Animal Life Cycles
advertisement

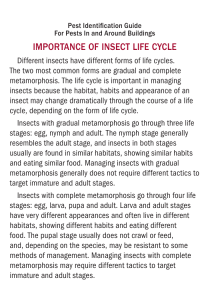
Unit 4, Lesson 6 A series of distinct growth stages in an animal’s life cycle that are different from one another. A series of four distinct growth stages in an animal’s life cycle. Egg, larva, pupa, adult An immature stage in complete metamorphosis where the organism does not resemble the adult A non-feeding stage in complete metamorphosis in which a hard, case-like cocoon surround the organism A series of three growth stages that occur gradually Egg, nymph, adult A stage of metamorphosis where the organism is similar to an adult form but is smaller Larva The organism gets bigger but keeps the same basic shape and form Complete metamorphosis has 4 distinct stages, while the incomplete metamorphosis has only 3 distinct stages. Most tadpoles are herbivores, or plant eaters Frog eggs are laid in the water. If tadpoles hatched with lungs rather than gills, they would not be able to breathe. Tadpoles are completely aquatic for the first part of their lives It moves onto land Breathes air Begins meat eating diet The shell keeps the embryo from drying out. The yolk provides food for the developing embryo. It is protected by a jellylike layer that surrounds the egg Butterflies Moths Flies Beetles Grasshoppers Termites Bedbugs In incomplete metamorphosis, the nymph stage is the same as the larva stage in a complete metamorphosis, and the pupa stage is skipped. Grasshoppers have an exoskeleton Amphibians go through metamorphosis, but other vertebrate do not. Animals have different eggs depending on their structures and the environments in which they live. Monotremes are the only mammals that lay eggs.