salt marsh en.wikipedia.org
advertisement

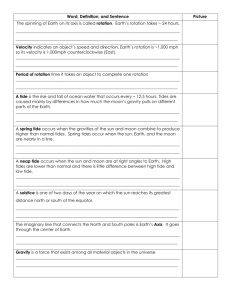
Salt marsh 鹽沼 en.wikipedia.org • The boundaries of the salt marsh roughly coincide with high spring tide and low spring tide • A salt marsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open salt water or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. Salt marsh • It is dominated by dense stands of salt-tolerant plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs.[1][2] These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh in trapping and binding sediments. • Salt marshes play a large role in the aquatic food web and the delivery of nutrients to coastal waters. They also support terrestrial animals and provide coastal protection Animation of spring and neap tides oceanservice.noaa.gov http://www.mmscrusaders.com/news cirocks/tides/tideanim.htm The bulge under the moon is produced due to gravity "stretching" the water, pulling it toward the moon. The bulge produced on the opposite side of the Earth is made because the moon tries to pull the Earth out from under the water! Tide 潮汐 • Together, the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun affect the Earth’s tides on a monthly basis. When the sun, moon, and Earth are in alignment (at the time of the new or full moon), the solar tide has an additive effect on the lunar tide, creating extra-high high tides, and very low, low tides — both commonly called spring tides. One week later, when the sun and moon are at right angles to each other, the solar tide partially cancels out the lunar tide and produces moderate tides known as neap tides. During each lunar month, two sets of spring and two sets of neap tides occur (Sumich, J.L., 1996). Tide潮汐 • When the moon is full or new, the gravitational pull of the moon and sun are combined. • At these times, the high tides are very high and the low tides are very low. http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_a_spring_tide aguahedionda.org http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_mar sh Rivers provide the salt marsh with a source of sediments沉積物 and nutrients.營養鹽 oceanclassrooms.com 濕地 鹽原 鹽沼 紅樹林 亞潮帶 ozcoasts.gov.au Effects of dredging 挖泥 1. Dredging results in the short term degradation of animals, vegetation and microbial communities that live in the dredged sediment. This reduces the estuary's capacity for nutrient cycling, primary production and habitat provision and can have flow on effects up the food web. Though these effects tend to be short lived, in some cases they may trigger long-term changes. 2. Changes in channel profile caused by dredging can increase tidal area, wave height and water velocity, resulting in bank erosion. Eroding banks threaten mangroves and other mud-bank communities and can lead to increased turbidity. Suspended sediment in the water column blocks light, reducing benthic primary productivity and inhibits the ability of benthic plants to recover from impacts of dredging. 3. Dredging exposes anaerobic layers of sediment, potentially disturbing and remobilising toxic sediments, releasing contaminants. This has implications for water quality. 4. Dredge spoil needs to be deposited somewhere, though this could be deemed habitat 2. Changes in channel profile caused by dredging can increase tidal area, wave height and water velocity, resulting in bank erosion. Eroding banks threaten mangroves and other Effects of dredging 挖泥 mud-bank communities and can lead to increased turbidity. Suspended sediment in the water column blocks light, reducing benthic primary productivity and inhibits the ability of benthic plants to recover from impacts of dredging. 3. Dredging exposes anaerobic layers of sediment, potentially disturbing and remobilising toxic sediments, releasing contaminants. This has implications for water quality. 4. Dredge spoil needs to be deposited somewhere, though this could be deemed habitat creation, it can smother existing habitats and frequently contains contaminants which often move and bioaccumulation through the food web. The impacts of dredge spoil disposal can range from short term to long term. 5. Changes to tidal range and wave action can result in mangrove encroachment into saltmarsh areas Food Webs in Specific Wetland Types. Salt Marsh kingfish.coastal.edu Supplimentory reading • http://kingfish.coastal.edu/biology/sgilman/7 78EcologyFoodWebs.htm • Producers: the marsh grasses, Spartina and Juncus mostly, plus various other salt tolerant plants as well as lots of algae Benthic Habitat Probably less than 10% of the above ground primary productivity in a saltmarsh actually gets grazed,. Most plant biomass dies and decays and is passed through the detrital food web where the major consumers are bacteria and fungi. These are then consumed by the smallest animals—worms, copepods, rotifers, larval stages of benthic invertebrates, in other words, plankton. The bigger benthic invertebrates are either scavengers (crabs, snails) or filterers (oysters, mussels). Reminder • 1. Ecology: a word comes from the Greek word oikos which means "home" and so ecology is the study of organisms with themselves, each other, and their habitat—their home. • 2. Population : a group of the same species living in the same place at the same time. • 3. Community: to all the organisms interacting with one another and sharing available resources within a defined area. Reminder • 4. An ecosystem: all communities in a particular area as well as all the abiotic factors affecting that area. • 5. Ecotones or ectones: Ecosystems sort of fade into one another as them meet. They are not sharply defined. These in-between zones are called ecotones or ectones. Salt marsh http://science.kennesaw.edu/~jdirnb er/oceanography/LecuturesOceanogr /LecSaltMarsh/LecSaltMarsh.html