Supplementary information S1 (animation) -
advertisement

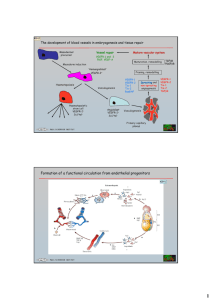
Supplementary information S1 (animation) Proposed role of syndecan-1 in the regulation of αVβ3 integrin- and VEGF-dependent angiogenesis. This interactive figure allows the user to navigate around the complex body of in vivo and in vitro data that relates to the functional interplay between αVβ3 integrin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR2) in the regulation of pathological angiogenesis. The figure specifically highlights how potentially syndecan-1 may differentially regulate the αvβ3 integrin and VEGF–VEGFR signalling network (green boxes/arrow). The downstream effects of perturbing β3 integrin-dependent functions can be seen by clicking on the purple buttons to the left of the page, or on the β3 integrin functions in the top row of the figure. Users can return to the base model by clicking the red ‘Home’ button or by re-clicking on the disrupted β3 integrin function. The potential role of syndecan-1 in regulating these processes can be viewed by clicking the green button. References are included throughout the slide show. Perturbing αvβ3 integrin function in vivo can have remarkably different effects on pathological angiogenesis, depending on the nature of the perturbation and the cell type that is expressing the integrin (tumour (red) or host/endothelial (blue)). β3 integrin-deficient mice exhibit enhanced pathological angiogenesis as a consequence of increased VEGFR2 expression and signalling. Perturbation of tumour-cell αvβ3 integrin activation reduces pathological angiogenesis and tumour growth by suppressing VEGF secretion. Endothelial cell β3 integrin phosphorylation is required for VEGF-stimulated, VEGFR2-phosphorylation-dependent, pathological angiogenesis. Cross-activation of αVβ3 integrin and VEGFR2 is required for the formation of the αVβ3 integrin–VEGFR2 complex and endothelial cell migration. Inhibition of αVβ3 integrin engagement induces caspase-8-dependent apoptosis of angiogenic vessels and reduces tumour growth. In vitro studies suggest that syndecan-1, through the regulation of integrin activation and growth-factor presentation, could possibly modulate this β3 integrin–VEGF–VEGFR2 signalling network at various points. Start The avb3-integrin-VEGF/VEGFR Signalling Network Home Potential Syndecan-1 Function b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Activation b3 Signalling avb3 Engagement VEGF Secretion b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 Normal Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis avb3 Antagonism Pathological Angiogenesis References Boxes/Arrows: The functional interplay between αvβ3-integrin, VEGF and VEGFR2 in the regulation of pathological angiogenesis; highlighting how potentially syndecan-1 may regulate this signalling network (green boxes/arrows) Functional regulation Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated Potential Syndecan-1 Function Soluble Syndecan-1 Ectodomain 1 Shedding Home 1 Syndecan-1 Potential Syndecan-1 Function 1 b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 b3 Activation VEGF Secretion Normal Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression 1 VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement 1 b3 Signalling avb3 Engagement 2, 3 2, 3 b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 avb3 Antagonism References Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis Pathological Angiogenesis Boxes/Arrows: Functional regulation In vitro studies suggest that syndecan-1, through regulation of integrin activation and growth factor presentation, could possibly modulate the β3-integrin-VEGF/VEGFR2 signalling network Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated Integrin b3- or b3/b5-Deficient Mice Home b3 or b3/b5 /- mice 4, 5 Potential Syndecan-1 Function b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Activation b3 Signalling avb3 Engagement VEGF Secretion b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression & Signalling b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis avb3 Antagonism Pathological Angiogenesis References Boxes/Arrows: Functional regulation β3-integrin-deficient mice exhibit enhanced pathological angiogenesis as a consequence of increased VEGFR2 expression and signalling Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated Tumour Cell Expression of Inactivatable-b3 Inactivatable b3 expression Home 6 Potential Syndecan-1 Function b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Activation b3 Signalling avb3 Engagement VEGF Secretion b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 Normal Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis avb3 Antagonism Pathological Angiogenesis References Boxes/Arrows: Functional regulation Perturbation of tumour cell αvβ3-integrin activation reduces pathological angiogenesis and tumour growth by suppressing VEGF secretion Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated Phospho-null-b3 Expression Phosphoincompetent b3 Home 7 Potential Syndecan-1 Function b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Activation b3 Signalling VEGF Secretion 8 avb3 Engagement 7 b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 Normal Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis avb3 Antagonism Pathological Angiogenesis References Endothelial β3-integrin phosphorylation is required for VEGFstimulated, VEGFR2-phosphorylation dependent, pathological angiogenesis. Cross-activation of αVβ3-integrin and VEGFR2 is required for the formation of the αVβ3-integrin–VEGFR2 complex and endothelial cell migration. Boxes/Arrows: Functional regulation Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated avb3 Antagonism avb3 antagonism Home 9, 10 Potential Syndecan-1 Function b3 or b3/b5 Expression b3 Activation b3 Signalling avb3 Engagement VEGF Secretion b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 Normal Endothelial VEGFR2 Expression b3-VEGFR2 Complex Formation VEGFVEGFR2 Engagement Caspase-8 Activation VEGFR2 Phosphorylation Phospho-null b3 Endothelial Cell Migration Endothelial Cell Apoptosis avb3 Antagonism Pathological Angiogenesis References Boxes/Arrows: Functional regulation Inhibition of αVβ3-integrin engagement induces caspase-8dependent apoptosis of angiogenic vessels and reduces tumour growth Syndecan-1-regulated Potentially Syndecan-1-regulated Reference List Home 1. Beauvais, D. M., Burbach, B. J. & Rapraeger, A. C. The syndecan-1 ectodomain regulates alphavbeta3 integrin activity in human mammary carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 167, 171-81 (2004). Potential Syndecan-1 Function 2. Fuster, M. M. et al. Genetic alteration of endothelial heparan sulfate selectively inhibits tumor angiogenesis. J Cell Biol 177, 539-49 (2007). 3. Subramanian, S. V., Fitzgerald, M. L. & Bernfield, M. Regulated shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 ectodomains by thrombin and growth factor receptor activation. J Biol Chem 272, 14713-20 (1997). b3 Knock-out Inactive b3 4. Reynolds, L. E. et al. Enhanced pathological angiogenesis in mice lacking beta3 integrin or beta3 and beta5 integrins. Nat Med 8, 27-34 (2002). 5. Reynolds, A. R. et al. Elevated Flk1 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) signaling mediates enhanced angiogenesis in beta3-integrin-deficient mice. Cancer Res 64, 8643-50 (2004). 6. De, S. et al. VEGF-integrin interplay controls tumor growth and vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 7589-94 (2005). Phospho-null b3 7. Mahabeleshwar, G. H., Feng, W., Phillips, D. R. & Byzova, T. V. Integrin signaling is critical for pathological angiogenesis. J Exp Med 203, 2495-507 (2006). 8. Mahabeleshwar, G. H., Feng, W., Reddy, K., Plow, E. F. & Byzova, T. V. Mechanisms of Integrin-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Cross-Activation in Angiogenesis. Circ Res (2007). avb3 Antagonism References 9. Brooks, P. C. et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79, 1157-64 (1994). 10. Stupack, D. G., Puente, X. S., Boutsaboualoy, S., Storgard, C. M. & Cheresh, D. A. Apoptosis of adherent cells by recruitment of caspase-8 to unligated integrins. J Cell Biol 155, 459-70 (2001).