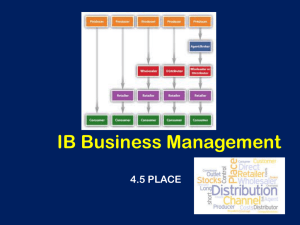
Chain of Productions and Channels of Distribution
advertisement

Chain of Productions and Channels of Distribution We will look at: • Revision of Chain of Production • Samples of Chain of Production • Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Activities • Channels of Distribution and samples • Wholesalers/Retailers Questions to consider • Definition of Chain of Production/ Channels of Distribution • List out sample chains and channels • Differentiate Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Activities • Explain wholesalers/ retailers/ cash and carry Chain of Production Taken from Economics chapter Production means combining these resources to produce goods/services that customers want Chain of Production and Channels of Distribution Think about the steps involved in providing consumers with the following: 1. Baker selling bread. 2. A kitchen table and chairs. 3. Cakes. The Chain of Production • The chain of production refers to the various production or processing stages that a good or service goes through before it is sold. For Bread: 1. Wheat-2. Millers for flour-3. Baker-4. Transport-5. Customer The Three Sectors of the Economy From this we can identify 3 distinct sectors involved in the manufacturing and distribution of products. • The Primary Sector (Raw Materials from land/sea) • The Secondary Sector (Manufacturing/ Construction) • The Tertiary Sector (Services Providers) The Primary Sector • Primary producers take materials from the land or sea or use the land or sea to make a product. • The main industries involved in primary production are: • Agriculture • Forestry • Fishing • Mining • Oil Production. Secondary Producers • These manufacture and process the raw materials supplied by the primary producers. • Some examples would be: • • • • The Building Industry Technological and Pharmaceutical Firms Food Processing Clothing Tertiary Producers • They do not make the products. Instead they supply services that businesses need to operate successfully. • Examples include: • • • • Insurance Banking Doctors Solicitors Exercise: List the following into three columns to show which are primary, which are secondary, and which are tertiary Insurance Companies Bakeries Agriculture Doctors Packaging Firms Forestry Furniture Firms Clothing Firms Banks Oil producers Pharmaceutical Firms Advertising Industries Mining Fishing Solicitors Primary Secondary Tertiary The Channels of Distribution Channels of distribution are the methods used to transfer finished goods from manufacturers to consumers. Common examples are: 1 Manufacturer wholesaler 2 Manufacturer 3 Manufacturer retailer consumer retailer consumer consumer R. Delaney 12 Examples of Channels of Distribution Tailor Made Prodcuts Producer Consumer Books Producer Manufacturer Retailer Consumer Wholesaling • A wholesaler is a company or person that buys large quantities of goods from many manufacturers and sells them in smaller quantities to retailers. E.G. A school may need large stocks of paper, which it purchases directly through the wholesaler in order to receive a discount 17 Cash and Carry Wholesalers • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 18 Cash and carry wholesalers act as supermarkets to retailers. Consumers are not permitted to shop in them. E.g. Musgraves. They differ from the traditional wholesaler because: They do not give credit. They do not deliver goods. They operate on a self-service basis. They provide ample parking space for retailers. Their prices tend to be lower than traditional wholesalers. R. Delaney Functions of a retailer • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 19 A retailer is somebody (or an outlet) who sells finished goods to consumers. E.g.Tesco, Johnny Ryan’s, Elvery’s. • Functions of a retailer: Provides a wide range of goods to consumers in one place Sells goods to consumers in small quantities Offers advice to consumers on products they may need Informs manufacturers of changing consumer trends Creates a demand for goods by advertising Arranges finance for consumers for expensive goods May accept “trade-ins” to make it easier for consumers to buy new goods R. Delaney Wholesaler aids retailer Role played by wholesaler Benefit to retailer Provides a wide range of goods Retailers need deal with only a small number of wholesalers rather than many manufacturers Sells goods in small quantities Retailers do not have to store large quantities of goods Delivers goods Reduces retailer’s transport costs and saves retailer’s time Provides credit facilities Retailers may be able to sell all their stock before payment is due Provides information about new products coming onto the market 20 Prevents retailers over-stocking goods that may be going out of fashion R. Delaney Wholesaler aids manufacturer Role played by wholesaler Benefit to manufacturer Buys very large quantities Manufacturers have a small number of customers, which reduces their overhead costs Stores the goods Manufacturers are saved the warehousing costs Promotes the goods to retailers and consumers Reduces the manufacturer’s advertising costs Pays promptly for goods Gives the manufacturer working capital for current expenditure Provides the manufacturer with information from retailers regarding consumer trends 21 Prevents the manufacturers from making goods that may be going out of fashion R. Delaney List a possible channel of distribution for the following • • • • Cereal A Tailored Suit Tickets to see a gig in the O2 New Audi