welfare; God is greatest; There is no lord except
God
Other Islamic Religious
Practices
Follow Muhammad ’ s example: The
Sunna; and the Hadith,
Muhammad ’ s collected sayings
Polygamy is allowed.
No alcohol or pork.
No gambling.
Sharia body of Islamic law to regulate daily living.
Three holiest cities in Islam:
* Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem.
Essential Question:
Why was Islam able to spread so quickly and convert so many to the new religion?
The Spread of Islam
Easy to learn and practice.
No priesthood (Ulama - those with knowledge; Imam - one who is front)
Teaches equality and tolerance.
Non-Muslims, who were “ Peoples of the Book, ” were allowed religious freedom, but paid additional taxes.
Easily “ portable ” nomads & trade routes.
Jihad ( “ struggle ” ) against pagans and other non-believers.
The Spread of Islam
• Muhammad ’ s successors or deputies, called caliphs, continued teaching the message of
Islam.
• “ Rightly Guided Caliphs ” were elected: Abu
Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali
• The Caliphate that followed Ali was hereditary
• The caliphs were able to expand the Muslim
Empire from the Atlantic ocean to the Indus
Valley
• The early Caliphs took advantage of the weakness of the Persian and Byzantine empires
• The Qur ’ an prohibits force conversion
– Islamic leaders allowed Christians and Jews to practice their beliefs but they could not spread their beliefs.
Split Within Islam
• Civil war erupted after the death of Hussein
Ibn Ali in Karbala, 680 CE.
• With the death, the process of electing
Caliphs ended
• The new leadership moved the capital to
Damascus (Syria) to make expansion easier
- the Ummayad Dynasty
• In addition to the move the new leaders moved away from the simple life of the caliphs and surrounded themselves with luxury
Shi ’ a / Sunni Split
• Sunni
– Meaning “ followers of Muhammad ’ s example ”
– Followed the new leadership
– A majority of the people accepted the new rulers, to maintain peace
Shi ’ a
- Meaning “ party ” of
Ali (Muhammad ’ s cousin and son-in-law)
- Resisted the new leaderships rule.
- Believed the Caliph needed to be a relative of the prophet Muhammad
- Another group, the Sufi, pursued a life of poverty in response to the luxury of the Sunni leadership.
Sunni and Shi ’ a Split
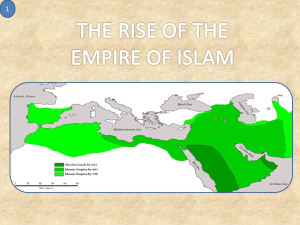
Spread of Islam to Three
Continents
Under the leadership of various leaders the
Muslims spread as far north as France and south into southern Africa.
A large Muslim settlement was established by the Berbers in Spain.
– Lead by Jabal Tariq
– He was so revered they named the Rock of
Gibraltar after him.
Corodoba, in Spain became a center for the spread of Islam in Europe
– 70 libraries, 700 mosques, 27 free schools
– Population of 500,000
– All religions were welcome in Corodoba
Caliphate in 750 CE
Muslim Society
• Throughout the Muslim Empire urban centers flourished
– Ummayad Caliphate: capital at Damascus (661-750 CE)
– Abbasid Caliphate: capital at Baghdad (750-1258)
– Ummayad Dynasty in Spain, followed the Berbers (North
African Muslims) who fought at the Battle of Tours in 732 and established the Al-Andalus
• There were four social classes
– The upper class - Muslims by birth
– Second class - converts to Islam (paid higher taxes)
– Third class “ The Protected People ” - Jews and
Christians, also Zoroastrians - higher taxes than 2nd class
– The Lowest Class - Slaves, all non-muslim, many were household workers or soldiers.
Muslim Society, cont.
• The Role of Women
– The Qur ’ an states that men will manage a women ’ s affair
– An obedient women is a righteous women
– Muslim women had more rights than European women.
– Responsibilities varied based on the income of the husbands.
– Women raised the children
– In early Muslim society women participated in religious activities and were encouraged to get an education
Seljuk Turks
• Turks who left central Asia and set up a
Muslim empire from Anatolia to the Punjab between 11th and 14th centuries
• Adopted Persian culture, eventually captured the Abbasid and Byzantine empires
• Principle enemy of Crusaders in the 11th-
15th centuries
• Set up the Ottoman Empire centered in
Anatolia, the Holy Lands, Arabia, North
Africa, and Persia - lasted until mid-15th century
Advances in Art and Science
• Many advances in medicine, mathematics, and astronomy are credited to the Muslim world
• Understanding of smallpox and measles
• Proper location for hospitals
• Muslims scholars charted stars, comets, and planets
• Many artists began the art of calligraphy, due to the banning of drawing images
Islam: the peaceful religion
• Islam comes from the Arabic word for
“ Peace ”
• Jihad can be interpreted many ways.
– Holy War, struggle against infidels (un-believers)
– Concept that includes “ struggle against evil inclinations against oneself, struggle to improve the quality of life in society, struggle in the battle for self-defense or fighting against tyranny and oppression, ” ( Islam: Opposing Viewpoints , p 14)
– “ Whoever killed a human being, except as a punishment for murder or villainy in the land, shall be looked upon as though he had killed all mankind, ” ( Islam: Opposing Viewpoints , p 14).