Propaganda - eNetLearning
advertisement

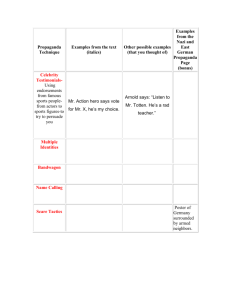
P ROPAGANDA , RHETORICAL DEVICES, AND P ERSUASIVE S PEECH P ROPAGANDA The spreading of ideas or information with the intent of influencing others. Commonly used in advertising or media. Known for stretching the truth for the speaker’s own purpose. Done through WORD GAMES and SPECIAL APPEALS Effective when the audience doesn’t examine the evidence. R EPETITION Building recognition of the product, person, or idea by constantly repeating key ideas. In order to be effective, it must be short and easy to remember. G LITTERING G ENERALITIES Reverse Name-Calling Linking the idea with a positive symbol or word. The speaker hopes the audience will associate the positive symbol or word with their idea. E UPHEMISMS Making an unpleasant reality seem more pleasant by using bland or unloaded words. “Shell shock” vs. “Post-traumatic Stress Disorder” “Politically Correct” B ANDWAGON Everyone else is doing it…. Plays on the idea that no one wants to be left out. P LAIN F OLKS Convincing the audience the idea is “of the people” The idea will benefit the average person, not just the elite or underprivileged. N AME C ALLING Links a person or idea to a negative symbol The speaker hopes the audience will associate the negativity with the person or idea and therefore come to dislike the idea or person. F EAR Can be positive or negative Playing on the audience’s fear of the consequences of doing or not doing a particular act. R HETORICAL Q UESTION Questions with obvious answers that are meant to provoke thought in the audience. Questions that aren’t meant to be answered. Examples: How far must we go to create peace? Teacher: Do I really want you getting up to sharpen your pencil now instead of listening to the directions? S ATIRE A literary work that ridicules the foolishness and faults of individuals, an institution, society, or even humanity in general. R EPETITION The use of any element of language more than once Elements of language include: Sound Word Phrase Clause Sentence Poetical devices A LLEGORY A story or tale with two or more levels of meaning – a literal level and one or more symbolic levels. Literal level – what is actually happening in the story Symbolic level – what the story and/or characters symbolize from real life. A LLUSION Reference to a well-known person, place, event, literary work, or work of art. Example: “But it was a time of vague optimism for some of the people: Maycomb County had recently been told it had nothing to fear but fear itself,” (Lee 6). Reference to Franklin D. Roosevelt’s inaugural speech. M ETAPHOR An analogy that compares two unlike things by saying they are the same thing. Examples: School is a prison. The clouds are marshmallows in the sky. A LLITERATION Repetition of initial consonant sounds. Used to give emphasis to words, imitate sounds, and create musical effects. Example: The ridiculously rabid rodent bit the child. P ROPAGANDA A SSIGNMENT Now it’s your turn to create a piece of your own propaganda. You have just been hired by Propaganda Inc. to create advertisements for their main products. You need to create an advertisement that portrays one of the types of propaganda we have discussed. You will need a visual which can be in the form a poster or you can act it out with your group. You will also need a paragraph explaining the type of propaganda you use. Things you will need to include in your paragraph: what type of propaganda your advertisement is, a description of the advertisement itself, and why the propaganda will work on the general public.