Articles - Altimira Middle School
advertisement

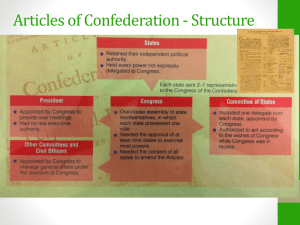
From the Articles of Confederation to The Constitution: U.S. History Changes in Government • During the Revolution the Second Continental Congress asked the colonies to establish new State Constitutions. • Most defined Executive Power, discussed voting rights, and created the separation of church and state. • Most had a bill of rights. • Look at the list of grievances in the Declaration of Independence • What rights do you think were included in these new bill of rights? The Republic of America • Republic: A form of Government in which the leaders get the power to rule from the citizens. • Who was very influential in the republican idea that citizens allow themselves to be ruled so that their property is protected? • What are other examples of Republican thought in America? Articles of Confederation: • Central Government: unify the colonies • The states were not willing to give up their own powers to a central government. • Why would the colonies be intimidated by the thought of having a strong central government? • Plan for a “perpetual union” the Articles of Confederation were adopted on Nov. 15, 1777. Provisions of the Articles: • The Articles created a loose confederation of independent states that gave limited powers to a central government. • The government would consist of a single house of Congress, where each state would get one vote. • Small states vs. Big States. Provisions of the Articles • Congress had the power to set up a postal department, to raise armed forces, and to control the development of the western territories. • The central government could also estimate the costs of the government and request donations from the states. Provisions of the Articles: • With the consent of nine of the thirteen states, Congress could also coin, borrow, or appropriate money as well as declare war and enter into treaties -and alliances with foreign nations. • Do you see anything that could lead to problems for the new Government? The Problem of Land: • The states with claims of frontier land wanted to control as much land as they could. • The states with no frontier claims wanted the government to sell the territories so that all states would profit. • The states finally agree to give control of all western lands to the federal government. • These lands will now be divided and sold. Other Problems of the Articles • Congress was denied the power to levy taxes. • Any amendment to the articles required the unanimous approval of all 13 states. • The weak central government had an inability to regulate trade • The government could not pay off the debts from the revolution; including paying soldiers who had fought in the war. Shays’ Rebellion: • In 1786, the Massachusetts legislature placed a tax on land. • Unable to make money off his crops, Shays was angry because farms were being shut down and auctioned off. • The former Revolutionary Captain Daniel Shays leads 1,200 farmers to seize the federal arsenal. • The rebellion was put down but it raised questions about how well the Articles could deal with civil issues, and people began to call for more central power. + Articles - Government is in place to allow us to win the war No power to tax A weak Government holds the very fragile country together. Gives the government many important powers Coining money causes inflation Leads to the Constitution Very inactive government Central Government is too weak Questions to Answer: • Why do you think the colonists wanted independence? • Why did the Articles of Confederation have to be abandoned? • Why did Shays’ Rebellion scare people so badly? Leaders of the Constitutional Convention