Neonatal Chest Compression Device
advertisement

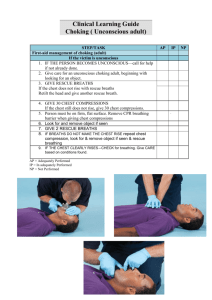
Neonatal Chest Compression Device Courtney Gallagher Jillian Zeber Advisor: Dr. Walsh, Vanderbilt NICU Problem Statement • When performed in conjunction with operations of the neck and lower abdomen, there is limited space for manual chest compressions. • Manual chest compressions require both hands to be wrapped around the chest. • 2 occurrences at the Vanderbilt NICU this past year. Project Goal • Small, easy to setup device that will perform automatic chest compressions on a 0-30 day old infant for use in the OR during a simultaneous procedure. Performance Criteria • Small but adjustable to fit the size of the baby. • Provide enough force for sufficient chest compressions to reduce the width to one third, 2 to 3 cm. • Apply the 11-12 lbs of force directly below the nipples in the center of the chest. • Verified with bathroom scale and free weights. • Maintain a rate of 80-100 compressions per minute for blood pumping. • Simple and easy to use by Dr. Walsh in the NICU Force Required for Chest Compressions Applied Force (lbs) Adequate Compression 11.1 Yes 11.6 Yes 12.3 Yes 13.1 Yes 14.7 Yes 18 Yes 10.8 No 10.1 No 9.9 No Desired Force Range: 11 – 12 lbs Solution Proposal Solenoid Valve Electronic Timer Power Supply 15 cm 2-3 cm 6-9 cm Adjustable depending on size of the baby Solution Proposal Solenoid Valve Electronic Timer Power Supply 15 cm 5 cm 4-6 cm Adjustable depending on size of the baby Solution Proposal Exhaust 3- WAY Air Cylinder Air Compressor Device Components • Single-acting spring return pneumatic cylinder • Air compressor with coil hose • Solenoid valve controlled by electronic timer • On/off time range: 0.1 s to 99 hr • Power supply: wall outlet • 1.1 inch diameter plunger to displace chest 2-3 cm • Wheel-up cart supporting electronic components & air compressor • Support structure: • Currently: stand with base and adjustable arm • Ideally: Swivel arm connected to side panel of GE OmniBed Calculations Air Cylinder Specs Timer Settings • Bore size: F = p A = p π d2/4 where F = force exerted (N) p = gauge pressure (N/m2, Pa) A = full bore area (m2) d = full bore piston diameter (m) F = 11 lbs = 50 N p = 100 psi = 689.5 kPa d = 10 mm ≈ 7/16” • Stroke length: > 3 cm with extra space 5 cm ≈ 2” • On/Off time: Cycle Length = 1/Cycle Freqency On/Off time = Cycle Length/2 80/min 90/min 100/min Cycle Frequency (s-1) 1.333 1.50 1.667 Cycle Length (s) 0.750 0.667 0.600 On/Off time (s) 0.375 0.335 0.300 Factors • • • • • • • Provide necessary but not excessive force (11-12 lbs = 5 kg) Materials that can be sterilized Comfortable Quick setup Potentially portable Safety Adjustable Implementation of Factors into Design • Sterilizing plunger and stopper with plastic drapes • Dr. Walsh • Vary force applied with the psi of compressed air applied to cylinder • Variable rate with micro-timer • Adjustable with flexible arm coming out of NICU bed Evaluation • Isabel in the NICU Simulation Lab • Responds like an alive baby • Provides vitals • Can determine if chest compression are adequate Previous Work • Researched existing adult compression devices • AutoPulse, Lucas, Thumper • Established goals and criteria that must be met • Discussed with advisors • Measured force required to provide chest compressions • Decided on a prototype design • Pneumatic cylinder • Researched and purchased materials to build prototype • Pneumatic cylinder and Air compressor • Solenoid valve, timer • All necessary connections • Tested simplified version of prototype • Verified applied force was correct • Ordered more parts Current Work • Finishing DesignSafe • Getting in touch with GE contact • Kent Meeks • Building complete version of prototype • Testing full prototype Future Work • After testing, make modifications and re-test • Build flexible arm • Test • Make Demo • Evaluate effectiveness against traditional method References • http://www.zoll.com/medical-products/cardiac-supportpump/autopulse/ • http://content.onlinejacc.org/cgi/content/full/44/11/2214/FIG2 • http://www.omega.com/auto/pdf/SimpValvesguide.pdf • http://www.gehealthcare.com/euen/maternal-infantcare/products/microenvironments/giraffe_omnibed/index.html • http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/pneumatic-cylinder-forced_1273.html