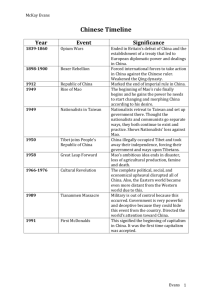
2014 East Asia Unit Study Guide Answer each question on a
advertisement

2014 East Asia Unit Study Guide Answer each question on a separate piece of paper. It may be as long as you would like. IT MUST BE TYPED UP. IT CANNOT BE HANDWRITTEN FOR THE FINAL DUE TO LIMITED GRADING TIME. IT MUST BE IN YOUR OWN WORDS AND NOT CUT AND PASTED FROM THE POWERPOINTS! The questions should be numbered as they appear on the study guide. When you answer the questions, you should do it in outline, chart, or use bullet form. Writing in paragraph form is not user-friendly and takes up too much time and makes it harder to use on the test. If you complete the study guide fully, you can earn up to TEN points extra credit added to the first unit test score and TEN points extra credit added to the final exam score. You may use your completed East Asia Unit Study Guide on the final exam. Geography of China Lesson: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. What are the population demographics for China? How are these geographic traits a positive for China with examples? How are these geographic traits a negative for China with examples? What are the climate and vegetation characteristics of China? How do they relate to farming and other agricultural issues with examples? What are the main rivers of China and their key characteristics? How does China use each? What are some of the issues with the rivers of China with examples? What are the main characteristics of the plains of China? How does China use them? What are some current issues China is facing with them? What are the main mountain ranges of China? How have they affected the history and development of China with examples? What are the main plateaus of China? What are the main characteristics of the plateaus? What is the Great Wall of China? 5Ws, How, and Importance of the Great Wall? What are the main deserts of China? What are the main characteristics of the deserts? Why is desertification an issue for China and how is the country responding to the issue? What natural resources is China rich with? How have these resources helped their economic development with examples? How have these resources created environmental problems with examples? China is facing several environmental problems. Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth a minimum of THREE different problems. China has built the largest dam in the world. But this dam is also very controversial. Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth as minimum of THREE POSITIVES and THREE NEGATIVES. Geography of Japan Lesson: 1. How is the size and the physical features of Japan affected population density and ways of life? 2. What are the main islands of Japan and the key characteristics of each? 3. What are the main mountains of Japan? How have they affected Japan’s development and history? 4. Where are the plains of Japan? What are their main characteristics? 5. What are the main climate regions of Japan? How do they compare to the United States? 6. What raw materials and natural resources does Japan possess and how are they utilized? How are they also an issue for Japan? 7. Japan has to contend with volcanoes, earthquakes, and the threat of a tsunami. What happened in 2011 and how did it affect Japan and the world? Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth a minimum of THREE EFFECTS. Religions and Philosophies of East Asia Lesson: 1. Confucianism: Main Beliefs and Practices? Founder and History? Impact on East Asian History? 2. Daoism: Main Beliefs and Practices? Founder and History? Impact on East Asian History? 3. Legalism: Main Beliefs and Practices? Founder and History? Impact on East Asian History? 4. Shintoism: Main Beliefs and Practices? Founder and History? Impact on East Asian History? 5. What is Yin and Yang? How does it relate to the other philosophies? 6. Be able to compare and contrast the religions/philosophies of Confucianism, Daoism, and Shintoism. First East Asia Unit Test: China and Imperialism Lesson: 1. What were the weaknesses of the Qing Dynasty that left if vulnerable to European Imperialism? 2. How was the Opium Trade used under European Imperialism and what were the effects of the trade, wars, etc for Europe and China? 3. What was the Taiping Rebellion? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the Taiping Rebellion? 4. What was the Self-Strengthening Movement? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the movement? 5. What were Spheres of Influence? How did they develop in China? What impact did they have? 6. What was the First Sino-Japanese War? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the war? 7. What was the Open Door Policy? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the policy? 8. What were the Hundred Days Reforms? What were the causes, main events, and effects of these reforms? 9. What was the Boxer Rebellion? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the rebellion? 10. How did European Imperialism give rise to Chinese nationalism and Sun Yat-Sen? 11. Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth the reasons for European Imperialism in China and THREE DIFFERENT WAYS this was carried out. Japan and Imperialism Lesson: 1. What were the weaknesses of the Tokugawa Shogunate that left it vulnerable to Western Imperialism? 2. Who was Commodore Perry? What was the Open Door Policy? How was this carried out? How did this affect Japan? 3. What was the Meiji Restoration? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the Meiji Restoration? 4. Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth at LEAST TWO SIMILARITIES and TWO DIFFERENCES of the Imperialism Process on China and Japan. Revolution in China in the 20th Century Lesson: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Chinese Nationalists: Main Goals, Leaders, Events, and Impact? Who was Sun Yat-Sen? What were his main beliefs and goals for China? Who was Chiang Kai-Shek? What were his main beliefs and goals for China? How did World War One and Two affect the political events of China? Why did many of the Chinese people turn to Communism and Mao Tse-Tung? Who was Mao? What were his main beliefs and goals for China? What happened in China during the Civil War between the Nationalists and Communists? What was the Long March? Causes, main events, and effects? What was the Manchurian Incident? How did the invasion of China by Japan in 1937 affect the political development of China? 10. Why did the Communists win in 1949? What happened to Chiang Kai-Shek and the Nationalists? Japanese Militarism through World War Two Lesson: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. How and why did Japan become an imperial and militaristic world power? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the Sino-Japanese War of 1894-1895? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-1905? What were the causes, main events, and effects of Japan annexing Korea in 1910? What militaristic actions did Japan take during World War One and what impact did they have on Japan and China? What militaristic actions did Japan take during the Inter-War Years and what impact did they have on Japan, China, and America? What were the causes, main events, and effects of the Second Sino-Japanese War/Invasion of Manchuria? What were the war atrocities of the Rape of Nanjing? What were the causes, main events, and effects of World War Two for Japan? Be able to identify, examine, and explain in depth at LEAST THREE DIFFERENT IMPERIALISTIC/MILTARISTIC actions of Japan? Communist China under Mao Lesson: 1. What was Mao’s political ideology? How did he carry out is ideas in the events of : a. the Five Year Plan, b. Great Leap Forward, 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. c. Thought Reform, d. Hundred Flowers Campaign, e. Anti-Rightist Campaign, f. and the Cultural Revolution? What were the Communes and Collectivization? What were the reasons, main events, and effects? What was the Great Famine? What were the causes, main events, and effects? What was the Backyard Steel Campaign? What were the reasons, main events, and effects? How did Mao use repression and terror to carry out his agricultural and political plans? Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth at least THREE DIFFERENT EXAMPLES. How did Mao create a Communist Dictatorship in China? Be able to identify, explain, and examine in depth at least FOUR DIFFERENT METHODS. Post-War Japan and Rise of Japanese Economic Power Lesson: 1. What condition was Japan in at the end of World War Two? Why? 2. What were the reasons for the United States for rebuilding Japan? 3. What were the political, economic, social, and cultural changes made to Japan? Impact of them? 4. How did Japan become an economic power in the last twenty-five years of the 20th century? Post-Mao China-China under Deng Xiaoping and Jiang Zemin Lesson? 1. What was the legacy of Mao in China? 2. What changes did Deng Xiaoping make in China? Impact of them? 3. What were the Four Modernizations? Causes, main events, and effects? 4. What was the Tiananmen Square Massacre? Causes, main events, and effects? 5. What changes did Jiang Zemin made in China? Impact of them? Final Exam: