Respiratory system
advertisement

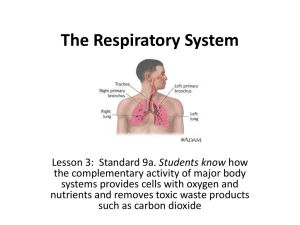
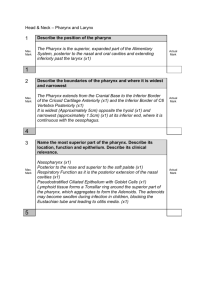
Respiratory system CH. 37.3 VIDEO CLIP HTTP://WWW.YOUTUBE.COM/WATCH?V=O2OCGGJBIUK Function exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood, the air. Respiration Cellular level Organism level the release of energy: from the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen. gas exchange: The respiratory system consists of nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs pollen Air entering the respiratory system must be: warmed, moistened, and filtered. Mucus moistens air and traps particles of dust or smoke. dust Cilia sweep particles and mucus to the throat. mucus Mucus and particles are either swallowed or spit out. Smog Pollution Coal Asbestos Pharynx vs. Larynx The Pharynx 1st serves as a passageway for both air and food. The Larynx It is at the top of the trachea. contains two elastic folds of tissue: vocal cords. The epiglottis: C O V E R S T H E E N T R A N C E TO T H E T R A C H E A W H E N Y O U S WA L L O W. Don’t speak: while you are eating!!! Why chocking http://auditoryneuroscience.com/?q=vocal_folds Vocal cords V I D E H T T P : / / W W W . Y O U T U B E . C O M / W AT C H ? V = X S S D E E Y _ 0 X C The 2 Bronchi (bronchus singular) • TWO LARGE AIR PA S S A G E S • E A C H L E A D S I N TO ONE OF THE LUNGS • SUBDIVIDE= BRANCH INTO BRONCHIOLES Purpose of branching? INCREASE SURFACE AREA • A P P R O X I M AT E LY A T E N N I S C O U R T S U R FA C E A R E A Functional units of the lungs Alveolus MILLIONS OF TINY AIR SACS AT THE END OF THE BRONCHIOLES IS WHERE THE GAS EXCHANGE TAKES PLACE O2 from the alveoli diffuses into the blood CO2 in the blood diffuses into the alveolus. O2 CO2 Respiratory and circulatory systems work together Hemoglobin Protein present in red blood cells It has Fe (iron) heme part that binds to O2 What is the diaphragm? F L AT M U S C L E T H AT S E PA R AT E S T H E A B D O M I N A L C AV I T Y FROM T H E T H O R A C I C C AV I T Y. H T T P : / / W W W . Y O U T U B E . C O M / W AT C H ? V = H P - GC V W 8 P RY Breathing The movement of air into and out of the lungs. Is driven by air pressure: ∆ the diaphragm contracts ∆ This expands the volume of the chest cavity. ∆ Creating a partial vacuum inside the cavity. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hHQ BFFu2ekw The medulla oblongata Controls breathing Monitors carbon dioxide in the blood. As carbon dioxide increases, nerve impulses make the diaphragm contract, bringing air into the lungs. The higher the carbon dioxide level, the stronger the impulses. Emphysema is most often caused by smoking and long-term exposure to air pollution. Lung tissue looses elasticity alveoli are unable to hold their functional shape upon exhalation. Lung cancer Lung cancer is deadly because its cells can spread to other locations.