CH 9 Vocab and Intro
advertisement

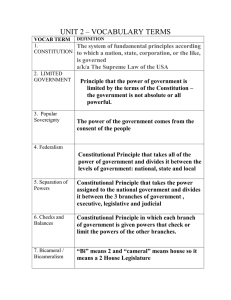
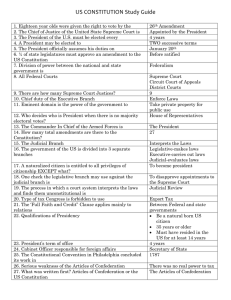
Chapter 9 Key Content Terms and Introduction Chapter 9 Key Content Terms • Popular Sovereignty: the principle that the authority of the government is created and sustained by the consent of its people, through their elected representatives (Rule by the People), who are the source of all political power. • The Legislative Branch Article I of the Constitution creates a bicameral Congress with a House of Representatives and a Senate. Every state is represented by two senators. Representation in the House is based on a state’s population. Congress’s primary job is to make laws. Chapter 9 Key Content Terms • The Executive Branch Article II creates the executive branch. The head of the executive branch is the president. The president serves a four-year term and may be reelected once. The president carries out laws passed by Congress. Other powers of the president include making treaties and appointing Supreme Court justices. • The Judicial Branch Article III establishes the Supreme Court and gives Congress the power to create lower courts. Supreme Court decisions are binding on all lower courts. The power of judicial review allows the Supreme Court to decide whether laws and actions by the legislative and executive branches are unconstitutional. Chapter 9 Key Content Terms • Judicial review : the doctrine under which legislative and executive actions are subject to review by the judiciary. A court with judicial review power may invalidate laws and decisions that are incompatible with a higher authority, such as the terms of a written constitution. • Checks and Balances The framers developed a system of checks and balances that enables each branch of government to limit, or check, the power of the other two branches. The Constitution provides checks and balances in the powers of each branch. • Interstate commerce: movement of goods or money, or transportation from one state to another, regulated by the federal government according to powers spelled out in Article I of the Constitution. Chapter 9 Key Content Terms • Federalism : a federal system of government in which power is shared between the national government and the states; a system based upon democratic rules and institutions in which the power to govern is shared between national and provincial/state governments, creating what is often called a federation. • majority rule: the principle that the greater number should exercise greater power; Laws are passed in Congress by majority vote. Elections are decided by a majority of voters. • Interest groups :The Constitution creates Popular Participation in Government Elections serve the vital function of expressing the will of the people. People also participate in government by joining political parties and taking part in interest groups. Chapter 9 Introduction • Read the Introduction on page 119 – as a class • Use the text and the images on the opposite page to address this question: “How does the Constitution create a more perfect union?” • Turn and talk with your neighbor and be prepared to share. To do… • Read Section 9.2 (pg 120) and finish the reading notes in your ISN (pg. 108) • Read Sections 9.3 – 9.6 (pgs. 121-126) and finish the reading notes in your ISN on pages 109 and 110. • This work is Due Wednesday at the beginning of the period!