Criminal Law and Procedure
advertisement

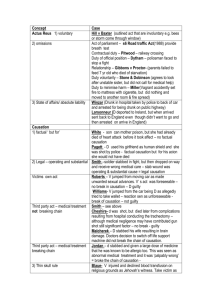
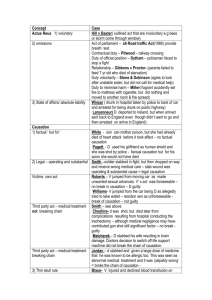
LSS Tutorial Program: Criminal Law and Procedure Revision Seminar Felicity Fox General Exam Advice Worth 60 marks Part A: 40 Marks 1 x 30 mark question 1 x 10 mark question Part B: 20 marks (second reading speech) 2 minutes = 1 mark General Exam Advice Use headings Refer to cases Apply the facts Speak to the alternative Guide the examiner through your train of thought How to answer a problem question generally Issue Relevant Law Application to facts Conclusion How to study for exams Past exams http://exams.lib.monash.edu.au/ Make your notes, and then your exam notes … and then your short exam notes … and the your exam script … Go through problems with friends Go through tutorial booklet problems Basic outline for Homicide Question Introduction Actus Reus Voluntariness Causation Mens Rea Defences Conclusion Basic outline for Manslaughter Introuction UDA MS; or Negligent Manslaughter; or Manslaughter by Omission Defences Basic outline: Common Law Assault Introduction Actus Voluntary & Positive Act Apprehension of Imminent Force Mens Reus Rea Intention/Recklessness Basic Outline: Statutory Assault Introduction (what is the section?) AR Will be defined by the particular words of section Mens rea Will be defined by the particular words of section Defences Murder: Introduction Introduction Murder is a common law offence punished at s3 of the CA Sir Edward Coke Murder: Actus Reus Voluntariness Presumption of voluntariness (R v Falconer) Intoxication? (R v O’Connor) Causation Operating and Substantial Cause? (R v Hallet) Was there an NAI? Contributory acts by a third party? (R v Pagett) Medical treatment? (R v Evans & Gardiner (no 2) Flight and self preservation? (Royall v R) Murder: Mens Rea Intention to kill? Intention to cause GBH? DPP v Smith Recklessness R v Crabb as to kill/to cause GBH Murder: Mens Rea Transferred malice (Saunders and Archer) Constructive murder? ‘in the course of furtherance of a crime the necessary elements of which include violence (s3A Crimes Act) R v Butcher R v Ryan & Walker R v Galas Murder: Mens Rea Mental MR? state defenses are relevant to Intoxication? (R v O’Connor) Manslaughter: Introduction Manslaughter is a common law offence and is charged under s5 of the Crimes Act Manslaughter: UDA MS Prosecution need to prove 3 things: 1. The act causing death must be unlawful (R v Franklin) 2. Causation: act must have caused death (refer to discussion of causation above) 3. The Act must be objectively dangerous (Wilson v R) Fault element: accused intended to commit the relevant act (R v Williamson) Manslaughter: Negligent Manslaughter Test in Nydam: “was there such a great falling short of the standard of care which a reasonable man would have exercised and which involved such a high risk that death or serious bodily harm would follow?” Manslaughter: Negligent Manslaughter 1. 2. 3. Is there a duty of care owed by the accused to the victim? If so, what is the standard of care required? Has there been a gross departure from the standard of care that constitutes criminal negligence? Manslaughter: Manslaughter by Omission 1. Was there a legal duty? R v Instan R v stone & Dobson R v Miller R v Tak Tak Defences: Self Defence Non fatal offences In Victoria, the defence of self-defence is found at common law The accused bears only an evidential burden; the Crown must disprove selfdefence beyond reasonable doubt Zecevic: Did the accused believe, on reasonable grounds that it was necessary in selfdefence to do what he or she in fact did? Defences: Self Defence Non Fatal Offences Subjective Test: In applying the subjective test, all of the personal circumstances of the accused are potentially relevant It is how the DEFENDANT saw the situation Objective test: ‘It is the belief of the accused, based upon the circumstances as the accused perceived them to be, which has no be reasonable, and not that of the hypothetical reasonable person in the position of the accused’ Defences: Self Defence Accused’s mental state Verdict Honest belief on reasonable grounds Acquittal Honest belief, not based on reasonable grounds Defensive Homicide No honest belief Murder Defences: Self Defence Murder Accused bears evidential burden, Crown must disprove self defence: BRD Subjective Test – s9AC Reasonable Grounds – s9AD Self Defence: Defensive Homicide s9AD A person who, by his or her conduct, kills another person in circumstances that, but for section 9AC, would constitute murder, is guilty of an indictable offence (defensive homicide) nad liable to level 3 imprisonment if he or she did not have reasonable grounds for the belief referred to in that section Defences: Family Violence s9AH Family Violence in relation to a person, means violence against that person by a family member (s9AH(4)) Violence includes physical, sexual and/or psychological abuse (s9AH(4) Violence may include a single act, or a series of acts even though some or all of those acts, when viewed in isolation, may appear to be minor or trivial (s9AH(5)) Defences: Self Defence Manslaughter s9AE Subjective test Objective Tes Defences: Necessity & Duress R v Dudley and Stephens Defences: Intoxication (SD) Relevant to MR & AR as discussed above s9AJ Reasonable belief Reasonable grounds for a belief Reasonable response Must be taken as a sober person, unless that intoxication was not self-induced Defences: Consent R v Brown Exceptions: Tattooing & branding: R v wilson Surgery Boxing Female genital mutilation Male circumcision Statutory homicide Defensive Homicide: s 9AD Culpable driving causing death: s.318 Dangerous driving causing death s319 Suicide pact: ss.6A, 6B, 463B (prevention of suicide) Abortion: s.65&66; Infanticide: s.6 Common Law Assault “An assault is any act which intentionally – or possibly recklessly causes another person to apprehend immediate and unlawful person violence” (Fagan) Common Law Assault AR Voluntary & positive act Omissions not sufficient Fagan Mere words may be enough R v Ireland, R v Knight Apprehension of imminent Force Must have actual knowledge Pemble v R Future violence Zanker v Vartzokas Condition threat will be an assault unless D has right to impose that condition Rosza v Samuels Apprehension Barton v Armstrong Fear Ryan v Kuhl Statutory Assault Offence Section Actus Reus Mens Rea Threats to kill S20 • Voluntary & positive Act • Threats o kill • Intention that V will fear threat will be carried out (20(a)) • Recklessness as to V threat will be carried out Threats to inflict serious injury S21 • Voluntary & • Intention that V positive act will fear threat • Threats to inflict will be carried serious injury out (s20(1)) (as per s15 – • Recklessness as combination of to V threat will injuries) be carried out Offence Section Actus Reus S16 • Voluntary and Statutory Assault positive act Intentionally causing serious injury Mens Rea • Intention • Causation/dir ectness • Serious injury Recklessly causing serious injury S17 • Voluntary & positive act • Causation/dir ectness • Serious injury • Recklessness Causing Injury Intentionally/rec klessly S18 • Voluntary & positive Act • Causation/dir ectness • Injury * Intention/reckles sness