Progressive President Foreign Policy
advertisement

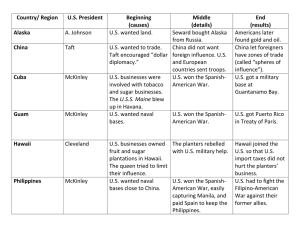
Progressive President Foreign Polcies US History Standards • C2D – Evaluate, take, and defend positions on the various US foreign policies of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. I. William McKinley A. Foreign Issues 1. Forced to deal with Spain in Cuba. This leads to the Spanish American War. 2. Negotiated control of Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippines from Spain. 3. Made a very strong effort to form stronger economic ties to China. I. William McKinley B. Philippines 1. Acquired for $20 million from Spain after the Spanish American War 2. Emilio Aguinaldo led a revolt in an attempt to gain independence from the U.S. 3. The U.S. responded to the revolt with brutal force by destroying villages and putting civilians into prison camps. 4. After 3 years of fighting 200,000 Filipinos and 5,000 Americans were killed. 5. US controlled the Philippines until 1946 I. William McKinley C. China 1. China was weak and unstable in 1890’s. Foreign countries controlled Spheres of influence. 2. Open Door Policy- Called on foreign nations to allow free trade in China. Insisted that foreign nations respect Chinese independence II. Teddy Roosevelt A. Foreign Issues 1. Had a desire to make the U.S. a great power 2. Big Stick Policy- “Speak softly and carry a big stick”. Use force when necessary to accomplish U.S. foreign policy goals. 3. Believed in America being an “international police power” to preserve peace and to protect American interests. Big Stick II. Teddy Roosevelt B. Great White Fleet 1. The Great White Fleet was the popular nickname for the United States Navy battle fleet that completed a circumnavigation of the globe 2. It consisted of 16 battleships divided into two squadrons, along with various escorts. II. Teddy Roosevelt C. Panama 1. Colombia ruled Panama and would not allow a canal to be built. 2. 1903 Roosevelt encouraged Panama to revolt and sent war ships to prevent Colombia from stopping the revolt. 3. Panama became independent and immediately signed a treaty allowing the U.S. to build the Panama Canal. America controlled the canal until 1999. Panama Canal III. William Howard Taft A. Foreign Issues 1. Dollar Diplomacy- Strong economic presence abroad would advance American interests. U.S. will encourage and protect American trade and investments. 2. Focused specifically on Latin America and Asia III. Woodrow Wilson A. Foreign Issues 1. Moral Diplomacy- The belief that the U.S. should use their power to aid the development of constitutional liberty in the world rather than for economic national interests or for a gain in power. III. Woodrow Wilson B. Mexico 1. The Mexican Revolution led to an unstable Mexico and gave power to a number of leaders including a military leader Victoriano Huerto 2. Wilson promoted a democratic leader and tried to stop Huerto from receiving weapons. A battle broke out leading to about 300 Mexicans dead. 3. Although Wilson thought he was trying to help Mexico, many Mexicans were upset III. Woodrow Wilson C. Puerto Rico 1. The U.S. set up infrastructure and developed Puerto Rico after the Spanish American War 2. Natives wanted to either become citizens of the U.S. or an independent country 3. President Wilson signed the Jones Act, making Puerto Ricans citizens but not giving them all rights. 4. There is still a debate on whether P.R. should remain a territory, become a state, or become independent Puerto Rico