Normal ECG: Rate and Rhythm
advertisement
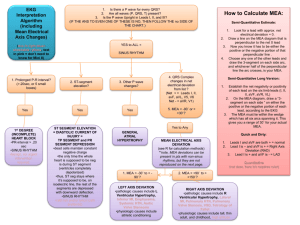
Normal ECG: Rate and Rhythm Read chapters 4 and 22 ECG Interpretation* Standardization Rate 1. RR interval 2. Heart rate Rhythm 3. PP interval 4. P wave width, height, shape, etc. 5. PR interval 6. QRS width (and height) *See Chapter 22 ECG Interpretation Univ. of Wisconsin Medical School • http://www.fammed.wisc.edu/pcc/ecg/ The Normal ECG Normal = normal sinus rhythm Rate 1. R-R interval Is it regular? 2. What is the heart rate? 300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50 300 / (# of large boxes) 1500 / (# of small boxes) Count the number of cardiac cycles in 10 seconds and multiple by 6. Rate Bradycardia less than 60 bpm Tachycardia greater than 100 bpm Rate 3. P-P interval Rhythm 4. P wave 5. PR interval 6. QRS 4. P Wave Lead II and aVR Positive in II Negative in aVR < 2.5 mm in amplitude < 0.12 sec. in width Normal P Wave Normal direction of atrial depolarization aVR? II? Figures 4-2 and 4-3 Abnormal P Wave Direction of atrial depolarization with junction rhythm This is an example of a retrograde conduction aVR? II? P wave The same direction as QRS Only one P wave in front of QRS Do all the P waves look alike? 5. PR interval 0.12 - 0.20 seconds 6. QRS Complex What is the width? (less than 0.10 seconds) Do all the QRS waves in the same lead look alike? R wave progression Axis Abnormal Q waves (infarction) QRS Complex Q waves Normal QRS Two phases brief phase; depolarization of ventricular septum longer phase; depolarization of both ventricles but the left is larger First Phase Depolarization of ventricular septum Second Phase Depolarization of both ventricles but the left is larger Precordial Leads V6 V1 Normal QRS V6? V6? V1? Fig. 4-6 V1? Normal QRS V1 V6 Normal QRS • Septal r wave • Septal q wave 6. QRS Complex R wave progression Normal R Wave Progression Transition Zone? R Wave Progression Transition Zone? Transition Zone Figure 4-7 Early & Delayed Transition V1 V2 V3 V4 • Figure 4-7 V5 V6 6. QRS Complex What is the electrical axis? normal left axis deviation right axis deviation extreme axis deviation 7. St Segment ST segment elevation or depression (see chapters 8 & 9) 8. T Wave Normally positive where QRS wave is positive V3- V6 and II, but negative in aVR Abnormally tall T waves Practice ECG Library http://www.ecglibrary.com/ecghome.html ECG: The Art of Interpretation http://www.12leadecg.com/full/ Normal Not normal PR interval Mobitz Type II block Not normal LAD, R wave progression RBB w/inferior MI Not normal First degree block, left atrial enlargement, left bundle branch block, & inferior MI Not normal Atrial fibrillation Normal Not normal Junctional rhythm Not normal LAD, late R wave progression Acute MI Not normal Premature ventricular contractions Not normal Ventricular tachycardia: note fast rate and wide bizarre QRS. Normal Not normal Second degree AV block - type II Not normal RAD, R wave progression Not normal Third degree AV block Not normal Right bundle branch block. Note the wide QRS waves Normal Not normal Left bundle branch block. Note the wide QRS waves a. yes b. vertical c. V3 d. yes e. yes f. yes 2. No. Although there are P waves, they are negative. negative P waves indicate a retrograde conduction likely coming from the AV junction.