Flower Structure - christophersonbiology
advertisement

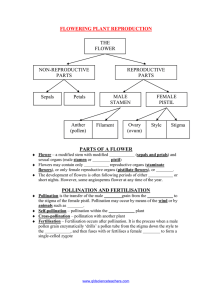
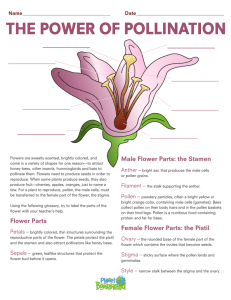
Wake-up Watch in presentation mode! 1. Explain the difference between a gymnosperm and an angiosperm. 1. List the four main groups of plants. Flower Structure There are several videos in these notes. Please watch them. I really think you will enjoy them!! If you are having trouble with the links, copy and paste the address in a different browser. What is a flower? Reproductive structure of Angiosperms (flowering plants) Pistil: Female Ovary: Eggs (Ovules) Petals: Stamen: Attract Pollinators Male Locule: Chamber of Eggs Sepals: First leaves on bud Stigma: Sticky to attract pollen Pistil: Female Style: “Neck” of the Pistil Ovary Eggs/Ovules Anther: Contains Pollen (Sperm) Stamen: Male Filament: Anther Stalk What is pollination? Transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma of a plant Type of Pollination: Self Pollination Plant fertilizes it own eggs Type of Pollination: Cross Pollination Pollen from one flower fertilizes the egg of another Methods of Cross Pollination 1. Wind: Plant produce lightweight pollen in great numbers with the hopes of landing on another plant of its kind Video LINK #1 Select “Yellow Pollen Coats State” Video Video LINK #2 Methods of Cross Pollination 2. Animals: Flowers have bright petals, nectar, and a sweet smell to attract animals. Pollen gets dropped off on animal and they carry to another plant Mutualistic Coevolution Plants and animals have changed (evolved) together over time to create a relationship that is completely depend on each other Example #1 Video LINK Plant: Corpse flower (Titan Arum) Animal: Flies Flies are attracted to the corpse flower because it smells like rotten meat; pick up the pollen Example #2 Video LINK #1 Video: Planet Earth Desert (23:50) Plant: Flowers Animal: Bats The Batsflower are attracted drops its pollen to theonlarge, the bat which strongcarries smelling it to another flowers flower Example #3 Plant: Flowers Animal: Bees Flowers provide bees with nectar and pollen, both of which are a food source. Example #3 LINK #1 LINK #2 Plant: Flowers Animal: Bees In turn the bee helps carry the flowers pollen to other flowers; bees are covered in tiny hairs Video Clip: Beauty of Pollination When complete with notes, get the Flower Structure Coloring Activity from the substitute and grab a plastic container with markers and colored pencils. With the time left in class, complete this activity. You need to color, label, and answer the questions. If you complete this activity, turn it into the bin and find something else to work on. If not, this is homework tonight.